Facts for UPSC Mains
Bills to Modernise India’s Maritime Laws
- 13 Aug 2025
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Parliament passed Merchant Shipping Bill, 2025, Carriage of Goods by Sea Bill, 2025 & Coastal Shipping Bill, 2025 with the aim to modernise India’s maritime legal framework by replacing outdated colonial-era laws.
What are the Key Provisions of the Recently Passed Maritime Bills?
- Coastal Shipping Bill, 2025:
- It amended the Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, (replacing Part XIV with new norms), modernizing the legal framework aligned with global cabotage norms.
- It aims to raise coastal cargo to 230 million tonnes by 2030 with simpler licensing and foreign vessel regulation.
- It provides for cutting foreign dependence, boosting supply security, jobs, and ease of business.
- It mandates a National Coastal and Inland Shipping Strategic Plan and a National Database to enhance infrastructure planning, transparency, and investor confidence.
- Merchant Shipping Bill, 2025:
- It replaced the outdated Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, aligning India’s maritime laws with International Maritime Organization (IMO) conventions for clarity and ease of compliance.
- It aims to enhance sea safety standards, emergency response, environmental protection, and seafarer welfare, while promoting Indian shipping tonnage and India’s global maritime reputation.
- It authorizes the central government to detain vessels without nationality or legal flag rights in Indian waters, boosting maritime security with a future-ready legal framework supporting India’s economic and trade ambitions.
- Carriage of Goods by Sea Bill, 2025:
- It replaced the Indian Carriage of Goods by Sea Act, 1925 and adopted the internationally accepted Hague-Visby Rules (1924) and its amendments, setting a global standard for maritime trade.
- The Hague-Visby Rules, 1924 govern sea carriage of goods, outlining carrier and shipper rights and liability for cargo loss or damage.
- It regulates Bills of Lading, documents detailing goods’ type, quantity, condition, and destination to enhance transparency and shipping efficiency.
- Empowers the Central Government to issue directions and amend rules on Bills of Lading, promoting ease of business and aligning India’s laws with global standards and trade agreements.
- It replaced the Indian Carriage of Goods by Sea Act, 1925 and adopted the internationally accepted Hague-Visby Rules (1924) and its amendments, setting a global standard for maritime trade.
What is the State of India’s Maritime Sector?
- State of India’s Maritime Sector: India is the 16th largest maritime nation, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value through 12 major and 200+ minor ports on key global shipping routes.
- Capacity and Fleet Growth: Major ports’ cargo-handling capacity grew by 87% (2014–24) to 1,629.86 million tonnes, with 819.22 million tonnes handled in FY24; the fleet comprises 1,530 registered ships.
- Global Rankings: India ranks 38th in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index 2023, while being the 3rd largest ship recycler globally with around 30% market share, home to the largest ship-breaking yard at Alang.
- Shipbuilding and Policy Initiatives: Despite lagging in shipbuilding, initiatives like the New Shipbuilding and Repair Policy, along with 100% FDI(under the automatic route for port and harbour construction and maintenance projects), tax holidays, and infrastructure upgrades, aim to boost domestic capacity and have helped raise exports to USD 451 billion in FY23.
Government Initiatives in India’s Maritime Sector
- One Nation-One Port Process (ONOP)
- Sagar Ankalan – Logistics Port Performance Index (LPPI) 2023-24
- Bharat Global Ports Consortium
- MAITRI Platform (Master Application for International Trade and Regulatory Interface)
- National Centre of Excellence in Green Port & Shipping (NCoEGPS)
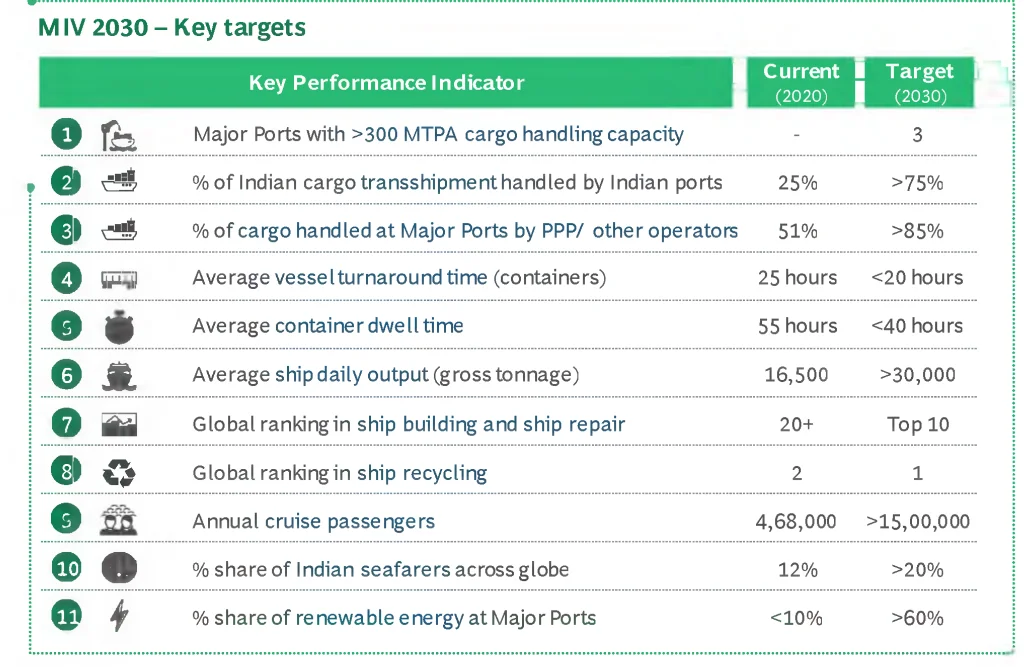
- Maritime India Vision 2030
- Green Tug Transition Program (GTTP)
|
Read More: Challenges in India’s Maritime Sector |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)