Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Operation Kagar
Why in News?
In the backdrop of rising violence and contentious security operations, Telangana's former Chief Minister has raised concerns over the Central Government's Operation Kagar.
- This operation, aimed at eliminating Maoist insurgents in Chhattisgarh, has sparked criticism for its heavy-handed approach, especially with allegations of the killing of tribals and youths.
Note:
- The Union Home Minister announced that the central government is working towards a Naxal-free India, setting a target to eliminate Naxalism by 31st March 2026, ensuring that no citizen has to lose their life because of it.
Key Points
Operation Kagar
- Operation Kagar, launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs, is aimed at eradicating Naxals and dismantling the political ideology of Maoism.
- However, the operation has been marked by significant casualties among those Maoists who have refused to surrender to the government.
- According to the South Asia Terrorism Portal, over 140 Maoists were reportedly killed by security forces in Chhattisgarh in the first three months of 2025.
- This figure already accounts for more than half of the total death toll in Chhattisgarh for 2024, which stood at 235.
Impact on Tribals and Local Communities
- While the government claims Operation Kagar aims to bring peace, its impact on local communities, especially tribals, has been severe.
- Many tribals have been caught in the crossfire, and the government’s aggressive approach has intensified local resentment.
- The rise in violence from both Naxals and security forces has deepened tensions between tribal communities and the government, fueling calls for addressing the socio-economic grievances driving the insurgency, rather than relying solely on military action.
Naxalism
- About: Naxalism, a form of Left Wing Extremism (LWE) inspired by Maoist ideology, seeks to overthrow the state through armed rebellion (violence and guerrilla warfare).
- The term Naxalism derives its name from the village Naxalbari in West Bengal, where an uprising of peasants occurred in 1967 against exploitative landlords.
- It has since evolved into a complex insurgency affecting several states across India.
- Indian Maoists: The Communist Party of India (Maoist) is the largest and most violent Maoist group in India. It was formed through the merger of two major Maoist factions:
- CPI (Marxist-Leninist) People’s War and the Maoist Communist Centre of India.
- The CPI (Maoist) and its organizations were banned under the UAPA, 1967.
- Geographic Spread: The Naxal movement is most active in the “Red Corridor,” spanning parts of several Indian states, including Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Maharashtra, and Bihar.
Causes for Naxalism
- Land Disputes and Exploitation: The unequal distribution of land and the exploitative practices of landlords, moneylenders, and intermediaries have created significant resentment in rural and tribal areas, fostering the rise of Naxalism.
- Poverty and Lack of Development: Regions affected by Naxalism suffer from a lack of basic infrastructure such as healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, which drives marginalised populations towards radical movements.
- Tribal Displacement: Industrial and mining projects often displace tribal communities without adequate rehabilitation, leading to anger, a sense of injustice, and a deep mistrust of the state, which motivates many to join Naxalite groups.
- Government Apathy and Repression: The absence of effective governance, coupled with the denial of essential services and instances of police brutality, including custodial deaths, has exacerbated local grievances, further fueling the Naxalite insurgency.
| Read More: India’s Strategy to Eliminate Naxalism |


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Padma Bhushan Awarded to the Former Deputy CM of Bihar
Why in News?
Bihar’s former Deputy Chief Minister, Sushil Kumar Modi, was posthumously awarded the prestigious Padma Bhushan for his exceptional contributions to public life. The honor was conferred by President Droupadi Murmu.
- Sushil Kumar Modi was one of the ten distinguished personalities to receive the Padma Bhushan.
Key Points
Contributions of Sushil Kumar Modi
- Fiscal Management and State Development: As Bihar’s longest-serving Deputy CM and Finance Minister, he played a crucial role in transforming Bihar into a revenue-surplus state.
- He was known for effective fiscal management and contributing to the state's development through improved governance.
- Introduction of GST: He was instrumental in the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India.
- As the Chairman of the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers (2011-2013), he played a pivotal role in building consensus among states for the rollout of GST, which was a landmark reform in India's tax structure.
- Political Career and Leadership: With over three decades in politics, he served in both Houses of Parliament and the Bihar Legislative Assembly.
- He also held leadership roles such as the Chairman of the Parliamentary Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law, and Justice.
- Gender Budget and Women’s Welfare: While serving as Bihar’s Finance Minister, Modi introduced the innovative concept of a gender budget, focusing on the welfare and empowerment of women, ensuring that their issues were addressed in the state’s financial planning.
- Advocacy for Organ Donation: He was a strong advocate for organ donation and founded the ‘Dadhichi Deh Daan Samiti’ campaign in Bihar, which promoted awareness about organ donation and encouraged people to donate their organs.
Padma Awards
- Background:
- The Padma Awards are announced annually on Republic Day (26th January).
- Instituted in 1954, it is one of the highest civilian honours of India.
- Objective:
- To recognise achievements in all fields of activities or disciplines where an element of public service is involved.
- Categories:
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Padma Vibhushan (for exceptional and distinguished service),
- Padma Bhushan (distinguished service of higher order) and
- Padma Shri (distinguished service).
- Padma Vibhushan is highest in the hierarchy of Padma Awards followed by Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri.
- The Awards are given in three categories:
- Disciplines:
- The awards are given in various disciplines/ fields of activities like art, social work, public affairs, science and engineering, trade and industry, medicine, literature and education, sports, civil service, etc.
- Eligibility:
- All persons without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex are eligible for these Awards.
- Selection Process:
- Padma Awards Committee:
- The Awards are conferred on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee, which is constituted by the Prime Minister every year.
- Awarded by President:
- The awards are presented by the President of India usually in March/April every year.
- Padma Awards Committee:


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Coastal States Fisheries Meet 2025
Why in News?
The "Coastal States Fisheries Meet: 2025" was held in Mumbai, chaired by the Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying (MoFAH&D) and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Earlier, the Maharashtra government decided to give agriculture status to fisheries business.
Note: As of April 2024, Maharashtra stands at 6th position in marine fishing while 17th position in inland fishing.
Key Points
Highlights of the Meet
- Union Minister Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for key projects across seven coastal states and Union Territories, with a total outlay of Rs. 255 crores under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- The meeting marked the commencement of the 5th Marine Fisheries Census (MFC) operations, which will include training supervisors, recruiting and training village-level data enumerators, and conducting the census over a three-month period.
- The entire operation is expected to be completed by December 2025.
- The Union Minister also distributed tablets equipped with the Digital Application VyAS-NAV and presented the first-ever aqua insurance under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY), along with the One-Time Incentive Sanction-cum-Release Order to beneficiaries.
MFC 2025 & VyAS-NAV App
- In a significant preparatory move for MFC 2025, the VyAS-NAV mobile application has been launched to facilitate digital-based data collection, aimed at enhancing transparency and efficiency. This marks a shift from traditional methods to a geo-referenced, app-based system.
- The MFC 2025 will cover 1.2 million fisher households nationwide, ensuring real-time validation of data.
- Coordinated by the Department of Fisheries (DoF) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, the census is part of the PMMSY.
- VyAS-NAV, developed by the ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), the nodal agency for implementing the marine fisheries census across nine coastal states, will be used by supervisors for field verification of fishing villages, fish landing centres, and fishing harbours.
Aquaculture Insurance
- The PM-MKSSY, a sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana, provides comprehensive aquaculture insurance aimed at mitigating risks and offering financial support, especially to small and marginalized farmers.
- This sub-scheme ensures digital accessibility through the National Fisheries Digital Platform (NFDP), allowing seamless access to insurance for fishers and fish farmers, thereby safeguarding their incomes against unforeseen losses.
- Eligible beneficiaries include registered aquafarmers, firms, companies, societies, cooperatives, Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs), and other entities involved in the fisheries value chain, as identified by the DoF.
- For intensive aquaculture systems, such as recirculatory aquaculture systems, the premium is capped at ₹1 lakh per farmer for 1800 m³.
- Farmers can choose between two insurance options:
- Basic Insurance – covers losses due to natural calamities and other parametric risks.
- Comprehensive Insurance – includes Basic Insurance and additional disease coverage.
- Additionally, Scheduled Caste (SC), Scheduled Tribe (ST), and women beneficiaries are eligible for an extra 10% incentive, further promoting inclusivity. The insurance is valid for one crop cycle, providing stability to incomes and encouraging further investment in aquaculture.
State of India’s Fisheries Sector
- As of 2023, India is the 3rd largest fish producer and 2nd largest aquaculture nation in the world after China.
- India ranks 4th globally in fish exports, contributing 7.7% to global fish production.
- Top fish-producing states: Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka.
- Government's Initiatives:


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
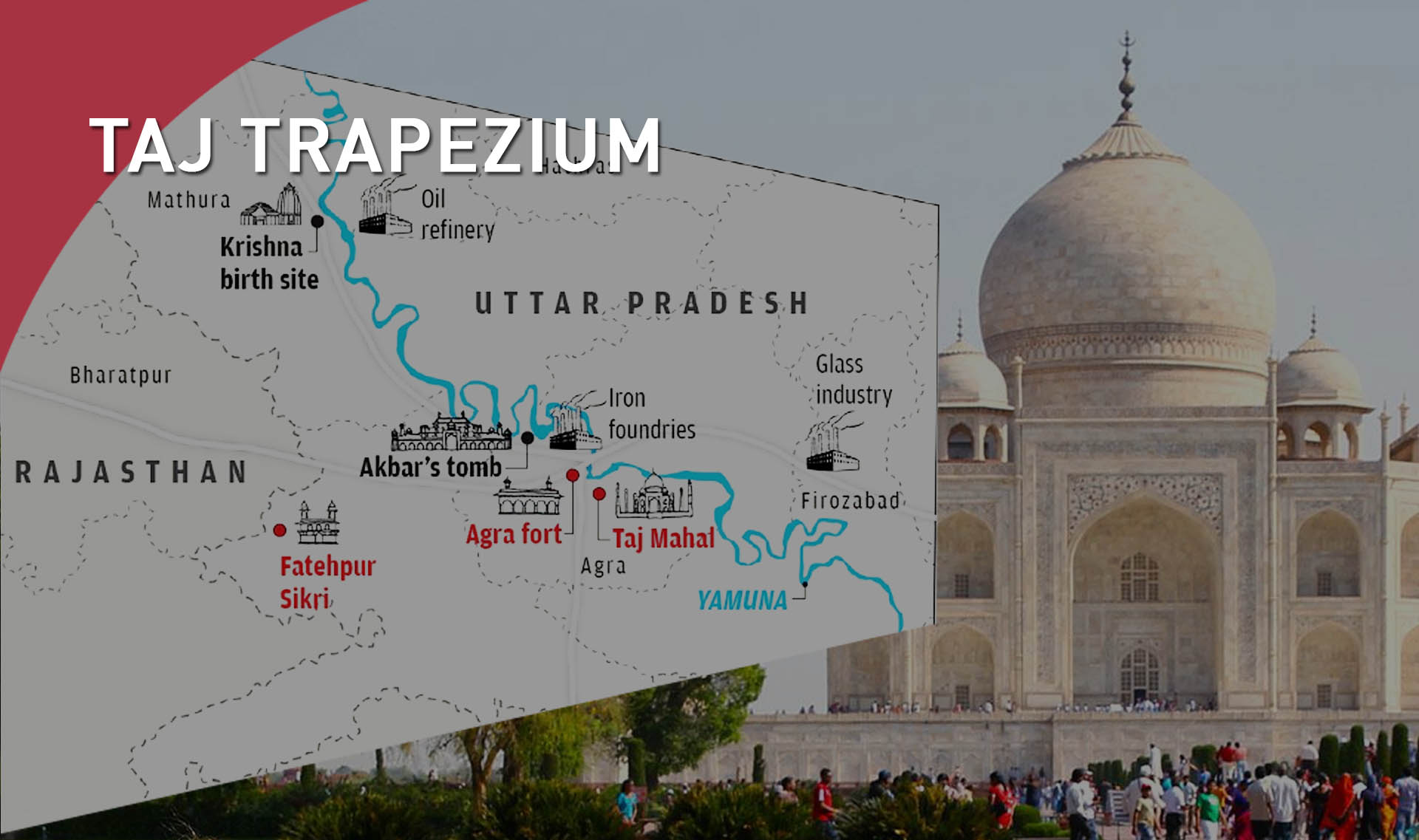
Taj Mahal Conservation Efforts
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has directed the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) to assess the environmental impact of glass industries on the Taj Mahal.
Key Points
- About the Court’s Instruction:
- The court directed NEERI to submit a report along with a timeline for evaluation.
- The court also directed the Uttar Pradesh Pollution Control Board to constitute a special team, which will inspect the affected industries, assess the pollution level and submit an interim report.
- It was clarified that if it is confirmed that glass industries are causing pollution, there will be no hesitation in ordering the shifting of these units.
- The direction comes in the context of earlier criticism by the Supreme Court regarding the environmental protection measures by the Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ) Authority.
- Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ):
- This is a designated area of 10,400 square km around the Taj Mahal to protect it from pollution.
- The TTZ comprises several monuments, including three World Heritage Sites (Taj Mahal, Agra Fort and Fatehpur Sikri).
- It is named so due to its trapezoidal shape.
- Industries under this zone are classified into red, orange, green and white categories depending on the level of pollution.
- The TTZ framework is responsible for pollution control, air quality monitoring and ensuring the long-term preservation of the Taj Mahal’s environmental integrity.
- Taj Mahal:
- Construction:
- The Taj Mahal was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal.
- Ustad Ahmad Lahori is considered its chief architect.
- Its construction began in 1632 AD and was completed in 1648 AD.
- It was built by artisans from the Mughal Empire, Central Asia, and Iran.
- The Taj Mahal was built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal.
- Location and Structure:
- Taj Mahal is situated on the right bank of Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh. It is enclosed within a 17-hectare Mughal garden which follows the Timurid-Persian Charbagh layout with four subdivided quarters.
- Constructed with brick-in-lime mortar, red sandstone, and white marble (quarried from Makrana (Rajasthan) for the main structure).
- It had extensive inlay work using gemstones like jade, crystal, turquoise, lapis lazuli, etc.
- The tomb chamber is octagonal with four additional corner rooms and a central space containing the tombs of Mumtaz Mahal and Shah Jahan.
- Real graves lie in the lower crypt, following Mughal tradition.
- The tomb’s structure forms a chamfered square, giving it eight sides with deep recessed arches.
- UNESCO World Heritage Recognition:
- In 1983, UNESCO inscribed the Taj Mahal on the World Heritage List under Criterion (i), recognizing it as a masterpiece of human creative genius.
- It is one of the famous Seven Wonders of the World.
- In 1983, UNESCO inscribed the Taj Mahal on the World Heritage List under Criterion (i), recognizing it as a masterpiece of human creative genius.
- Conservation and Management:
- The Taj Mahal was declared a centrally protected monument of national importance in the year 1920.
- It is managed by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- It is protected under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958 and the 1959 Rules and is enclosed within TTZ.
- Construction:
National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI)
- NEERI, established in 1958 at Nagpur, is a premier research institute under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), functioning under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It plays a vital role in environmental management, pollution control and sustainable development through research and development, policy development and technological innovation.
- Headquartered in Nagpur, NEERI operates five regional laboratories located in Chennai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, and Mumbai.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India to Bring Cheetahs from Botswana
Why in News?
To revitalize the cheetah rehabilitation efforts in India, eight cheetahs will be brought from Botswana in two phases.
- As per the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the process is underway to bring more cheetahs from South Africa and Kenya.
Key Points
- Rehabilitation of Cheetahs:
- Project Cheetah, launched in 2022, is India’s ambitious initiative to reintroduce the extinct species of cheetahs in the wild.
- So far, more than Rs. 112 crore has been spent on the project, with about 67% allocated to cheetah rehabilitation activities in Madhya Pradesh alone.
- Cheetahs will be rehabilitated in the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary located in Madhya Pradesh.
- Located near the Rajasthan border, Gandhi Sagar will serve as a second home for the cheetahs, following the Kuno National Park.
- An inter-state conservation corridor is being developed through an agreement between Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in Madhya Pradesh on the northern border of Mandsaur and Neemuch districts adjoining Rajasthan.
- It is characterized by vast open landscapes and rocky terrain.
- The vegetation includes northern tropical dry deciduous forest, mixed deciduous forest, and shrubland.
- The sanctuary is home to various flora, including Khair, Salai, Kardai, Dhavda, Tendu, and Palash.
- Its fauna comprises species such as chinkara, nilgai, spotted deer, striped hyena, jackal, and crocodile.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- It was established in 2005 following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It was constituted under the provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (amended in 2006) with the powers and functions entrusted to it, it aims to strengthen tiger conservation.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Jal Ganga Sanvardhan Abhiyan in MP
Why in News?
Under the Jal Ganga Sanvardhan Abhiyan (Water Ganga Conservation Campaign) in Madhya Pradesh, the "Paani Chaupal" organised by the Horticulture Department in every village has become a major center of attraction.
Key Points
- About Pani Chaupal:
- In these Pani Chaupals, field staff are educating village farmers about water conservation, the cultivation of crops that require less water, integrating agriculture with horticulture for higher profits, and imparting knowledge about new horticultural techniques.
- Additionally, during the campaign, online registrations are being made for the benefits of schemes such as fruit orchards, drip lines, plastic mulching, vegetable areas, spice areas, and flower area expansion plans.
- Under the Prime Minister's Agricultural Irrigation Scheme "Per Drop, More Crop", the Department of Horticulture and Food Processing has set a target to provide 76.68 crore rupees worth of sprinkler and drip facilities to 13,500 farmers.
- The target also includes planting fruit plants on nearly 5,000 hectares, conducting workshops on appropriate water management through micro-irrigation using available water in all development blocks, and ensuring the availability of over 25 lakh fruit-bearing plants for the campaign.
- To fulfill these objectives, farmers are being provided with information about the online application process at the Pani Chaupal.
- Jal Ganga Samvardhan Abhiyan:
- The campaign, which began on the banks of the Kshipra River on 30th March 2025, will continue until 30th June 2025.
- Objective:
- The main objective is to conserve and revive the water structures (rivers, ponds, wells, stepwells etc.) of the state.
- This also includes a plan to purify dirty water drains under Swachh Bharat Mission-2.0.
- Efforts are being made by the urban bodies to ensure the participation of citizens, especially women, in this campaign.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
- The scheme was launched in the year 2015 with the aim of ensuring adequate availability of water for agriculture, expanding the cultivable area under irrigation, improving water use efficiency and promoting sustainable water conservation practices.
- This is a centrally sponsored scheme with Centre-State sharing ratio being 75:25.
- In the case of North-Eastern region and hilly states, this share is in the ratio of 90:10.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
National Panchayat Awards 2025
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India presented the National Panchayat Awards during an event organized on the occasion of National Panchayati Raj Day (24th April 2025) at Madhubani, Bihar.
Key Points
- Motipur Panchayat:
- Motipur Panchayat of Bihar has been awarded the National Panchayat Award 2025. The Prime Minister presented this award to Mukhiya Prema Devi
- As part of this award, an amount of Rs 50 lakh was also awarded to the Panchayat.
- Motipur Panchayat is the only one selected from Bihar for the 'Climate Action Special Panchayat Award.'
- Only three panchayats have been selected from across the country in this category.
- This award is given for outstanding contributions to environmental protection, green development, and climate-friendly schemes.
- Motipur Panchayat of Bihar has been awarded the National Panchayat Award 2025. The Prime Minister presented this award to Mukhiya Prema Devi
- About National Panchayat Awards:
- This is to encourage top performing Panchayats that are in line with the 9 themes of Local Development Goals (LSDGs), which cover all the 17 SDGs.
- For this, the Union Ministry of Panchayati Raj has established special categories of National Panchayat Awards to encourage them.
- Climate Action Special Panchayat Award (CASPA): To encourage Panchayats to act as climate-responsive local governments.
- Atma Nirbhar Panchayat Special Award (ANPSA): To promote Atmanirbharta through augmentation of Own Source Revenue (OSR) by Panchayats.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirman Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar (PKNSSP): To recognize excellence in capacity building and training of Panchayati Raj representatives and functionaries.
- The winners are awarded trophies, certificates, and cash prizes.
- The first-place winner receives Rs 1 crore, the second-place winner gets Rs 75 lakh, and the third-place winner is awarded Rs 50 lakh.
National Panchayati Raj Day
- The day is being celebrated on April 24 since 2010.
- It marks the enactment of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992, through which Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) were granted statutory status.
Panchayati Raj
- Panchayats are mentioned in Article 40 of the Indian Constitution and Article 246 empowers the State Legislature to make laws on any matter relating to local self-government.
- To establish democracy at the local level, PRIs were given constitutional status through the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 and they were entrusted with the task of rural development in the country.
- PRI is a system of rural local self-government in India.



























.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.png)