Science & Technology
Facial Recognition Technology
- 22 Aug 2022
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Facial Recognition Technology, Right to Information, Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022, Biometric Technology, Artificial Intelligence
For Mains: Facial Recognition Technology, Uses of FRT, Challenges in FRT
Why in News?
Right to Information (RTI) responses received by the Internet Freedom Foundation, a New-Delhi based digital rights organisation, reveals that the Delhi Police treats matches of above 80% similarity generated by its facial recognition technology (FRT) system as positive results.
What did the 2022 RTI Responses by Delhi Police Reveal?
- Right to Information Responses:
- Facial Recognition Threshold:
- The Delhi Police has revealed that matches above 80% similarity are treated as positive results while matches below 80% similarity are treated as false positive results which require additional “corroborative evidence”.
- Collection of Data:
- Delhi Police is matching the photographs/videos against photographs collected under Section 3 and 4 of the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920, which has now been replaced by the Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022.
- Facial Recognition Threshold:
- Concerns:
- 80% Threshold:
- It is unclear why 80% has been chosen as the threshold between positive and false positive.
- The categorisation of below 80% results as false positive instead of negative shows that the Delhi Police may still further investigate below 80% results.
- People who share familial facial features, such as in extended families or communities, could end up being targeted.
- This could result in targeting communities who have been historically overpoliced and have faced discrimination at the hands of law enforcement authorities.
- Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022:
- It is feared that the Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022 will lead to overbroad collection of personal data in violation of internationally recognised best practices for the collection and processing of data.
- 80% Threshold:
What is Facial Recognition Technology?
- About:
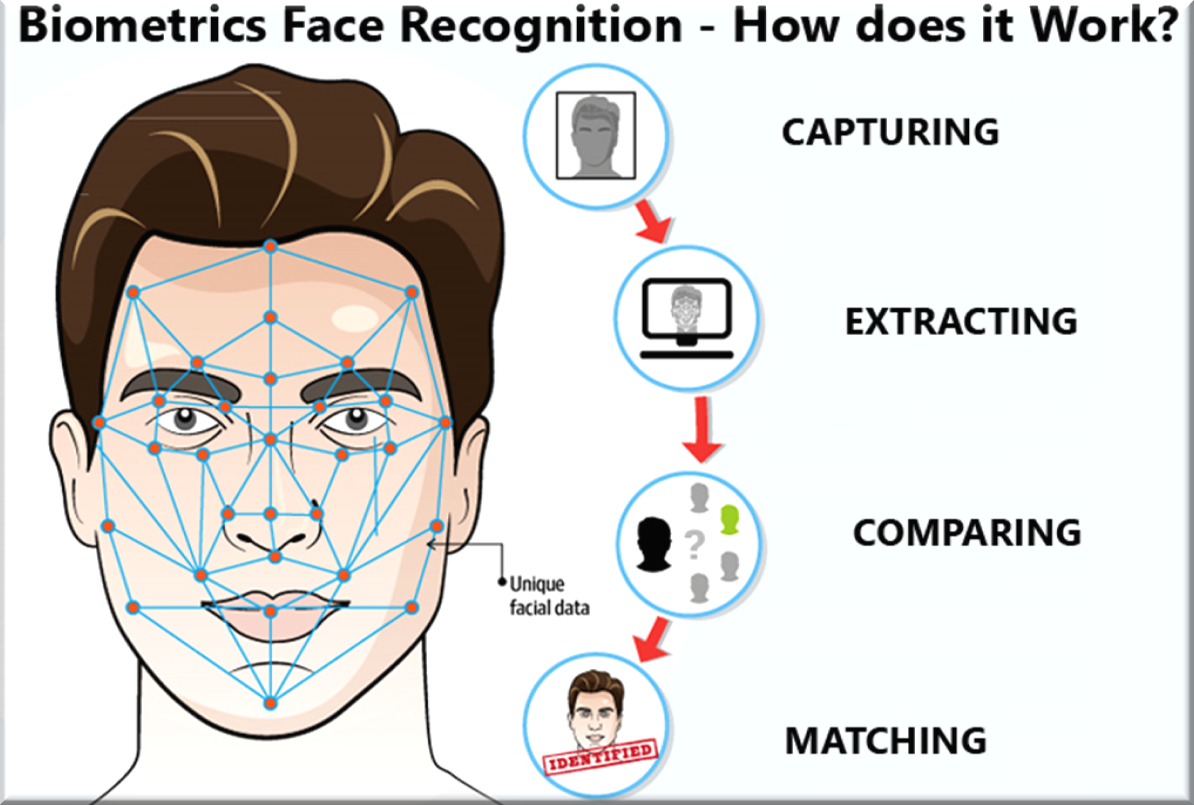
- Facial recognition is an algorithm-based technology which creates a digital map of the face by identifying and mapping an individual’s facial features, which it then matches against the database to which it has access.
- In the Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS), the large database (containing photos and videos of peoples’ faces) is used to match and identify the person.
- Image of an unidentified person, taken from CCTV footage, is compared to the existing database using Artificial Intelligence technology, for pattern-finding and matching.
- Working:
- The facial recognition system works primarily by capturing the face & its features through the camera and then using various kinds of software to reconstruct those features.
- The captured face along with its features is stored into a database, which can be integrated with any kind of software that may be used for security purposes, banking services, etc.
- Uses:
- 1:1 verification:
- The facial map is obtained for the purpose of matching it against the person’s photograph on a database to authenticate their identity.
- For example, 1:1 verification is used to unlock phones.
- The facial map is obtained for the purpose of matching it against the person’s photograph on a database to authenticate their identity.
- 1: n identification:
- The facial map is obtained from a photograph or video and then matched against the entire database to identify the person in the photograph or video.
- Law enforcement agencies such as the Delhi Police usually procure FRT for 1: n identification.
- The facial map is obtained from a photograph or video and then matched against the entire database to identify the person in the photograph or video.
- 1:1 verification:
- Need:
- Authentication:
- It is used for identification and authentication purposes with a success rate of almost 75%.
- Force Multiplier:
- In India, where there are just 144 constables per 1 lakh citizens, this can act as a force multiplier.
- It neither requires too much manpower nor regular upgradation.
- Hence, this technology coupled with the present manpower in place can act as a game-changer.
- In India, where there are just 144 constables per 1 lakh citizens, this can act as a force multiplier.
- Authentication:
Why is the Delhi Police using facial recognition technology?
- The Delhi Police first obtained FRT for the purpose of tracing and identifying missing children.
- The procurement was authorised as per the 2018 direction of the Delhi High Court in Sadhan Haldar vs NCT of Delhi.
- In 2020, the Delhi Police stated that “though they obtained FRT as per the Sadhan Haldar direction which related specifically to finding missing children, they were using FRT for police investigations”.
- The widening of the purpose for FRT use clearly demonstrates an instance of ‘function creep’ wherein a technology or system gradually widens its scope from its original purpose to encompass and fulfil wider functions.
- Delhi Police has consequently used FRT for investigation purposes and also specifically during the 2020 northeast Delhi riots, the 2021 Red Fort violence, and the 2022 Jahangirpuri riots.
Why is the Use of Facial Recognition Technology Harmful?
- Inaccuracy & Misuse:
- Issues related to “Misidentification” due to inaccuracy of the technology.
- Issues related to “Mass Surveillance” due to misuse of the technology.
- Race & Gender:
- It has also been reported that its accuracy rates fall starkly based on race and gender.
- This can result in a false positive, where a person is misidentified as someone else, or a false negative where a person is not verified as themselves.
- Cases of a false positive result can lead to bias against the individual who has been misidentified.
- It has also been reported that its accuracy rates fall starkly based on race and gender.
- Exclusion:
- Cases of false negative results can also lead to exclusion of the individual from accessing essential schemes which may use FRT as a means of providing access.
- For example, failure of the biometric based authentication under Aadhaar which has led to many people being excluded from receiving essential government services which in turn has led to starvation deaths.
- Violation to Privacy:
- Government although plans to address the question of privacy through the legal framework like data privacy regime, but keeping in mind the objectives it aims to achieve with the use of such technology, it comes into conflict with one another.
- Reliability & Authenticity:
- As the data collected may be used in the court of law during the course of a criminal trial, the reliability and the admissibility of the data along with the standards and procedure followed would be taken into consideration.
- Absence of Data Protection Law:
- FRT systems in the absence of data protection laws that would mandate necessary safeguards in the collection and storage of user data is also a point of concern.
Way Forward
- In this digital age, data is a valuable resource that should not be left unregulated. In this context, the time is right for India to have a robust data protection regime.
- The government would also have to respect the privacy of the citizens while strengthening the right to information.
- Additionally, the technological leaps made in the last two to three years also need to be addressed knowing that they have the capacity to make the law redundant.
- Every country has its own challenges which are uncomparable.
- Given the size of India’s population and comparatively understaffed administration, the well-planned use of such nascent technology is a probable solution, provided there are sufficient safeguards to address its inherent concerns including the issue of privacy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The identity platform ‘Aadhaar’ provides open “Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)”. What does it imply? (2018)
- It can be integrated into any electronic device.
- Online authentication using iris is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- API is the acronym for Application Programming Interface, which is a software intermediary that allows two applications to communicate with each other.
- Open API allows for building Aadhaar enabled applications. Such applications can integrate the app or website with Aadhaar and use authentication services. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- APIs support multi-mode authentication (Iris, fingerprint, OTP and biometric). Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. In addition to fingerprint scanning, which of the following can be used in the biometric identification of a person? (2014)
- Iris scanning
- Retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- Biometric verification is any means by which a person can be uniquely identified by evaluating one or more distinguishing biological traits.
- Unique identifiers include fingerprints, hand geometry, earlobe geometry, retina and iris patterns, voice waves, DNA, and signatures. The oldest form of biometric verification is fingerprinting.
- All the given processes, namely, Iris scans, Voice recognition and Retinal scanning can be used for biometric identification. Hence, 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. E-governance is not only about utilization of the power of new technology, but also much about critical importance of the ‘use value’ of information. Explain. (2018)
Q. Two parallel run schemes of the Government, viz the Adhaar Card and NPR, one as voluntary and the other as compulsory, have led to debates at national levels and also litigations. On merits, discuss whether or not both schemes need run concurrently. Analyse the potential of the schemes to achieve developmental benefits and equitable growth. (2014)