Important Facts For Prelims
ISRO’s Heaviest Launch: BlueBird Block-2
- 26 Dec 2025
- 8 min read
Why in News?
ISRO marked a major milestone by launching its heaviest satellite, BlueBird Block-2 (6,100 kg, by the US firm AST SpaceMobile), using the Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) rocket, showcasing India’s strong heavy-lift launch capability.
Summary
- BlueBird Block-2, weighing 6,100 kg, is the heaviest payload deployed by ISRO, injected into LEO (160 - 2,000 km) to provide direct-to-mobile 4G/5G connectivity.
- LVM-3 upgrades, including C32 cryogenic stage, semi-cryogenic engines, and bootstrap reignition, enhancing its payload capacity.
What is BlueBird Block-2?
- About: The BlueBird Block-2, is the heaviest payload ISRO has placed into orbit, surpassing the previous record of 5,700 kg (OneWeb satellites).
- The satellite was injected into a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) of approximately 520 km altitude.
- Objective: It will provide direct-to-mobile connectivity, enabling 4G and 5G connectivity directly to mobile phones without requiring specialized ground stations.
- Commercial Significance: This is ISRO's 3rd commercial mission using LVM-3, following two OneWeb satellite launches in 2022 and 2023.
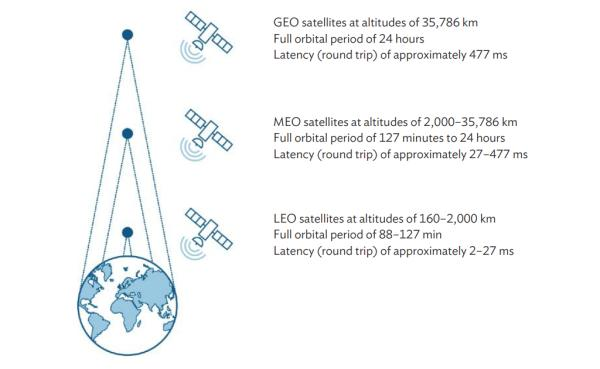
Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Overview: LEO extends from about 160 - 2,000 km above Earth’s surface, where satellites complete an orbit roughly every 90–120 minutes.
- Satellites in LEO: It hosts satellites used for communications, Earth observation, scientific missions, and navigation.
- Orbit Types: While many LEO satellites follow circular orbits, some operate in elliptical orbits.
- Special Elliptical Orbits: Molniya and Tundra orbits provide longer dwell times over high-latitude regions and are used for communications and observation where geostationary coverage is limited.
What is the LVM3 Launch Vehicle?
- About: The LVM3 is ISRO's largest and most powerful heavy-lift rocket, with three stages. This rocket can carry payloads of up to 4,000 kilograms to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit and 8,000 kg in LEO.
- Previously called the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III, it launched for the first time in December 2014.
- 3 Stages:
- First Stage: Uses two large S200 solid rocket boosters, which burn solid propellant HTPB (hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene).
- Second Stage (Core): Uses liquid-fuelled stage, powered by two Vikas engines, burning UDMH (unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine) and nitrogen tetroxide.
- Third Stage (Upper): Uses the C25 cryogenic stage,, equipped with the CE20 engine, burning liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen.
- Engine Optimization for Higher Efficiency:
- Cryogenic Stage Upgrade: ISRO is developing the C32 cryogenic stage for higher thrust and fuel capacity.
- Semi-Cryogenic Engine Development: ISRO is developing semi-cryogenic engines using kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will raise LEO payload capacity from 8,000 kg to 10,000 kg.
- Bootstrap Reignition Technology: ISRO is developing bootstrap reignition capability for cryogenic engines, allowing the upper stage to restart without external gases like helium, reducing fuel weight and increasing payload capacity for multi-orbit missions.
- Role in Future Missions: A modified LVM-3 with added human-safety redundancies will support Gaganyaan missions and later carry modules for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, India’s planned space station.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is BlueBird Block-2?
BlueBird Block-2 is a 6,100 kg commercial satellite by AST SpaceMobile, providing direct-to-mobile 4G/5G connectivity in LEO (160 km to 2,000 km).
2. What is the significance of LEO?
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) hosts communication, Earth observation, and navigation satellites, enabling low-latency global connectivity.
3. What are the stages of the LVM-3 rocket?
LVM-3 has three stages: S200 solid boosters, L110 liquid-fueled core, and C25 cryogenic upper stage, optimized for heavy-lift missions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q. In which of the following activities are Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites used? (2015)
- Assessment of crop productivity
- Locating groundwater resources
- Mineral exploration
- Telecommunications
- Traffic studies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 4 and 5 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)