International Relations
India-Argentina Relations
- 09 Jul 2025
- 13 min read
For Prelims:17th BRICS Summit, Argentina, India-Argentina Business Council (IABC), India–MERCOSUR Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA), Lithium, Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
For Mains: India- Argentina Relations, India’s Relation with Latin America: Prospects & Challenges
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India visited Argentina for the first time in 57 years, commemorating 75 years of diplomatic relations and 5 years of Strategic Partnership.
- He was awarded the "Key to the City of Buenos Aires," recognizing India's growing global prominence and the strengthening of bilateral ties.
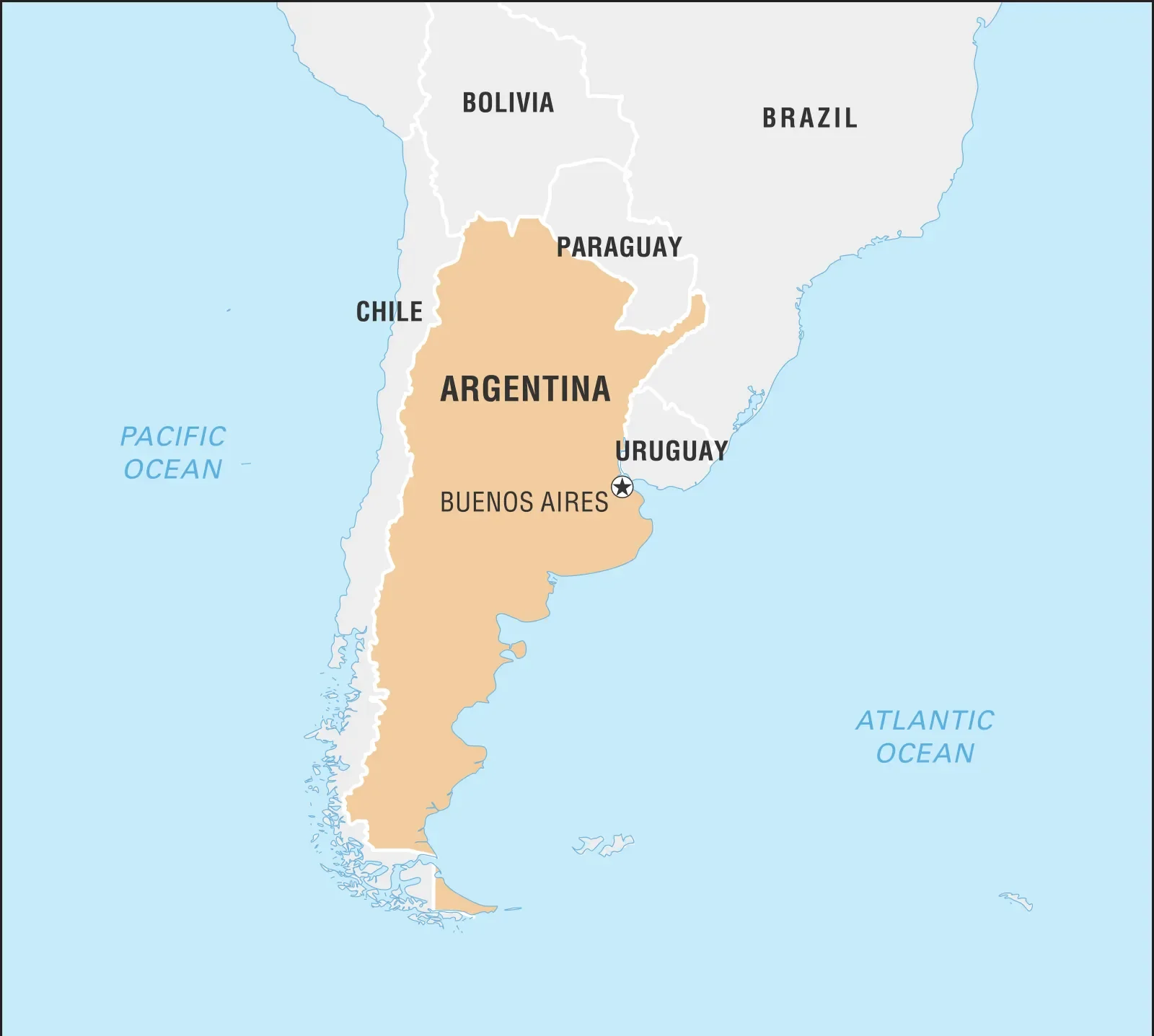
Argentina
- Capital: Buenos Aires
- Location: Southern South America, 8th largest country (area wise) globally and 2nd largest in South America (after Brazil).
- It borders Chile (W/S), Bolivia & Paraguay (N), Brazil (NE), Uruguay & Atlantic Ocean (E).
- Topography: Divided into 4 key regions- Andes Mountains (with highest peak Cerro Aconcagua), Northern region, Pampas (agricultural heartland), and Patagonia (south).
- Economy: Resource-rich, industrialized economy with a skilled workforce; among South America’s largest economies.
What are the Key Highlights of the PM's State Visit to Argentina?
- Strategic and Economic Engagement: India and Argentina agreed to expand India–MERCOSUR Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) to boost bilateral trade and economic ties.
- Focus areas include trade diversification, reducing reliance on primary commodities, and enhancing investment in emerging sectors.
- Energy Security and Critical Mineral Cooperation: Both nations committed to shale energy collaboration, leveraging Argentina’s 2nd largest shale gas and 4th largest shale oil reserves.
- India also signalled interest in expanding oil & gas cooperation under the ONGC Videsh & Argentina's state-owned energy company YPF, to support its growing energy needs.
- Defence & Digital Cooperation: India and Argentina agreed to boost defence manufacturing via co-development and tech transfer, and expand adoption of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure like UPI, telemedicine, and digital health, enhancing strategic and tech partnerships.
- Shared Democratic Values & Soft Power Diplomacy: Both leaders reaffirmed commitment to democratic values, South-South cooperation, and multilateralism.
- PM’s visit to General San Martín’s (Argentinian statesman national hero) statue symbolised strong people-to-people ties and India’s rising soft power in Latin America.
What are Key Areas of Cooperation Between India & Argentina?
- Political Relations: India established an embassy in Buenos Aires in 1949, while Argentina has maintained a Consulate General in Mumbai since 2009.
- India and Argentina celebrated 75 years of diplomatic relations in 2024 and their diplomatic relations were elevated to a Strategic Partnership in February 2019, after a visit by the President of Argentina to India.
- India and Argentina share strong democratic ties rooted in shared values and mutual respect.
- Economic Cooperation: India-Argentina trade reached USD 5.2 billion in 2024, with 53.9% growth in 2025. India is Argentina’s 4th largest trading partner. The India-Argentina Business Council (IABC) plays a key role in promoting trade and investment.
- Key exports from India: Petroleum products, agrochemicals, textiles, and pharmaceuticals
- Key Imports to India: Soybean oil, leather, and cereals.
- The India–MERCOSUR PTA is a trade agreement signed in 2004 and operational since 2009, between India and the MERCOSUR bloc (a Latin American trading bloc established in 1991).
- It offers tariff concessions on select goods to boost bilateral trade and aims to strengthen economic ties, potentially paving the way for a future Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Energy and Critical Minerals: Argentina, part of the Lithium Triangle, supplies lithium, copper, and rare earth elements vital for India’s clean energy transition.
- Indian PSU KABIL has secured strategic lithium exploration and mining concessions in Argentina enhancing India’s resource security and reducing reliance on external sources.
- Existing bilateral accords in other energy sectors include HAL–Argentine Air Force collaboration (defence), and the Heavy Water Board–Nuclear Electric Company partnership (nuclear energy).
- Technical and Development Cooperation: India has strengthened development cooperation with Argentina through ITEC scholarships, ICCR programs, and capacity building initiatives.
- The India-Argentina Centre of Excellence in IT (IA-CEIT), established at the National University of Hurlingham with C-DAC support, promotes skill development.
- Argentina has also participated in ISRO’s UNNATI program and space training courses at IIT Kanpur.
- Cultural and Values-Based Relations: India and Argentina share deep cultural ties and democratic values, reinforced through shared advocacy for South-South cooperation.
- Argentina has a strong presence of Indian cultural institutions (Art of Living, ISKCON, etc.),
- Events like International Day of Yoga (IDY), Ayurveda Day, and Gandhi@150 have seen large participation.
- Literary and intellectual links were celebrated through Tagore@160 events.
Note:
- Prime Minister Indira Gandhi visited Argentina in 1968 during her South America tour and met noted Argentine intellectual Victoria Ocampo and conferred on her an honorary doctorate from Visva-Bharati University, founded by Rabindranath Tagore.
- Rabindranath Tagore, during his 1924 visit en route to Peru fell ill in Buenos Aires and was hosted by Argentine intellectual, writer Victoria Ocampo.
- He composed Purabi, dedicating it to her.
- The meeting forged a lasting cultural bond and Ocampo promoted Indian thought through her magazine Sur, deepening Argentina’s interest in Indian music, dance, yoga, and spirituality.
How Have India’s Relations with Latin America Evolved over the Years?
- Historical Background: India shares long-standing cultural and ideological linkages with Latin America through personalities like Pandurang Khankhoje (who advanced agriculture in Mexico) and M.N. Roy (founder of the Indian and Mexican Communist parties).
- Bilateral ties were formalized with PM Nehru’s 1961 visit to Mexico and Indira Gandhi’s tour of 8 Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) nations in 1968, laying a diplomatic foundation.
- India’s participation in the BRICS Summit (Brazil, 2014) renewed India’s strategic outreach to the region.
- India launched the FOCUS LAC Programme (1997) and signed trade agreements with 7 LAC nations to promote bilateral trade and economic collaboration.
- Economy, Trade & Commerce:
- Trade Figures: India–LAC trade reached USD 43.2 billion in 2023, and is projected to touch USD 100 billion by 2027.
- Trading Partners: Brazil (top), Mexico, Colombia, Peru, Argentina.
- Strategic Economic Fit: Latin America is seen as a “goldilocks zone” for India, striking a balance between the strict regulations of markets like the US and Europe and the lower competition levels found in African markets.
- PTA Signed: India has signed Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs) with Chile and the Mercosur bloc. Mercosur is now advancing toward a Common Market.
- Political and Bilateral Cooperation: India’s foreign policy approach toward Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is witnessing a strategic recalibration.
- In April 2023, External Affairs Minister of India undertook the first-ever official visit to Guyana, Panama, Colombia, and the Dominican Republic.
- Brazil is India’s most politically connected partner in the region, with active collaboration in multilateral forums like BRICS, IBSA (India, Brazil and South Africa) and the G20.
- Both regions align on strategic autonomy, with India’s doctrine resonating with Latin America’s Active Non-Alignment (ANA) stance, especially evident in shared positions on global issues like the Russia–Ukraine conflict.
- Cultural Ties: Mahatma Gandhi’s legacy of non-violence holds deep relevance in Latin America.
- His philosophy is actively promoted by civil society groups, notably Palas Athenas in Brazil, reinforcing shared ethical and ideological values between India and the region.
| Click Here to Read: Significance of Latin America for India, Challenges in Deepening Engagement with Latin American Nations |
Conclusion
India–Argentina relations are evolving into a strategic and multidimensional partnership. With growing synergies in energy, digital technology, space, and trade, and shared Global South aspirations, the relationship has the potential to serve as a model for South-South cooperation in the 21st century.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the opportunities and challenges in strengthening India–Argentina ties in the context of India’s global outreach strategy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as(2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India? (2018)
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post Cold War international scenario. (2016)