Important Facts For Prelims
51st G7 Summit
- 21 Jun 2025
- 4 min read
Why in News?
India’s Prime Minister attended the 51st G7 Summit at Kananaskis, Canada. Though India is not a part of the G7 grouping, it has been invited for the global summit each year for the last six years and twelve times in total as an outreach country.
- The President of the European Commission was invited to attend the G7 Summit for the first time.
What are the Key Outcomes of the G7 Summit?
- Kananaskis Wildfire Charter: It commits to addressing wildfire threats through science-based, local actions and nature-based solutions, aligning with the goal to halt and reverse deforestation and land degradation by 2030 under the Glasgow Leaders' Declaration (2021).
- G7 Critical Minerals Action Plan: It focuses on diversifying critical mineral production, boosting investment and local value creation, and promoting innovation, building on the 2023 Five-Point Plan for Critical Minerals Security (also endorsed by India).
- The G7 also committed to strengthening the World Bank-led Resilient and Inclusive Supply Chain Enhancement (RISE) Partnership.
- Condemned Transnational Repression (TNR): The G7 condemned Transnational Repression (TNR), which refers to aggressive foreign interference where states or their proxies seek to intimidate, harass, harm, or coerce individuals or communities beyond their own borders.
- Prevent Migrant Smuggling: G7 committed to preventing migrant smuggling through the G7 Coalition to Prevent and Counter the Smuggling of Migrants and the 2024 G7 Action Plan targeting this issue.
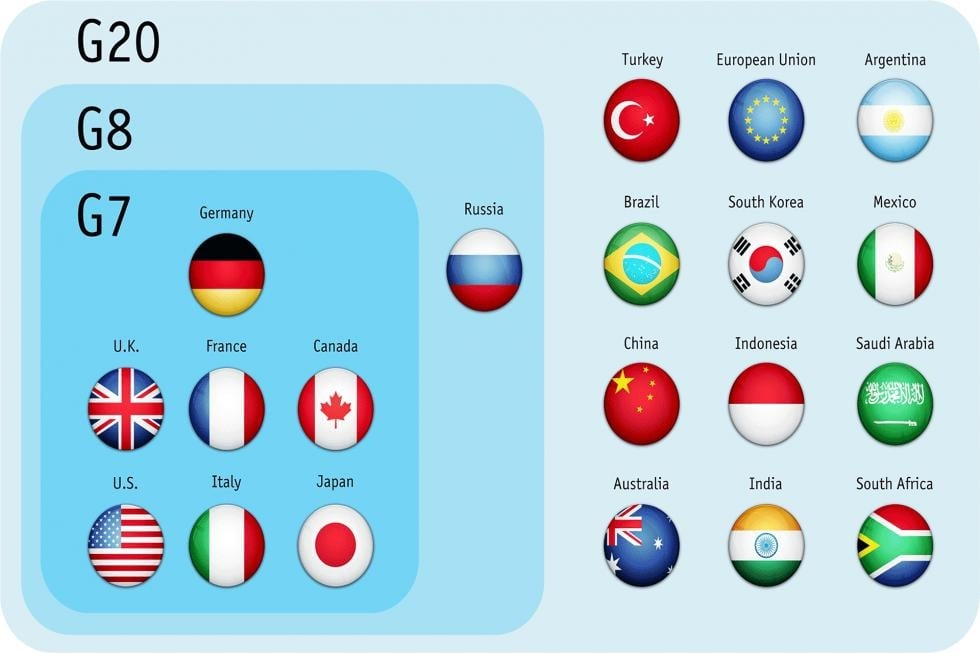
What is G7?
- About: The G7 (Group of Seven) is an informal forum of the world’s most advanced economies — France, Germany, Italy, the UK, Japan, the US, and Canada.
- The European Union (EU) participates as a non-enumerated member, with leaders from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and United Nations (UN) often invited to its meetings.
- Origin & Evolution: The G7 was formed in 1975 as the G6 (US, UK, France, West Germany, Japan, Italy) in response to the 1973 oil crisis and financial turmoil, with Canada joining in 1976 to make it G7. The year 2025 marked the 50th anniversary of the G7.
- It became G8 in 1997 with the inclusion of Russia, but reverted to G7 in 2014 after Russia’s expulsion over the annexation of Crimea.
- Nature of G7:
- Informal grouping: No formal treaty, no permanent secretariat or bureaucracy.
- Rotating Presidency: Each member hosts and leads discussions in turn.
- Decisions by consensus: No binding laws (no legislative authority), but significant global influence due to members’ economic and political strength.
- Economic Significance:
- 40% of the global economy and 10% of the world's population live in G7 countries.
- 36% of global power generation capacity.
- 30% of global energy demand.
- 25% of global energy-related carbon dioxide (C02) emissions.
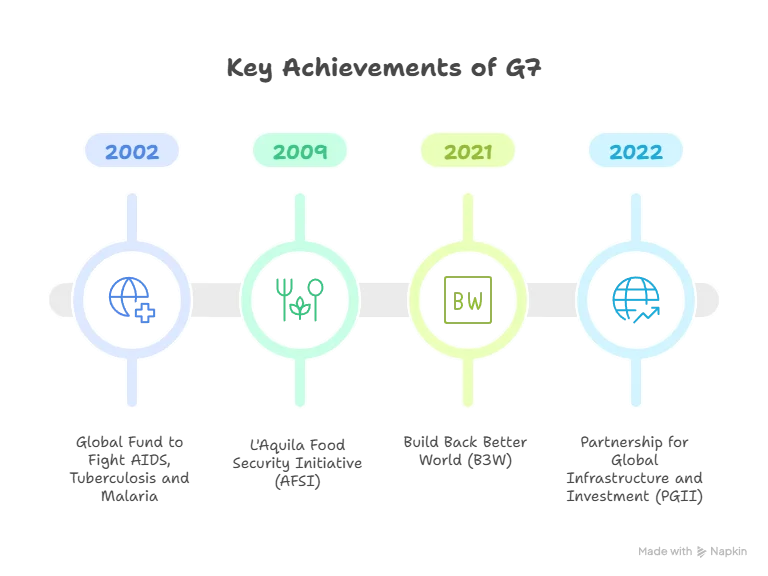
- Key Achievements:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)