Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
29th Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)
Why in News?
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs chaired the 29th meeting of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
Key Points
- About FSDC:
- The FSDC is a non-statutory apex council established by an executive order in 2010. It functions under the aegis of the Ministry of Finance.
- The idea for creating the FSDC was first recommended by the Raghuram Rajan Committee on Financial Sector Reforms in 2008.
- It is chaired by the Union Finance Minister and includes the heads of financial sector regulators such as the RBI, SEBI, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI), and Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) and Chief Economic Adviser (CEA) among others.
- Key Objectives:
- To monitor macroeconomic and financial sector developments.
- To assess and manage systemic risks that may threaten financial stability.
- To enhance inter-regulatory coordination among key financial sector regulators.
- To foster financial sector development and promote financial inclusion across the country.
- Deliberations of the 29th FSDC Meeting:
- Focus on Macro-Financial Stability:
- The FSDC discussed key issues concerning macro-financial stability and India’s preparedness to manage associated risks.
- The Council emphasised vigilance in light of both domestic and global macroeconomic trends.
- Cybersecurity and Resilience Strategy:
- Based on the analysis of sectoral cybersecurity preparedness and the Financial Sector Assessment Programme (FSAP) 2024–25 recommendations, the FSDC proposed a financial sector-specific cybersecurity strategy.
- The aim is to strengthen the cyber resilience framework across financial regulators and institutions.
- Focus on Macro-Financial Stability:
Note: The Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) is a periodic assessment jointly conducted by the IMF and World Bank in countries with significant financial sectors, which aims to comprehensively analyse financial stability and sector development.
- India underwent its first FSAP in 2011-12 and the second in 2017 and India's third FSAP is scheduled for 2023-24, with reports expected to be published by February 2025.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Multitracking Projects Under PM Gati Shakti
Why in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved two multitracking railway projects worth Rs 6,405 crore, covering seven districts across Jharkhand, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
Key Points
- Details of Approved Projects:
- Koderma–Barkakana Doubling (133 km) – Jharkhand
- The project passes through Jharkhand's key coal belt and provides the shortest, most efficient rail link between Patna and Ranchi.
- Ballari–Chikjajur Doubling (185 km) – Karnataka & Andhra Pradesh
- The line covers Ballari and Chitradurga districts in Karnataka and Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh.
- These projects are part of the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, which enables integrated, multi-modal connectivity through better planning.
- Koderma–Barkakana Doubling (133 km) – Jharkhand
- Operational and Economic Benefits:
- The increased line capacity will boost train mobility, reduce congestion, and improve service reliability.
- These routes play a vital role in transporting key commodities like coal, iron ore, steel, cement, fertilizers, agricultural goods, and petroleum products.
- The capacity upgrade is expected to generate additional freight traffic of 49 MTPA (Million Tonnes Per Annum).
- Environmental and Sustainability Gains:
- The railway upgrades will help reduce oil imports by 52 crore litres, cutting CO₂ emissions by 264 crore kg, equivalent to planting 11 crore trees.
- The shift to rail – a cleaner, energy-efficient mode of transport – supports India’s climate goals and helps lower the country’s logistics cost.
- About Jharkhand Coal Belt:
- Jharkhand has large deposits of minerals.
- The region comprising seven districts – Bokaro, Chatra, Dhanbad, Giridih, Hazaribagh, Koderma and Ramgarh is also known as the state’s coal belt.
- 40% of the total minerals of the country are available in the state.
- The state is the sole producer of cooking coal, Uranium and Pyrite.
- It ranks first in the production of coal, mica, Kyanite and copper in India.
- Jharkhand has large deposits of minerals.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- The PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, launched in October 2021 is a transformative Rs. 100 lakh crore initiative aimed at revolutionising India’s infrastructure over the next five years.
- It has been developed as a Digital Master Planning tool by BISAG-N (Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics).
- It has been prepared in a dynamic Geographic Information System (GIS) platform wherein data on specific action plans of all the Ministries/Departments have been incorporated within a comprehensive database.
- The plan seeks to accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by breaking down inter-ministerial obstacles.
- The vision of PM GatiShakti is to create a world-class infrastructure that improves the ease of living, boosts economic growth and makes Indian businesses more competitive.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Inland Fisheries & Aquaculture Meet 2025
Why in News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying organized the “Inland Fisheries & Aquaculture Meet 2025,” focusing on the development of inland fisheries and aquaculture in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- Inauguration of Key Fisheries Projects under PMMSY:
- The Union Minister inaugurated and laid the foundation stone for major fisheries projects under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- The Minister launched the Reservoir Fisheries Cluster at Halali Dam and laid the foundation for various PMMSY-supported initiatives aimed at enhancing aquaculture infrastructure, boosting fish production, and generating livelihoods in inland regions.
- Support to Beneficiaries and Technological Integration:
- The Minister distributed certificates to a range of beneficiaries including fisheries cooperatives, Fish Farmers Producers Organisations (FFPOs), and fisheries start-ups.
- Fishers received Kisan Credit Cards (KCCs) and aquaculture insurance, targeting marginalized communities with integrated digital access and focused insurance coverage.
- Growth of Inland Fisheries Since 2015
- Since 2015, the Government invested Rs 38,572 crore under various flagship schemes to strengthen the fisheries sector.
- As a result, India’s fish production grew by 104%, rising from 95.79 lakh tonnes in 2013–14 to 195 lakh tonnes in 2024–25.
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture contributed over 75% of this output, growing by 140% to reach 147.37 lakh tonnes in 2024–25.
- This sector enables year-round production, efficient resource use, and transforms underutilised land into income-generating assets, supporting livelihoods of rural and small-scale farmers.
- Technology-Driven Growth and Innovation:
- Under PMMSY and Blue Revolution, the Government approved 45,000 inland units boosting productivity by up to 20 times.
- A pilot initiative with ICAR-CIFRI (Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute) was also launched to explore the use of drones for fish transport, monitoring, and sustainable fisheries management.
- State of India’s Fisheries Sector:
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer and 2nd largest aquaculture nation in the world after China.
- India ranks 4th globally in fish exports, contributing 7.7% to global fish production.
- Inland fisheries account for over 75% of total output.
- Top fish-producing states: Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka.
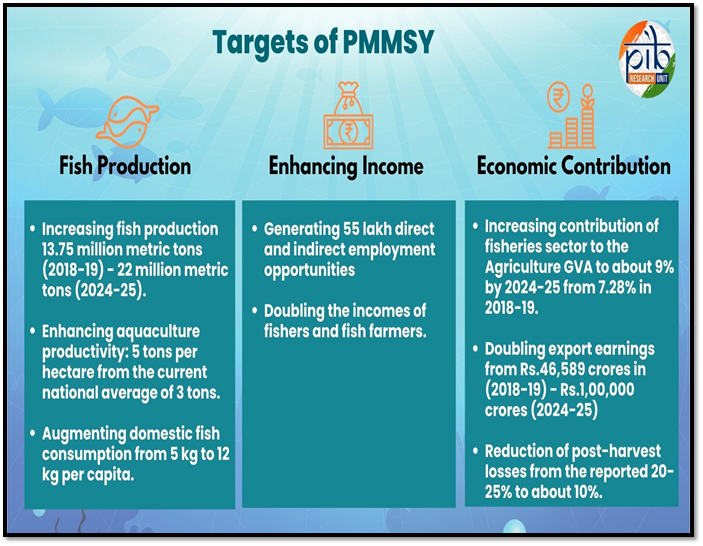
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- About:
- The Department of Fisheries is implementing the PMMSY, a scheme aimed at ushering in a Blue Revolution through the sustainable and responsible development of India's fisheries sector.
- It focuses on the comprehensive growth of the sector while ensuring the welfare of fishers.
- PMMSY is being implemented in all the States and Union Territories for a period of 5 years from FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- The Department of Fisheries is implementing the PMMSY, a scheme aimed at ushering in a Blue Revolution through the sustainable and responsible development of India's fisheries sector.
- Objective:
- PMMSY addresses gaps in fish production, productivity, quality, and post-harvest infrastructure, modernizing the value chain while ensuring fishers’ socio-economic welfare.
Blue Revolution
- The Blue Revolution refers to the integrated and sustainable development of the fisheries sector to boost fish production and productivity through inland, marine fisheries, and aquaculture.
- The Government restructured all ongoing fisheries schemes into a single umbrella programme called “Blue Revolution: Integrated Development and Management of Fisheries.”
- Implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, the scheme ensures targeted support across the sector.
- Objectives:
- Boost fish production sustainably and responsibly.
- Modernize the sector by adopting new technologies.
- Ensure food and nutritional security.
- Generate employment opportunities and boost exports.
- Promote inclusive growth and empower fishers and fish farmers.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Government Approves Procurement Under PSS
Why in News?
The Government has approved the procurement of Moong in Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Gujarat, as well as Groundnut in Uttar Pradesh, under the Price Support Scheme (PSS) for the 2025–26 summer crop season.
Key Points
- Procurement of Pulses:
- To boost domestic pulse production and reduce import dependency, the Government allowed procurement of Tur (Arhar), Urad, and Masur up to 100% of state production under the PSS for the procurement year 2024–25.
- In the Union Budget 2025, the Government extended PSS initiative for four more years till 2028–29, authorizing Central Nodal Agencies National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Limited (NAFED) and National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF) to procure pulses up to full state production levels.
- PM-AASHA:
- Pradhan Mantri Annadata Aay Sanrakshan Abhiyan (PM-AASHA), launched in 2018, has been approved for continuation during the 15th Finance Commission Cycle up to 2025-26.
- In September 2024, the government approved the continuation of the Integrated scheme of PM AASHA with the Price Support Scheme (PSS), Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) & Market intervention Scheme (MIS) as its components.
- The scheme aims to ensure assured and fair prices for farmers’ produce, protect their income, and safeguard them against market volatility.
- The PSS is triggered when market prices of notified pulses, oilseeds, or copra fall below the Minimum Support Price (MSP) during peak harvest, ensuring farmers receive remunerative prices.
Note:
- The Government implements the Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) to safeguard farmers from distress sales during sharp price drops, especially for perishable agricultural and horticultural produce during peak harvest periods.
- The Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) is a mechanism to compensate farmers for price fluctuations when the market price of their produce falls below the MSP.
National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd
- NAFED is registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002.
- It was set up in 1958 with the objective to promote Cooperative marketing of Agricultural Produce to benefit the farmers.






















.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan