Facts for UPSC Mains
Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025
- 18 Apr 2025
- 7 min read
Why in News?
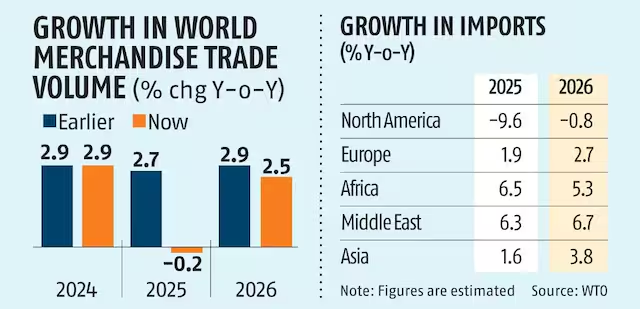
The World Trade Organization's (WTO) Global Trade Outlook and Statistics 2025 reveals that global merchandise trade is projected to decline by 0.2% in 2025. This reflects ongoing tariff tensions, particularly between the US and China, and broader trade policy uncertainty.
What is the Global Trade Outlook for 2025-26?
- Projected Decline in Merchandise Trade: The WTO’s revised forecast for global merchandise trade shows a 0.2% decline in 2025.
- If trade tensions escalate further, especially with new tariff measures, the decline could deepen to 1.5%. This marks a sharp contrast from the 2.9% growth in 2024.
- Impact of Tariffs: The reactivation of US reciprocal tariffs could cut global trade growth by 0.6% points, while ongoing US-China tariff escalation in 2025 may reduce trade by an additional 0.8% points.
- Modest Growth in Services Trade: Despite the challenges in merchandise trade, the global services trade is projected to grow by 4.0% in 2025, slower than expected due to tariff-induced disruptions.
- The decline in goods trade impacts services like transport and travel, while broader uncertainty dampens investment-related services.
- Regional Impact: North America is expected to face a sharp 12.6% decline in exports, significantly affecting global trade.
- Asia and Europe are projected to see modest trade growth, with Asia’s exports growing by 1.6%, and Europe’s exports growing by 1.0%.
- Vulnerable Economies: Least-developed countries (LDCs), heavily reliant on a narrow range of exports, are particularly vulnerable to the downturn in global trade.
- Trade Diversions: US-China trade disruption may drive significant trade diversion, with Chinese exports projected to rise by 4%-9% in regions outside North America.
- Meanwhile, US imports from China are expected to fall, creating opportunities for other suppliers, including LDCs, to fill the gap.
- Risk of Economic Recession: The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) forecasts global growth to slow to 2.3% in 2025, signaling a potential shift toward recession, with developing countries being particularly vulnerable.
- As the risks of economic fragmentation and geo-economic confrontation rise, UNCTAD urges increased regional and international policy coordination to strengthen global economic resilience.
- India’s Trade Position: In 2024, India’s rank among leading merchandise exporters (excluding intra-EU trade) dropped to 14th, while its share of global merchandise trade remained steady at 2.2%.
- Similarly, India’s rank among major merchandise importers (excluding intra-EU trade) fell to 7th, with its share unchanged at 3.4%.
- As for commercial services (excluding intra-EU trade), India’s rank as an exporter declined to 6th, with a slight drop in share from 5.4% to 5.3%. In terms of imports, India’s rank remained at 6th, although its share fell slightly from 4.2% to 4.1%.
World Trade Organization
- About: The WTO is an international institution established in 1995 to regulate global trade among nations. It was created under the Marrakesh Agreement, 1994 signed by 123 countries, following the Uruguay Round negotiations (1986-94) of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
- The WTO succeeded GATT, which had governed world trade since 1948. While GATT focused primarily on goods, the WTO expanded its scope to cover trade in goods, services, and intellectual property, including creations, designs, and inventions.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Members: 166 members, representing 98% of global trade. India has been a member since 1995 and was part of GATT since 1948.
- Key WTO Agreements: TRIMS (Trade-Related Investment Measures) prohibits measures that discriminate against foreign products. TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) resolves disputes over intellectual property rights.
- AoA (Agreement on Agriculture) promotes agricultural trade liberalization, focusing on market access and domestic support.
- Key Reports: World Trade Report, Global Trade Outlook and Statistics, Aid for Trade in Action.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the impact of the tariff escalation on global trade, economic growth, and regional trade patterns. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. The terms ‘Agreement on Agriculture’, ‘Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures’ and ‘Peace Clause’ appear in the news frequently in the context of the affairs of the (2015)
(a) Food and Agriculture Organization
(b) United Nations Framework Conference on Climate Change
(c) World Trade Organization
(d) United Nations Environment Programme
Ans: C
Q2. In the context of which of the following do you sometimes find the terms ‘amber box, blue box and green box’ in the news? (2016)
(a) WTO affairs
(b) SAARC affairs
(c) UNFCCC affairs
(d) India-EU negotiations on FTA
Ans: A
Mains:
Q1. What are the key areas of reform if the WTO has to survive in the present context of ‘Trade War’, especially keeping in mind the interest of India? (2018)
Q2. “The broader aims and objectives of WTO are to manage and promote international trade in the era of globalisation. But the Doha round of negotiations seem doomed due to differences between the developed and the developing countries.” Discuss in the Indian perspective. (2016)