Indian Economy
India’s MSME Sector
This editorial is based on “MSMEs are not paid on time. They need to be” which was published in The Hindu on 07/05/2024. The article brings into picture the issues of delayed payments in MSME Sector and need for subsequent reforms.
For Prelims: MSME sector, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development Act of 2006 , Gross Domestic Product , Textile industry, Food processing, Indian handicraft sector
For Mains: Significance of MSMEs in India’s Growth Trajectory and Related Challenges.
The MSME sector has become a key driver of India's economy, fostering entrepreneurship and creating significant employment opportunities with low capital investment. It plays a vital role in the country's inclusive industrial development, complementing large industries as ancillary units.
Despite its contributions, the MSME sector grapples with significant challenges, including access to finance, technology adoption, and global market competitiveness.
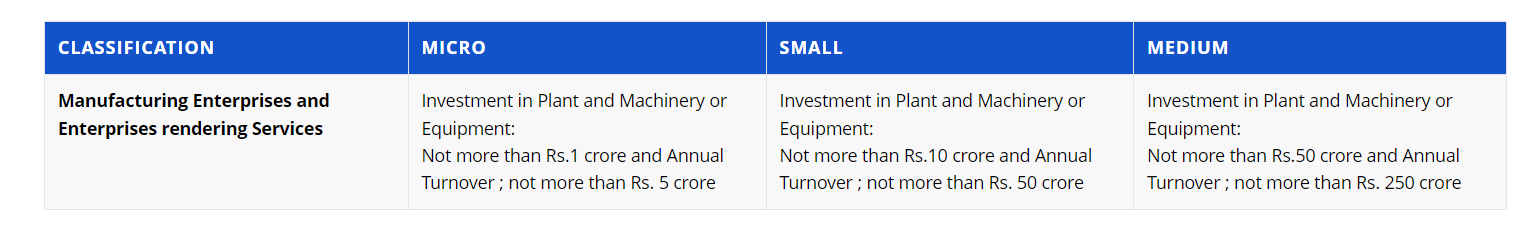
What are MSMEs?
- About: MSME stands for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. MSMEs are businesses that produce, process, and preserve goods and commodities.
- These are broadly classified based on their investment in plant and machinery for manufacturing or equipment for service enterprises, as well as their annual turnover.
- MSME Regulation in India: In 2007, the Ministry of Small Scale Industries and the Ministry of Agro and Rural Industries merged to form the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises.
- This ministry develops policies, facilitates programs, and monitors implementation to support MSMEs and aid in their growth.
- The Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development Act of 2006 addresses various issues affecting MSMEs, establishes a National Board for MSMEs, defines the concept of "enterprise," and empowers the Central Government to enhance MSME competitiveness.
What is the Significance of MSMEs in India’s Growth Trajectory?
- GDP Contribution and Employment Generation: MSMEs currently contribute approximately 30% to India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP), playing a crucial role in driving economic growth.
- Als, MSMEs are labor-intensive and play a vital role in creating employment opportunities across various sectors. They currently provide employment to over 11 crore people in India.
- For instance, the textile industry, which is dominated by small-scale units, employs a significant number of workers in activities like spinning, weaving, and apparel manufacturing.
- Contribution to Manufacturing Output: MSMEs contribute significantly to the country's manufacturing output, particularly in sectors like food processing, engineering, and chemicals.
- For example, the Agra footwear industry, which is primarily composed of MSMEs, accounts for 28% of India's footwear exports.
- Export Promotion: Currently MSMEs contribute nearly 45% of India's total exports. Their diverse product range, often catering to niche markets, strengthens India's presence in the global trade arena.
- The Indian handicraft sector, which is dominated by small-scale artisans and enterprises, has a global market and generates significant export revenue for the country.
- Rural Industrialization: MSMEs play a pivotal role in driving rural industrialization and promoting inclusive growth.
- The Khadi and Village industries sector, consisting of small-scale units, has been instrumental in providing employment opportunities in rural areas and empowering local communities.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The MSME sector fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, as it is often easier for small businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and introduce new products or services.
- For instance, the startup ecosystem in India (third largest in the world), which is largely driven by MSMEs, has given rise to numerous innovative solutions across various sectors, such as e-commerce and fintech.
What are the Key Indian Government Initiatives Related to MSMEs?
- Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana: It provides loans up to 10 lakh to the non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises. These loans are classified as MUDRA loans.
- Credit Guarantee Schemes: It is offered by the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) to mitigate the risk for banks and financial institutions, making it easier for MSMEs to access credit.
- MSME SAMADHAAN: It is an online Delayed Payment Monitoring System, governed by the Micro and Small Enterprise Facilitation Council for settlement of disputes on getting references/filing on Delayed payments by aggrieved MSMEs (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises), who can do the filing of cases and tracking of status online
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM): This online platform facilitates public procurement from MSMEs, providing them with access to a wider market.
- Udyam Registration: A simplified online registration process for MSMEs to avail government benefits and schemes.
- CHAMPIONS Portal: It is an ICT-driven Control Room and Management Information System focused on enhancing output and national strength through modern processes.
- It aims to help Indian MSMEs become National and Global CHAMPIONS by addressing their issues and providing guidance, support, and assistance along the way.
What are the Major Challenges Related to MSME?
- Lack of Adequate Access to Finance: Despite government schemes like Mudra loans, obtaining credit remains a major challenge for MSMEs.
- Traditional banks often perceive them as high-risk borrowers due to limited credit history and collateral.
- This restricts their ability to invest in expansion, innovation, and working capital.
- Delayed Payments: One of the major challenges faced by MSMEs is the issue of delayed payments from larger enterprises or government agencies.
- This can severely strain their working capital and cash flow, hampering their ability to operate smoothly.
- A small supplier or contractor may face significant financial difficulties due to delays in receiving payments for goods or services rendered, jeopardizing their business continuity.
- Limited Skilled Workforce: Many MSMEs struggle to find workers with the necessary skills to operate advanced machinery or implement new technologies. This can lead to inefficiencies, production delays, and reduced product quality.
- Limited Branding and Outreach: MSMEs often lack the resources and expertise to effectively market their products and build brand awareness. This makes it difficult to compete with larger companies or established brands, especially in the online marketplace.
- Infrastructure Constraints: Inadequate infrastructure, such as poor road connectivity, unreliable power supply, and lack of access to modern facilities, can significantly hinder the operations and growth of MSMEs.
- A small food processing unit in a rural area may face challenges in transporting its products to markets due to poor road conditions or may experience frequent disruptions in production due to erratic power supply.
Way Forward
- MSME Innovation Hubs: Establishing physical or virtual MSME innovation hubs. These hubs could connect MSMEs with industry experts, researchers, and mentors.
- They would facilitate knowledge sharing, co-creation of innovative products, and access to advanced technologies or design expertise.
- An MSME apparel manufacturer can collaborate with a design expert at the hub to develop a new clothing line, fostering innovation and market differentiation.
- Blockchain-Powered Smart Contracts: Leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts can revolutionize the payment cycle for MSMEs.
- A blockchain-based platform could be developed to facilitate secure and transparent transactions between MSMEs and their clients (larger enterprises or government agencies).
- AI-powered Mentorship Programs: Developing AI-powered mentorship program that provides MSMEs with personalized guidance and advice based on their specific needs and industry data.
- This can bridge the gap in mentorship access, especially for MSMEs in remote locations.
- Embracing Digital Transformation: In the digital age, MSMEs must embrace technology to remain competitive.
- This includes leveraging e-commerce platforms, adopting digital marketing strategies, and implementing automation and digitization in their operations.
- Initiatives like upskilling programs, digital literacy campaigns, and incentives for technology adoption can drive this transformation.
- Fostering Sustainable Entrepreneurship: Encouraging sustainable and socially responsible business practices among MSMEs can create a positive impact on the environment and society.
- This can include promoting eco-friendly production methods, supporting green entrepreneurship, and incentivizing the use of renewable energy sources.
- Navigating the Global Market: With the rise of globalization, MSMEs should be equipped to tap into international markets.
- Initiatives like export promotion programs, international trade facilitation centers, and mentorship from successful exporters can help MSMEs navigate the complexities of global trade.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the hurdles encountered by Indian MSMEs and assess the government's efforts in mitigating these obstacles. Propose strategies for fostering the growth and resilience of the MSME sector, given its pivotal role in India's economy and job creation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:(PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2. Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q3. Consider the following statements with reference to India : (2023)
- According to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between `15 crore and `25 crore.
- All bank loans to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)