Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Pushpak Drone Mission
Why in News?
The central government has appointed the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT-B) to lead the ‘Pushpak – National Mission on Drone Technology’, which promotes the development of indigenous drone technology across various sectors.
Key Points
- Overview of the Mission:
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launched the ‘Pushpak – National Mission on Drone Technology’ with a total grant-in-aid of Rs 82.7 crore.
- Participating Institutes and Their Focus Areas:
- IIT Bombay has been appointed to lead the mission. It will focus on:
- Developing hybrid drones and indigenous processors.
- Creating Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) for disaster management, coastal monitoring, and specialised uses.
- Facilitating collaboration between academia and industry to drive innovation in next-gen drone technologies.
- Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute (VJTI) Mumbai will focus on:
- Developing secure embedded systems and enhancing drone communication security.
- Establishing a dedicated drone security lab and forensic unit to:
- Track drone flight patterns within Indian airspace.
- Detecting and mitigating drone-related threats.
- Contribute to long-term cybersecurity solutions for drones.
- Other participating institutions include:
- CDAC-Thiruvananthapuram
- CDAC-Bengaluru
- IIT-Gandhinagar
- IISER-Bhopal
- Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education (Tamil Nadu)
- IIT Bombay has been appointed to lead the mission. It will focus on:
- Mission Objectives and Strategic Vision:
- The Pushpak mission aims to make India self-reliant in drone technology through:
- Advanced research and development (R&D).
- Strategic partnerships with industry players.
- Real-world testing and rapid commercialisation of technologies.
- The mission will function under the oversight of a National Steering Committee (NSC), comprising senior government officials and domain experts.
- The Pushpak mission aims to make India self-reliant in drone technology through:
- The mission aims to:
- Reduce reliance on foreign technologies.
- Enhance safety and national security.
- Create employment opportunities in the drone sector.
- Advance core capabilities in AI integration, UAV traffic management, and indigenous manufacturing.
- Support for Innovation and Talent Development:
- Pushpak will promote faster technology transfer from research labs to the market.
- It will provide:
- Incubation support to drone-based startups.
- Advanced training opportunities for students and researchers in drone-related fields.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Water Resource Atlas 2025
Why in News?
The Haryana Water Resources (Conservation, Regulation and Management) Authority (HWRA) has launched the Haryana Water Resource Atlas 2025- an AI-powered geospatial platform that monitors, manages, and conserves the state’s rapidly depleting water reserves.
Key Points
- Key Features of the Atlas:
- HWRA developed the atlas in collaboration with the Haryana Space Applications Centre (HARSAC).
- The platform is publicly accessible and provides real-time, layered insights on:
- Groundwater levels and aquifers
- Surface water bodies and canal systems
- Recharge zones and water-intensive cropping patterns
- It offers interactive thematic maps and dashboards.
- It tracks district and block-level water stress, with a focus on over-extraction zones and areas facing erratic rainfall.
- Urgency Behind the Initiative:
- Internal assessments reveal that over 76% of Haryana’s administrative blocks are either “critical” or “over-exploited” in terms of groundwater use.
- The platform aims to enable data-driven interventions at both administrative and grassroots levels.
- Data Scope and Update Cycle:
- Most core datasets (like groundwater depth and soil composition) won’t be revised annually.
- Such parameters typically require updates once in a decade, making the platform low-maintenance in terms of data renewal.
- The atlas integrates data from:
- Satellite observations and GPS surveys
- Meteorological inputs and agriculture records
- Inputs from Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), Irrigation Department, and Agriculture Department.
- The National and State-level agencies have validated the data to ensure accuracy and operational relevance.
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB)
- About: The CGWB, established under the Ministry of Water Resources, (now Ministry of Jal Shakti), is the apex body for managing, exploring, monitoring, assessing, and regulating groundwater resources in India.
- Established in 1970, CGWB was initially formed by renaming the Exploratory Tube Wells Organization and was later merged with the Ground Water Wing of the Geological Survey of India in 1972.
- The Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), constituted under the Environmental Protection Act, 1986, regulates groundwater development to ensure its sustainability.
- Key Functions and Responsibilities: CGWB provides scientific expertise for groundwater management, including exploration, monitoring, and water quality assessments.
- It also implements schemes for artificial recharge and rainwater harvesting to augment groundwater levels.
- Scientific Reports: CGWB releases State and District hydrogeological reports, ground water year books and Atlases.
India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- About:
- It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India.
- Objectives:
- To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information for optimum operation of weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc.
- To warn against severe weather phenomena like tropical cyclones, norwesters, duststorms, heavy rains and snow, cold and heat waves, etc., which cause destruction of life and property.
- To provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities.
- To conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
India's First AI-Based Data Park
Why in News?
On 4 May 2025, Chief Minister of Chhattisgarh inaugurated the Artificial Intelligence Aided Data Centre Park in Nava Raipur.
Key Points
- About the Initiative:
- This first-of-its-kind initiative in India is being developed with an investment of Rs 1,000 crore, to be utilised over two years.
- The 13.5-acre park includes a 2.7-hectare Special Economic Zone (SEZ) dedicated exclusively to AI-based services.
- Empowering Tribal Communities Through Technology:
- The AI Data Centre Park is envisioned as a catalyst for socio-economic transformation in Chhattisgarh.
- It aims to deliver advanced AI-driven solutions in agriculture and education, directly benefiting students, farmers, and rural populations.
- By hosting a dedicated SEZ, the park is expected to attract domestic and international tech firms, fostering an ecosystem of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Strategic Vision:
- It represents a milestone in Chhattisgarh’s push toward digital governance and public service transformation.
- The government plans to use AI to enhance service delivery, resource management, and economic productivity across the state.
- Complementary initiatives such as the creation of Data AI Clubs in schools and educational partnerships aim to strengthen digital literacy and infrastructure.
Special Economic Zone
- A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws that are more liberal than a country's domestic economic laws.
- The category 'SEZ' covers a broad range of more specific zone types, including, but not limited to:
- Free Trade Zones (FTZs)
- Export Processing Zones (EPZs)
- Free Zones (FZs)
- Industrial Estates (IEs)
- India was one of the first in Asia to recognize the effectiveness of the Export Processing Zone model in promoting exports, with Asia's first EPZ set up in Kandla, Gujarat in 1965.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
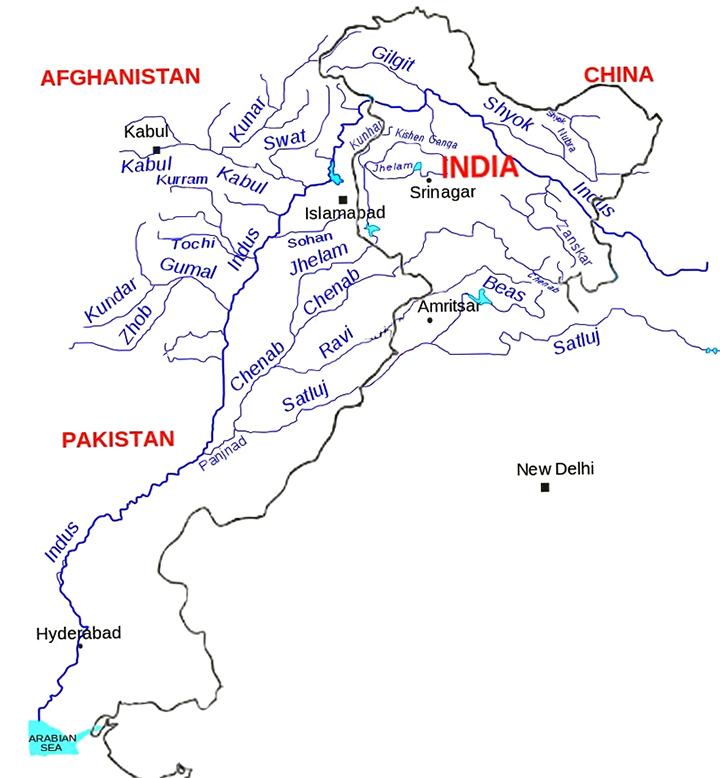
Baglihar Dam
Why in News?
In a significant move, India has blocked the flow of water to Pakistan through the Baglihar Dam on the Chenab River and is planning to take similar action at the Kishanganga Dam on the Jhelum River.
Key Points
- About Baglihar Dam:
- The Baglihar Dam, officially known as the Baglihar Hydroelectric Power Project, is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric facility located on the Chenab River in Doda district, Jammu and Kashmir.
- The dam is a concrete gravity structure, measuring 144.5 metres in height and 363 metres in length, with a total volume of 1.9 million cubic metres.
- It creates a reservoir with a storage capacity of approximately 475 million cubic metres.
- The underground powerhouse spans 221 metres in length, 24 metres in width, and 51 metres in height.
- Project planning began in 1992, received official approval in 1996, and construction started in 1999.
- The project was implemented in two phases, each with an installed capacity of 450 MW.
- The first phase was completed in 2004, and the second phase was commissioned on 10 October 2008.
- The dam currently has a total installed capacity of 900 MW.
- Kishanganga Dam:
- The Kishanganga project is located 5 km north of Bandipore in Jammu and Kashmir, India.
- It is a run-of-the-river project that includes a 37 m tall concrete-face rock-fill dam.
- It requires diverting water from the Kishanganga River through a tunnel to a power plant in the Jhelum River basin.
- It will have an installed capacity of 330 MW.
- The construction of this hydroelectric project began in 2007.
- Pakistan objected to the project arguing that it will affect the flow of the Kishanganga River (called the Neelum River in Pakistan).
- In 2013, The Hague’s Permanent Court of Arbitration (CoA) ruled that India could divert all the water with certain conditions.
Chenab River
- Source: It rises in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul and Spiti district of Himachal Pradesh state.
- The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga, at Tandi, 8 km southwest of Keylong, in the Lahaul and Spiti district.
- The Bhaga river originates from Surya taal lake, which is situated a few kilometers west of the Bara-lacha la pass in Himachal Pradesh.
- The Chandra river originates from glaciers east of the same pass (near Chandra Taal).
- The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga, at Tandi, 8 km southwest of Keylong, in the Lahaul and Spiti district.
- Flows Through: It flows through the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before flowing into the Indus River.
- Some of the important projects/dams on Chenab:
- Ratle Hydro Electric Project
- Salal Dam- hydroelectric power project near Reasi
- Dul Hasti Hydroelectric Plant- power project in Kishtwar District
- Pakal Dul Dam (under construction)- on a tributary Marusadar River in Kishtwar District.
Jhelum River
- About:
- The Jhelum River flows through northwestern India and northern and eastern Pakistan, serving as a major tributary of the Indus River.
- Known as Vyeth in Kashmiri, Vitasta in Sanskrit, and Hydaspes in Greek, it is the principal river of the Kashmir Valley.
- Among the five rivers of Punjab, it is the largest and westernmost, flowing through Jhelum District in northern Punjab, Pakistan.
- River Course and Origin:
- Origin: The Jhelum originates from the Verinag Spring in Anantnag, located at the base of the Pir Panjal range in Jammu and Kashmir.
- It flows northwestward through the Vale of Kashmir, entering Wular Lake near Srinagar, which helps regulate its flow.
- After Wular, the river carves a deep and narrow gorge as it moves towards Pakistan.
- Eventually, it merges with the Chenab River near Trimmu, in Pakistan's Punjab province.
- Total Length: Approximately 725 km (450 miles).
- Origin: The Jhelum originates from the Verinag Spring in Anantnag, located at the base of the Pir Panjal range in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Major Tributaries:
- The Kishanganga (Neelum) River is the largest tributary, joining the Jhelum near Muzaffarabad.
- The Kunhar River, the second-largest tributary, links Pakistan-occupied Kashmir and Pakistan near the Kohala Bridge in the Kaghan Valley.
- Other important tributaries include:
- Sandran River
- Bringi River
- Arapath River
- Watlara River
- Lidder River
- Veshaw River
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
World Asthma Day 2025
Why in News?
World Asthma Day is observed on the second Tuesday of May to raise awareness about the condition and the risks it poses.
Key Points
- World Asthma Day 2025:
- In 2025, it falls on Tuesday, 6 May, with the theme “Make inhaled treatments accessible for all.”
- The theme emphasizes the need to make inhaled medications widely available for both disease management and emergency care.
- About Asthma:
- Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease where a person’s airways become inflamed, narrowed, and swollen, producing excess mucus, which makes breathing difficult.
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), defines asthma as a condition that can cause recurring episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing.
- Global Burden:
- Over 250 million people around the world live with asthma, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- In 2019, asthma caused approximately 455,000 deaths globally, highlighting the urgent need for better disease control and treatment access.
- History and Origin:
- The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) launched the first World Asthma Day in 1998 during the World Asthma Meeting in Barcelona, Spain, with participation from 35 countries.
- Since then, the event has grown globally and is now considered one of the most significant asthma education and awareness days.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank
Why in News?
Aryavart Bank, Prathama Bank, and Baroda UP Bank—three regional rural banks in Uttar Pradesh—have been merged into a single entity, named ‘Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank’.
Key Points
- About Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank :
- The objective of this bank is to ensure financial inclusion , integrated management and better customer services in rural areas .
- This new bank came into existence from 1st May 2025 under the notification of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India .
- The jurisdiction of this newly formed bank will extend to 26 districts of Uttar Pradesh, in which operations will be carried out through a total of 22 regional offices.
- The headquarters of this newly formed bank will be established in Lucknow and it will be operated under the sponsorship of Bank of Baroda .
- Benefits:
- Ease in loan disbursal : Quick loan approval to farmers, self-employed rural entrepreneurs.
- Expansion of digital services : Facilities like mobile banking, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), net banking will reach remote villages.
- Monitoring of Facilities : A special committee has been formed by NABARD which will assess the convenience of the customers.
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- NABARD is a development bank that primarily focuses on the rural areas of the country. It is the apex banking institution for providing finance for agriculture and rural development.
- Its headquarters is located in Mumbai, the financial capital of the country.
- Apart from agriculture, it is responsible for the development of small industries, cottage industries and rural projects.
- It is a statutory body established in the year 1982 under the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act, 1981.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Ration Card for Transgenders
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has announced a special drive to issue ration cards to transgender citizens under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
Key Points
- Status of Transgender Community:
- The Government was informed through the report by the Uttar Pradesh Transgender Welfare Board that a large number of transgender persons are deprived of permanent employment and government schemes.
- Due to social discrimination they are also deprived of basic facilities like food security, pension, health services.
- Intervention of Chief Minister :
- Taking cognizance of this report, the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh has directed that:
- The ration card distribution process should be made simple, fast and transparent
- This work should be completed before the launch of the state's 'Zero Poverty' programme .
- All districts have been instructed to identify transgender persons who do not have ration cards and issue them documents .
- These beneficiaries should be added to the ' eligible household ' category and brought under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- Taking cognizance of this report, the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh has directed that:
- Importance:
- This will promote social inclusion and provide equal rights and dignity to the transgender community.
- By ensuring food security , their economic condition will be strengthened.
- Administrative reforms and transparency will make the reach of welfare schemes more effective.
National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013
- Notified: September 10, 2013
- Objective: It aims to provide food and nutrition security to the people by providing them with an adequate quantity of good quality food at affordable prices to lead a dignified life.
- Coverage: 75% of rural population and 50% of urban population eligible to receive subsidized food grains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA) overall covers 67 per cent of the country's total population.
- Eligibility:
- Priority households covered under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS), as per State Government guidelines.
- Houses covered under Antyodaya Anna Yojana.
- Provision:
- 5 kg food grains per person per month, including rice at Rs 3 per kg, wheat at Rs 2 per kg and coarse grains at Rs 1 per kg.
- However, under the Antyodaya Anna Yojana, the existing provision of 35 kg foodgrains per family per month will continue.
- There is a provision to provide maternity benefit of at least Rs 6000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers in addition to food during pregnancy and six months after the birth of the child.
- Food for children upto 14 years of age.
- Food security allowance to the beneficiaries in case of non-supply of food grains or meals.
- Establishing grievance redressal mechanisms at district and state levels.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Cheetah Conservation Corridor
Why in News?
Rajasthan has become a part of India's first inter-state Cheetah conservation corridor along with Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- About the Protected Area:
- The total area of the corridor is 17,000 sq km , out of which 10,500 sq km is spread in Madhya Pradesh and 6,500 sq km in Rajasthan .
- This corridor includes Kuno National Park in Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh as the main site, where cheetah reintroduction project is being implemented.
- Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary, located on the banks of Chambal River in Mandsaur district, has been selected to develop the second habitat for cheetahs in Madhya Pradesh.
- Districts like Kota, Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar, Sawai Madhopur, Karauli and Chittorgarh of Rajasthan are included in this project .
- In future, it is proposed to include the forest areas of Jhansi and Lalitpur of Uttar Pradesh in this corridor.
- Institutional support:
- The project has technical guidance from the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
- Experts have described this project as a unique model of wildlife conservation in Asia, which can become an example for other countries.
- Features of the Corridor:
- This corridor will facilitate natural and uninterrupted migration of cheetahs between protected areas .
- It establishes a strategic wildlife connectivity between the two states, the first of its kind initiative in India.
- The goal of the project is restoration and conservation of grassland-based ecosystems .
- The corridor is being designed to bring together the friendly, safe and natural habitats of the cheetahs.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- Introduction:
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change .
- It was established in the year 2005 with the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force .
- It was constituted under the enabling provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006 to strengthen tiger conservation .
- Objective:
- To provide statutory powers to Project Tiger so that its directions are legally complied with.
- To promote Centre-State accountability in the management of tiger reserves by providing a basis for MoUs with States within a federal framework .
- Ensuring oversight by Parliament .
- Addressing the livelihood interests of local people in the areas around Tiger Reserves.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India's First Stratospheric Airship
Why in News?
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the maiden test flight of the Stratospheric Airship Platform from its testing facility in Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- About Airship:
- Developed by the Agra-based Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE), this airship platform can be deployed in the stratosphere at an altitude of about 17 km.
- It can remain stable at one place for a long time and has the ability to send real time data .
- The stratosphere is a layer of the Earth's atmosphere that lies above the troposphere and below the mesosphere, ranging in altitude from about 10 to 50 km.
- It provides a stable atmosphere different from weather changes on Earth, making the region a suitable for satellites and other high-altitude equipment.
- Structure:
- This airship is equipped with lightweight and highly sensitive technologies, giving it the capability to operate at high-altitudes.
- It is equipped with state-of-the-art payloads and sensor systems for ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance and Recon) missions.
- The system can be safely recovered after the mission, allowing for longer periods of operation.
- Strategic Use:
- This airship strengthens the surveillance capability of the security forces by remaining beyond the range of radar .
- This platform can prove to be extremely useful for military operations in inaccessible and sensitive areas such as Kashmir and Arunachal Pradesh.
- This technology is much more efficient and sustainable than traditional monitoring systems.
- It can give accurate information about enemy activities covering a wide area.
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- About:
- DRDO is the research and development arm of the Ministry of Defence aimed at empowering India in cutting-edge defence technologies.
- Efforts towards self-reliance and successful indigenous development and production of strategic systems and platforms like Agni and Prithvi missile series, light combat aircraft Tejas, multi-barrel rocket launcher Pinaka, air defence system Akash, a wide range of radars and electronic warfare systems etc. have enhanced India's military capabilities.
- Formation:
- It was formed in 1958 by the integration of the Technical Development Establishments (TDEs) and Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) of the Indian Army and the Defence Science Organisation (DSO) .
- DRDO is a network of more than 50 laboratories intensively engaged in development of defence technologies covering various disciplines such as aeronautics, armament, electronics, combat vehicles, engineering systems etc.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Pulitzer Prize 2025
Why in News?
The Pulitzer Prizes 2025, honoring outstanding contributions to journalism and the arts, were announced by the Pulitzer Prize Board.
Key Points
- About Pulitzer Prize:
- The Pulitzer Prize is considered America's most prestigious honor in the field of journalism.
- This award was started in the year 1917, which is administered by Columbia University and the 'Pulitzer Prize Board'.
- The Pulitzer Prize Board is composed of judges appointed by Columbia University.
- This award is named in honor of renowned newspaper publisher Joseph Pulitzer, who bequeathed funds in his will to establish the School of Journalism at Columbia University and to institute the Pulitzer Prize.
- Reward:
- Each award winner carries a certificate and prize money of USD 15,000 and the award winner in the 'Public Service Category' receives a gold medal.
- Pulitzer Prize 2025:
- The Pulitzer Prizes for the year 2025 were given in a total of 23 categories, including 15 categories of journalism and 8 categories of books, drama, music etc.
- List of winners include:
- Fiction: Percival Everett won the award for his novel 'James' , which tells the story of 'Huckleberry Finn' from the point of view of a slave.
- Drama: Branden Jacobs-Jenkins was honored for “Purpose,” which delves into the inner complexities of a wealthy black family.
- Journalism: The New York Times won four Pulitzers, The New Yorker three, and The Washington Post three for their swift reporting on the Trump assassination attempt.
- Public Service: Kavita Suarna, Lizzie Presser, Cassandra Jaramillo and Stacy Kranitz (reporting on deaths of pregnant women due to obscure abortion law exceptions).
- Investigative Reporting: Reuters Staff (Supply chain expose on fentanyl crisis).
- Explanation: Azam Ahmed, Christina Goldbaum and Matthew Aikins (NYT).
- Local reporting: Alissa Zhu, Nick Thiem and Jessica Gallagher (Baltimore fentanyl crisis).
- National Reporting: Wall Street Journal Staff (reporting on Elon Musk).
- International reporting: Declan Walsh and NYT staff (reporting on the Sudan conflict).
- Special Writing: Mark Warren (Esquire).
- Commentary: Mosab Abu Toha (The New Yorker).
- Review: Alexandra Lang (Bloomberg CityLab).
- Editorial writing: Raj Mankad, Sharon Steinman, Lisa Falkenberg and Leah Binkowitz (Houston Chronicle).
- Featured reporting and commentary: Ann Telnes (Washington Post).
- Breaking News Photography: Doug Mills (NYT).
- Exclusive photography: Moises Saman (The New Yorker).
- Audio reporting: The New Yorker Staff.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan