Indian Economy
Collapse of Multiple Infrastructures
- 18 Jul 2024
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI), Morbi Bridge, Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLAD), Covid-19, PM Gati Shakti Scheme, Bharatmala scheme, IIPDF (India Infrastructure Project Development Fund) Portal
For Mains: Building Resilient Infrastructure for Development and Disaster Mangement.
Why in News?
Recently, several physical infrastructures, like bridges in Bihar and airport canopy structures in Delhi and Rajkot of Gujarat collapsed.
What are the Causes of the Collapse of Physical Infrastructures?
- Natural causes:
- Heavy Rainfall: Prolonged and intense rainfall can saturate the soil and increase the weight of bridge structures, leading to potential failures.
- Incase of Bihar, significant water flow from upstream Nepal has also contributed to the factor.
- Disasters: Disasters like earthquakes can cause weakening of infrastructure.
- Heavy Rainfall: Prolonged and intense rainfall can saturate the soil and increase the weight of bridge structures, leading to potential failures.
- Administrative Causes:
- Corruption: Corruption in administration and tender allocation causes administrative failures related to the implementation and monitoring of projects.
- For example- India ranked 93 out of 180 countries on the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) for 2023.
- Management issue: Lack of proper maintenance, monitoring and management of crowds leads to infrastructure failure.
- For example: One of the reasons for the collapse of the Morbi Bridge was failure in regular maintenance and crowd management.
- Corruption: Corruption in administration and tender allocation causes administrative failures related to the implementation and monitoring of projects.
- Procedural Causes:
- Failure to Follow Design Protocols: Deviations from established engineering designs and safety protocols can lead to structural vulnerabilities.
- Poor Quality Control: Lack of inspections and insufficient quality control measures during construction can result in undetected flaws that compromise safety.
- The use of inferior materials can significantly weaken structural integrity, reducing the capacity to bear environmental stresses.
Which are Schemes for Building Rural Infrastructure?
-
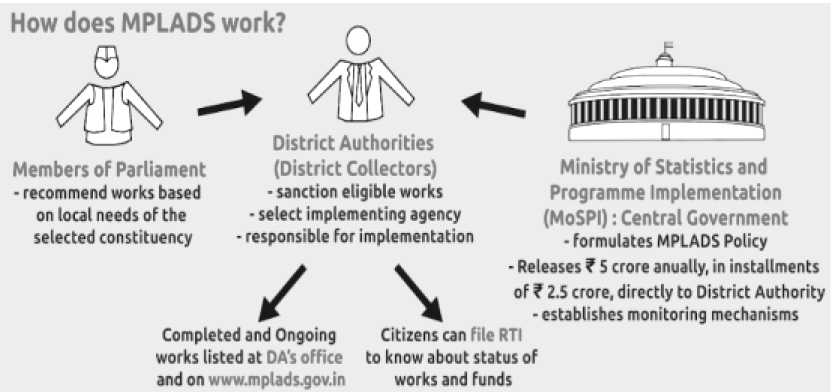
Member of Legislative Assembly Local Area Development Scheme (MLALAD):
- It is the state’s version of a central government scheme- MPLAD.
- The objective of this scheme is to create local need-based infrastructure, to create assets of public utility and to remove regional imbalances in development.
- The MLALAD programme provides funding for each constituency directly from the state government.
- While MLAs and MPs do not directly receive the funds, they can recommend projects for the scheme.
- The projects funded by them are usually restricted to “durable infrastructure work”, from repairing roads to building community centres.
- The funds have also been used for natural disaster relief in some states, as in the case of Covid-19.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana:
- It was launched in 2000 to provide connectivity, by way of an all-weather road to unconnected habitations.
- Eligibility: Unconnected habitations of designated population size (500+ in plain areas and 250+ in North-Eastern States, Himalayan States, Deserts and Tribal Areas as per 2001 census) in the core network for uplifting the socio-economic condition of the rural population
- Latest Funding Pattern: The Union Government bears 90% of the project cost in respect of projects sanctioned under the scheme in North-Eastern and Himalayan States, whereas for other states the Union Government bears 60% of the cost.
Other Major Initiatives for Building Physical Infrastructure
Way Forward
- Administrative Reforms: It will ensure better monitoring and implementation of projects with a transparent system.
- Adopting Modern Engineering Practices: Utilise advanced design techniques and materials that enhance durability.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Encourage collaboration between government and private sector for funding and expertise to bring more investments.
- Strict Regulatory Standards: Implement rigorous standards for materials and construction practices.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent assessments to ensure compliance with safety and quality benchmarks.
- Resilience Planning: Design infrastructure to withstand climate change impacts and natural disasters.
- Capacity Building: Invest in training programs for engineers, architects, and construction workers to enhance skills.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Assess the role of infrastructure development in achieving sustainable economic growth in India. What are the key challenges faced in this sector? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. “Investment in infrastructure is essential for more rapid and inclusive economic growth.” Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (2021)