Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Leads in PM-Surya Ghar Yojana
Why in News?
In July 2025, Uttar Pradesh (UP) became the leading state in the country for daily solar installations under the PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
Key Points
- About: In July, UP surpassed Gujarat (830/day) and Maharashtra (781/day) by installing 891 solar units per day, compared to being behind them in April 2025.
- The state has set a new daily solar installation target of 1,300 to further scale up efforts.
- Key Strategies: UP is prioritizing solar installations in its development strategy, with a revised focus on training and empowering Surya Mitras (solar workers), emphasizing entrepreneurship and customer satisfaction.
- As part of this effort, the five best-performing Surya Mitras were felicitated during an in-house program marking Akshay Urja Diwas.
- Impact: The state's efforts have led to the expansion of the renewable energy vendor network, which has grown from 86 vendors at the launch of the PM Surya Ghar Scheme to over 3,000 vendors currently.
- This growth is driving employment in the solar sector and supporting UP's goal of becoming a one trillion-dollar economy by 2029.
- Long-Term Goals: UP plans to achieve 22 gigawatts of installed solar capacity by 2027, supported by a favorable policy framework and public-private partnerships to accelerate progress.
|
Category |
Details |
|
State Solar Potential |
23 GW |
|
Installed Solar Power Capacity |
2,632 MW |
|
Solar Capacity to be Added under PM KUSUM Scheme |
2,000 MW |
|
Total Electricity Generation Capacity (by FY 2028) |
40,191 MW (30,003 MW operational) |
|
Uttar Pradesh Solar Energy Policy 2022 |
14 GW of Utility Scale Solar Energy power projects planned by FY 2028 |
|
Green Power Tariff |
Rs. 0.54 per kWh (50% of additional cost) |
|
Net Billing / Net Feed-In |
Introduced under UPERC for Rooftop Solar PV Grid-Interactive System (Gross/Net Metering) |
Key Facts About PM-Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- About: The PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, launched in February 2024 by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), aims to provide free electricity to one crore households by installing rooftop solar panels.
- With a total budget of Rs 75,021 crore, the scheme is planned for implementation until FY 2026-27.
- It offers up to 300 units of free electricity per month and provides a subsidy covering up to 40% of the installation cost, promoting widespread solar energy adoption across the country.
- Eligibility: Indian citizens, homeowners, valid electricity connection, and no prior solar subsidy.
- Implementation: It will be implemented by the National Programme Implementation Agency (NPIA) at the national level and State Implementation Agencies (SIA) at the state level.
- Key Components:
- Central Financial Assistance (CFA): Provides financial support to residential consumers for installing rooftop solar panels through the National Portal.
- Model Solar Village: Create one Model Solar Village per district, promoting solar energy adoption.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Sanskrit in Rajasthan’s Pre-Primary Classes
Why in News?
Rajasthan is set to introduce Sanskrit as a subject for pre-primary classes in state government schools, a first in the country, aiming to teach the ancient language to children aged 3 to 5.
Key Points
- Curriculum Development: Sanskrit books tailored for pre-primary students have been developed by the Rajasthan State Council of Educational Research and Training (RSCERT) and have been approved by NCERT and the state government.
- These books are designed for use in both Sanskrit and Hindi/English medium government schools, demonstrating the initiative’s inclusive approach.
- Each book also includes a list of taught words in Sanskrit, Hindi, and English, along with space for children to write the words in their mother tongue.
- The material includes illustrations of everyday items (numbers, animals, birds) with corresponding Sanskrit words.
- State’s Long-Term Vision: Rajasthan currently has 2,369 Sanskrit schools. The project will roll out in three phases:
- Phase 1: Sanskrit will be introduced in 757 new pre-primary Sanskrit schools, set to open within a month.
- Phase 2 & 3: Sanskrit will be introduced in 962 Mahatma Gandhi English Medium Schools (MGEMS) and 660 PM-Shree Schools across Rajasthan by next year.
- Alignment with NEP: The books align with the National Education Policy (NEP) and include concepts such as numbers, days of the week, body parts, and moral stories.
Sanskrit Language
- It is an Indo-Aryan language and is considered to be one of the oldest languages, and is known as the mother of most languages of India.
- It is believed to have originated in India around 3500 years ago and is often referred to as Dev Vani (the language of the deities).
- It is divided into two parts which are Vedic and classical.
- Vedic Sanskrit is the older and more archaic form of Sanskrit, which is attested in the Rig Veda, the Upanishads, and the Puranas.
- Classical Sanskrit is the later and more standardised form of Sanskrit, which is based on the grammar of Panini and used in literature, philosophy, science, and art.
Note
- Sanskrit is among the 22 official languages included in the Eight Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- It is also included among 11 Classical languages besides Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali.
- In 2010, Sanskrit was declared the second official language of Uttarakhand.
- In Mattur village of Karnataka, everyone speaks in the Sanskrit language.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Shree Kashi Vishwanath Dham is Plastic-Free Zone
Why in News?
The Shree Kashi Vishwanath Dham in Varanasi was officially declared a plastic-free zone from 11th August 2025.
Key Points
- About: A series of measures were introduced to eliminate plastic use within the temple premises, making it a model of sustainability and eco-friendliness.
- Initiative and Ban: Following a complete ban on single-use plastics ahead of the Shravan month, the authorities at Kashi Vishwanath Dham have also imposed a blanket ban on plastic utensils used for carrying water, milk for offerings, and plastic baskets used for carrying flowers and other worship materials.
- Eco-Friendly Alternatives: To support this initiative, vendors were provided with eco-friendly baskets made of bamboo strips and stainless steel along with other metal utensils.
Shree Kashi Vishwanath Temple
- Location: Varanasi, on the western bank of the Ganga River, India’s holiest river.
- Significance:
- Oldest surviving city and cultural capital of India.
- It enshrines the Jyotirlinga of Shiva, Vishweshwara (Vishwanath), which is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas.
- The temple has been a spiritual center for many great saints such as Adi Shankaracharya, Ramkrishna Paramhansa, Swami Vivekananda, Goswami Tulsidas, Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati, Gurunanak, etc.
- Temple Construction:
- Built in 1780 by Maharani Ahilya Bai Holkar of Indore.
- Naubatkhana (Naqqar Khana) was added in 1785 by Collector Mohd. Ibrahim Khan (at the behest of Governor General Warren Hastings).
- In 1839, Maharaja Ranjit Singh donated gold to cover two domes; the third dome remains uncovered.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Integrated Manufacturing Cluster (IMC) in Hisar
Why in News?
The Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor (AKIC) initiative achieved an important milestone with the signing of the State Support Agreement (SSA) and Shareholder Agreement (SHA) between the National Industrial Corridor Development and Implementation Trust (NICDIT), Government of Haryana, and Haryana Airports Development Corporation (HADC).
- The agreements focus on the development of the Integrated Manufacturing Cluster (IMC) at Hisar in Haryana.
Key Points
- About: Under the SSA and SHA, the National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC) will assist the Government of Haryana in developing the IMC at Hisar, one of 20 ongoing projects with State Governments across India.
- IMC Hisar: IMC Hisar in Haryana is expected to become a major driver of economic growth in the state.
- The development spans 2,988 acres and is part of the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor, near the newly inaugurated Maharaja Agrasen International Airport in Hisar.
- The project has an investment potential of ₹32,417 crore, with a project cost of ₹4,680 crore, and is expected to create 1.25 lakh jobs.
- It is strategically located between the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC), offering excellent connectivity through NH-52, NH-09, rail links, and proximity to major logistics hubs.
- With advanced infrastructure and close proximity to Hisar city, IMC Hisar is poised to play a crucial role in the industrial development of Haryana and North India.
Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor
- It is being developed by the Government of India as a major industrial corridor along the alignment of the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC), covering a route length of 1,839 km across six states.
- AKIC is proposed to be developed in a band of 150-200 km on either side of EDFC, in a phased manner.
- AKIC will have an influence area across seven states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- In the first phase, following Integrated Manufacturing Clusters (IMCs) have been identified for development:
- Hisar Integrated Manufacturing Cluster IMC, Haryana
- PragKhurpia Integrated Manufacturing Cluster, Uttarakhand
- Rajpura-Patiala IMC, Punjab
- IMC at Agra, Uttar Pradesh, & Saraswati Hi Tech city, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh
- New Bahri Node, Jharkhand
- IMC at Gaya, Bihar
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
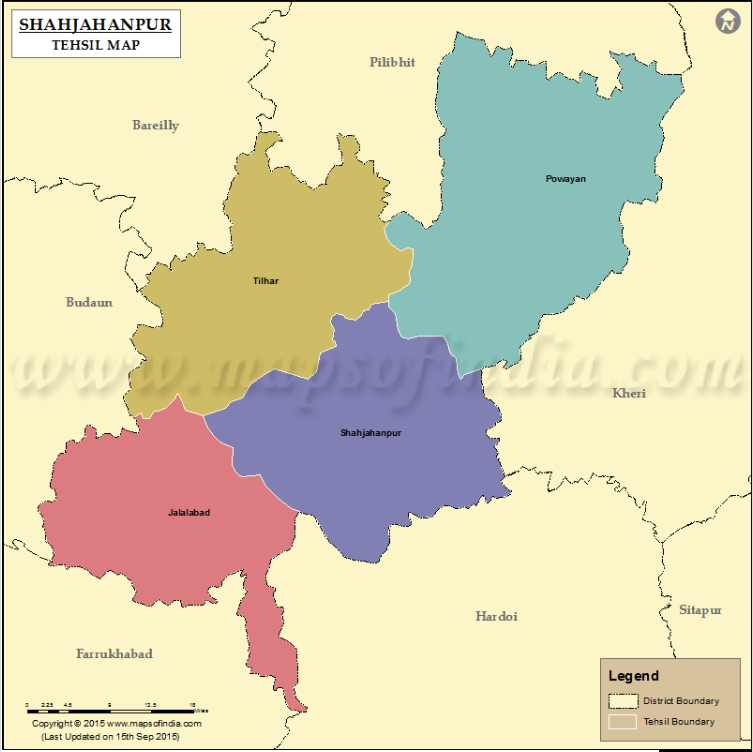
Renaming of Jalalabad to Parashurampuri
Why in News?
The Union Home Ministry has officially approved the renaming of Jalalabad town in Uttar Pradesh’s Shahjahanpur district to Parashurampuri.
Key Points
- About: The Union government has directed the Uttar Pradesh government to notify the new name, Parashurampuri, and register it in both Devnagri (Hindi) and Roman (English) scripts, along with all regional languages.
- The Uttar Pradesh government, in its request to the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), had emphasized that Jalalabad is recognized as the birthplace of Parashuram, the saint, and is home to an ancient temple dedicated to him.
- History: Jalalabad was established around 1560 and was named after Mughal emperor Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (Son of Humayun), popularly known as Akbar the Great.
- The state government began developing Jalalabad as a tourist destination in 2016.
- Process of Renaming District: The Centre has no role in altering or creating districts, as states have the authority to make such decisions, but the Home Ministry is involved when a state seeks to change the name of a district or railway station.
- The State government’s request is sent to other departments and agencies such as the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Intelligence Bureau, Department of Posts, Geographical Survey of India Sciences and the Railway Ministry seeking clearance.
- A no-objection certificate may be issued after examining their replies.
|
Places Previously Renamed in UP |
|
|
Old Name |
New Name |
|
Allahabad |
Prayagaraj |
|
Faizabad |
Ayodhya |
|
Mughalsarai Railway Station |
Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyay Nagar |
|
Jhansi Railway Station |
Veerangana Laxmi Bai |
|
Banaras |
Varanasi |
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
'Ek Bagiya Maa Ke Naam' Project
Why in News?
In an ambitious move to empower women and promote sustainable agriculture, Madhya Pradesh has launched the ‘Ek Bagiya Maa Ke Naam’ project, aiming to develop orchards on the private lands of Self-Help Group (SHG) women.
Key Points
- Project Overview: The project is part of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and is set to benefit more than 31,000 women across the state.
- Over 34,000 women have already registered through the dedicated ‘Ek Bagiya Maa Ke Naam’ app.
- The government is providing essential resources like saplings, manure, irrigation tanks, and barbed-wire fencing for protection.
- App-Driven Selection Process: The selection of beneficiaries is being done exclusively through the ‘Ek Bagiya Maa Ke Naam’ app, developed by M.P. State Electronics Development Corporation Ltd (MPSEDC) under the guidance of the MGNREGA Council.
- Only women with 0.5 to 1 acre of land are eligible to participate in the project.
- In cases where the beneficiary woman does not own land, plantations may be carried out on land owned by her husband, father, father-in-law or son, subject to their consent.
- Beneficiary Details and Training: At least 100 eligible women are being selected in each block for the project.
- These women will receive bi-annual training on orchard management, including fertilizer use, irrigation, pest control, and intercrop cultivation to ensure proper care and growth of their orchards.
- Support Through Krishi Sakhis: For every 25 acres, one Krishi Sakhi (Agriculture Companion) will be appointed to support beneficiaries, providing hands-on guidance and advice on sustainable farming practices, including the preparation of organic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Monitoring and Transparency: Plantation activities will be closely monitored through drone and satellite imagery, ensuring transparency.
- A separate dashboard has also been created for supervision. Based on performance, the top 3 districts, 10 Janpad Panchayats and 25 Gram Panchayats will be awarded.
- Leading Districts for Beneficiary Selection: The districts leading in beneficiary selection include Singrauli, Dewas, Khandwa, Niwari, and Tikamgarh, which have shown active participation in the project.
- Potential: More than 31,000 SHG women will benefit from this project, which will plant over 3 million fruit-bearing trees on their private land, laying the foundation for women's economic empowerment.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Footwear, Leather, and Non-Leather Area Development Policy 2025
Why in News?
In a move to enhance UP's status in the global footwear, leather sector, the Uttar Pradesh (UP) government has approved the Uttar Pradesh Footwear, Leather, and Non-Leather Area Development Policy 2025.
Key Features of Policy
- Export Boost: The policy seeks to boost Uttar Pradesh's share in leather and non-leather exports by attracting international investments, with dedicated investment drives conducted in countries like China and Japan.
- Modernization: Emphasis on upgrading technology, modernizing production facilities, and launching training programs to improve product quality and generate employment.
- Establishment of Centres of Excellence (CoEs) in the leather and footwear sector.
- Grants to support IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) development, covering up to Rs. 1 crore per unit.
- Skill Development: Training centers will focus on upskilling youth, with specialized courses designed in partnership with educational institutions.
- Targeted to create approximately 22 lakh jobs in the sector over the next five years, with a significant focus on employing women and people with disabilities.
- Dedicated Leather Parks: The government will create large plots of land and establish dedicated leather parks with plug-and-play facilities, waste treatment plants, and state-of-the-art infrastructure.
- Kanpur, Agra, and Unnao will see the establishment of mega-leather parks to cater to growing demand.
- Special incentives for setting up operations in underserved areas like Bundelkhand and Purvanchal.
- Financial Incentive: The policy includes provisions to support both new and existing businesses by providing incentives and subsidies for setting up new leather parks and clusters.
- 25% Capital Subsidy for setting up leather parks or clusters on 50+ acres.
- 100% Exemption on Stamp Duty for land purchase related to the project.
- Reimbursement of 50% transportation costs for exporting products to markets outside Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan for the first three years.
- Sustainability Focus: 50% Reimbursement for adopting carbon credit certification, renewable energy certifications, and energy audits.
- 75% Subsidy for obtaining international sustainability certifications.
- Support for adopting biodegradable tanning agents and waterless dyeing technologies.
Industry Insights
- Market Positioning: UP is one of India’s leading hubs for leather and footwear, contributing nearly 46% of India’s total leather exports.
- Key Locations: Agra is renowned as the 'Footwear Capital of India,' while Kanpur is a major player in leather accessories and saddlery.
- Estimated Market Size: The market size of UP's leather industry is valued at approximately $3.5 billion, with the footwear segment being a significant contributor.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Sampoornata Abhiyan
Why in News?
Chief Minister Dr. Mohan Yadav has lauded the ‘Sampoornata Abhiyan’ for its transformative impact on aspirational districts in Madhya Pradesh.
- The Abhiyan has driven development in backward districts, improving maternal health, child immunization, soil health card distribution, electricity in schools, and textbook availability, while enhancing governance, administrative efficiency, and fostering healthy competition among districts.
Sampoornata Abhiyan
- About: ‘Sampoornata Abhiyan’ was launched by NITI Aayog as a nationwide campaign aimed at achieving 100% saturation of 12 key social sector indicators in 500 Aspirational Blocks and 112 Aspirational Districts across India.
- The campaign, which ran from 4th July to 30th September 2024, focused on health, nutrition, agriculture, social development, and education.
- Key Focus Areas: The campaign’s main objective is to ensure complete saturation of critical social sector indicators, including:
- Maternal Health: Timely registration of pregnant women for Antenatal Care (ANC).
- Child Immunization: Ensuring full immunization for children aged 9-11 months.
- Soil Health: Distribution of Soil Health Cards and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
- Infrastructure: Providing electricity to secondary schools and ensuring the timely distribution of textbooks.
Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) and Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP)
|
Programme |
Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) |
Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP) |
|
Launched |
2018 |
2023 |
|
Aim |
To quickly and effectively transform 112 districts across the country. |
For saturation of essential government services in 500 blocks (329 districts) across the country. |
|
Themes |
|
|
|
Number of Indicators |
81 |
40 |
National Current Affairs Switch to Hindi
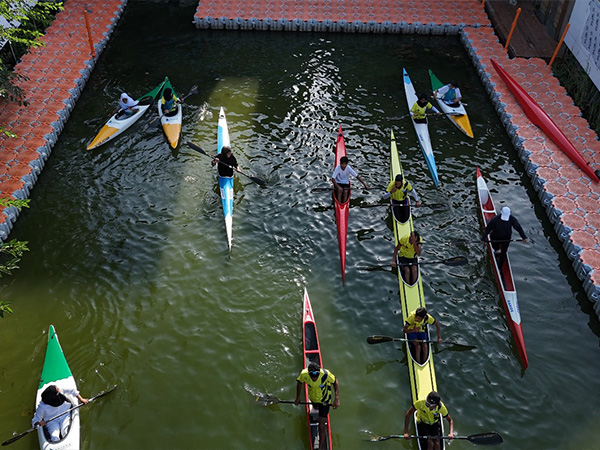
First Khelo India Water Sports Festival 2025
Why in News?
The inaugural Khelo India Water Sports Festival (KIWSF) 2025 will be held at Dal Lake from 21st August 2025 to 23rd August 2025, with over 400 participants competing in rowing, canoeing, and kayaking.
- This will be the 2nd Khelo India event in Jammu & Kashmir, following the Khelo India Winter Games in Gulmarg, further establishing the region as India’s winter sports hub.
Key Points
- About: KIWSF 2025 is being organised jointly by the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and the Jammu & Kashmir Sports Council under the government’s Khelo Bharat initiative.
- Objective: It aims to expand grassroots sports, generate local employment, and upgrade infrastructure.
- Events: It will be the first consolidated Open-age category championships where all 14 kayaking and canoeing events and the 10 rowing events are Olympic events.
- There will also be three demonstration events – water skiing, shikhara boat spring, and dragon boat race.
- Qualifications: The November 2024 kayaking and canoeing nationals in Tehri (Uttarakhand) served as a qualifier, with the top 15 in singles and doubles, and the top eight in fours, advancing to KIWSF.
- For rowing, the top eight from the nationals held in Bhopal in March 2025 will take part.
- Participants: The KIWSF will include athletes from 36 states and Union Territories, with the absence of a Services team.
- The Games will feature almost equal representation, with 409 athletes competing for medals, including 202 women.
- Madhya Pradesh (44), Haryana (37), Odisha (34), and Kerala (33) will have the largest contingent at KIWSF 2025.
- Gujarat, Puducherry, and West Bengal will have the smallest teams.
Khelo India
- Launched by the Indian government in 2017, Khelo India aims to revitalize the nation's sporting culture by engaging children at the grassroots level and enhancing infrastructure and academies for various sports.
- The initiative began with the Khelo India School Games in 2018 in New Delhi, and after the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) joined in 2018, the games were renamed to Khelo India Youth Games, with the first edition held in Pune in 2019.
- The Khelo India movement introduced the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG), Khelo India University Games (KIUG), and Khelo India Winter Games (KIWG) as annual national sports events where youth from various states and universities showcase their skills and compete for medals.
- A new addition to the Khelo India calendar, the Khelo India Water Sports Festival and the Khelo India Beach Games, which took place in Diu in May 2025, highlight the expansion of events under this initiative.
- The Khelo India Youth Games, which started in 2018 with 18 sports, expanded to 27 sports in 2025 when held in Bihar, with competitions organized in the Under-17 and Under-21 categories for both boys and girls.
- The Khelo India Centres initiative, part of the Khelo India State Centres of Excellence (KISCE) scheme, focuses on strengthening sports infrastructure at the grassroots level in India.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Highest Infant Mortality Rate in MP
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has been reported to have the highest infant mortality rate (IMR) in India, with 40 out of every 1,000 newborns dying in the state, according to statistics revealed by Deputy CM and Health Minister Rajendra Shukla in the state assembly.
Key Points
- According to the latest Sample Registration System (SRS) 2022 data from the Registrar General of India, Madhya Pradesh’s IMR (40) is not only above the national average (26), but also the highest among all states.
- In an effort to combat this issue, the government has allocated Rs 110 crore for various health schemes and initiatives, including programs such as Anaemia Mukt Bharat, nutritional rehabilitation centres, and Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, among others.
- Causes of Infant Deaths: The primary causes of infant deaths in Madhya Pradesh include premature birth, pneumonia, sepsis, low birth weight, birth asphyxia, and diarrhea.
- The government has listed these factors as key areas of focus in its efforts to reduce IMR.
Zero Maternal and Infant Deaths in MP’s Gram Panchayats
On Independence Day, the Madhya Pradesh National Health Mission (MP-NHM) recognized the outstanding efforts of grassroots healthcare workers and community leaders who achieved remarkable results in maternal and child healthcare.
- Achieving Zero Deaths in Dhakoni: Dhakoni Gram Panchayat, with a population of 8,107, successfully reported zero maternal and infant deaths for two consecutive years.
- Efforts in Garauli Gram Panchayat (Chhatarpur): Similarly, Garauli Gram Panchayat in Naugaon block, Chhatarpur district, with a population of 6,598, also reported zero maternal and infant deaths over two years.
- Institutional Deliveries in Ratlam: In Ratlam district, Primary Health Centre (PHC) in Rawti, Bajna block emerged as a leader in institutional deliveries for 2024-25.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan