Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
National Ayush Mission Conclave 2025
Why in News?
The National Ayush Mission (NAM) Conclave 2025 began at Kaivalyadhama, Lonavala (Maharashtra), showcasing the progress made by various States and Union Territories in the Ayush sector.
Key Points
- NAM Conclave 2025:
- The event aims to set a roadmap for integrating Ayush into mainstream healthcare.
- Ayush and Health Ministers from several states, including Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Mizoram, attended the conclave.
- Objective:
- Organised by the Ministry of Ayush, the event brought together experts, policymakers, and innovators.
- Its goal is to make traditional Indian medicine more accessible, affordable, and evidence-based.
- Key Achievements:
- Since the 2023 NAM Conclave, efforts have led to the formulation of an action plan for better NAM execution.
- The establishment of 12,500 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs increased healthcare access from 1.5 crore (2021) to over 11.5 crore beneficiaries (2025).
- State-Level Successes:
- Uttar Pradesh: Now has 3,959 operational Ayush hospitals.
- Chhattisgarh: Promotes integrative medicine for holistic healthcare.
- Rajasthan: Preparing a comprehensive Ayush policy.
- Himachal Pradesh: Uses tech-based integrated Ayush model focusing on women’s health.
- Mizoram: Witnessed rapid growth in Ayush popularity post establishment of Wellness Centres.
- Sikkim: Strengthened rural outreach with NAM support.
- Key Outcomes and Announcements:
- 5.6 crore people accessed tertiary care in Ayush institutions.
- National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH) entry-level certification granted to 1,372 Ayush Health & Wellness Centres.
- 189 Integrated Ayush Hospitals have been established.
- Launch of Standard Treatment Guidelines (STGs):
- STGs for metabolic disorders—Diabetes, Obesity, Gout, NAFLD, and Dyslipidemia—were released.
- Developed with inputs from Research Councils and allopathic experts.
- Guidelines integrate Yoga, dietary protocols, and clinical procedures for wider adoption.
National Ayush Mission (NAM)
- Launched in 2014 to integrate traditional Indian medicine into mainstream healthcare.
- Focuses on increasing availability and quality of Ayush services through Ayushman Arogya Mandirs.
- NAM 2023 resolutions included expanding Health & Wellness Centres and integrating Ayush with National Health Programs.
National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH)
- NABH is a constituent board of Quality Council of India, set up to establish and operate accreditation programmes for healthcare organisations.
- Scope of NABH /Objectives:
- Accreditation of healthcare facilities
- Quality promotion: initiatives like Safe-I, Nursing Excellence, Laboratory certification programs (but not limited to these)
- IEC activities: public lecture, advertisement, workshops/ seminars
- Education and Training for Quality & Patient Safety
- Recognition: Endorsement of various healthcare quality courses/ workshops


West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Corporate Bhavan
Why in News?
Union Finance and Corporate Affairs inaugurated the ‘Corporate Bhavan’ in New Town, Kolkata.
Key Points
- Corporate Bhavan:
- The seven-storey building spans approximately 13,239 square metres and was constructed at a cost of around Rs 150.43 crore.
- The Corporate Bhavan integrates key offices under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs under one roof, such as:
- Regional Directorate (East), Registrar of Companies, Official Liquidator, Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO), National Company Law Tribunal (Kolkata Bench), Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI).
- The Minister stated that the facility will act as a single-window interface for startups, investors, auditors, companies, and insolvency professionals.
- The Minister also emphasised the need for regulatory frameworks that:
- Promote good governance
- Support enterprise and formalisation
- Build public trust in regulatory systems
- PM Internship Scheme (PMIS) Facilitation Centre:
- The first-ever PMIS Facilitation Centre was also launched during the event, located on the 7th floor of Corporate Bhavan.
- The centre will serve as a resource hub for aspiring interns seeking guidance and support under the PM Internship Scheme.
- Objectives:
- Established as a collaborative initiative between MCA and Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- Targets youth aged 21–24 who are not in full-time education or employment.
- Key functions:
- Facilitating registration and application under PMIS
- Offering professional career counselling and guidance
- Matching candidates with suitable internships
- Raising awareness through outreach programmes
PM Internship Scheme
- The scheme aims to provide students with internship opportunities to address youth unemployment.
- It seeks to provide internships to 1 crore young people over the next five years.
- Applicants will get a monthly stipend of Rs 4,500 from the government, and an additional Rs 500 by companies as part of their Corporate Social Responsibility initiatives consisting of one year.
- A one-time grant of Rs 6,000 will be provided upon enrollment, along with insurance coverage under the PM Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana and PM Suraksha Bima Yojana.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Water Sharing Issues
Why in News?
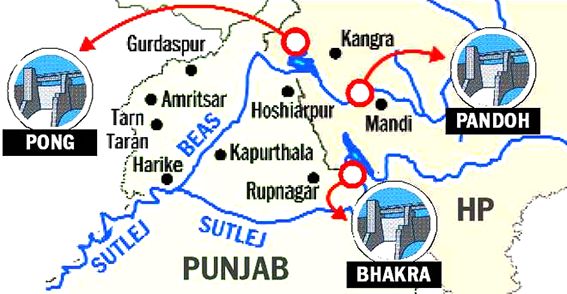
Punjab and Haryana clashed over water sharing after the Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB) decided to release water to Haryana.
Key Points
- BBMB Decides to Release Water to Haryana:
- On April 30, the BBMB decided to release 8,500 cusecs of water to Haryana.
- The decision followed Haryana's demand for drinking water amid rising summer needs.
- BBMB manages water from Bhakra, Pong, and Ranjit Sagar dams, supplying Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan for irrigation and other uses.
- Punjab's Allegations on Water Share Misuse:
- According to Punjab Chief Minister, Haryana exhausted its annual water quota (May 21–May 20 cycle) by March 2025.
- He accused Haryana of now trying to grab extra water at Punjab’s expense.
- He said Punjab holds a 60% stake in BBMB, and releasing water without its consent is "dictatorial and undemocratic."
Bhakra Nangal Dam
- Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam across the Sutlej River and is near the border between Punjab and Himachal Pradesh in northern India.
- It is India’s second tallest at 225.55 m high next to the 261m Tehri Dam.
- Its reservoir, known as the “Gobind Sagar”, stores up to 9.34 billion cubic meters of water.
- Nangal dam is another dam downstream of Bhakra dam. Sometimes both the dams together are called Bhakra-Nangal dam though they are two separate dams.
Pong Dam
- In 1975, Pong dam was built across the Beas River. It is also called the Pong reservoir or the Maharana Pratap Sagar.
- In 1983, the entire reservoir was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary by the Himachal Pradesh government.
- In 1994, the Government of India declared it a “Wetland of National Importance”. Pong Dam Lake was declared as Ramsar Site in November 2002.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Merger of Banks in Madhya Pradesh
Why in News?
The Central Government will implement the One State-One RRB policy from 1 May 2025, to improve the quality of rural banking services.
Key Points
- About One State-One RRB Policy :
- Under this policy, the number of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) will be reduced from 43 to 28, with one RRB serving all rural areas in each state.
- Each new RRB will have an authorised capital of Rs 2,000 crore and operate with improved efficiency, management, and customer service.
- Objective:
- To improve the effectiveness and organization of rural banking services .
- Providing integrated services and improved access to customers .
- Reduce operating costs and grow business .
- Accelerating financial inclusion .
- Historical background of Unification:
- In the first phase (2006-2010), the number of RRBs was reduced from 196 to 82.
- In the second phase (2013-2015), it was reduced from 82 to 56 and in the third phase, it was reduced from 56 to 43.
- Now there will be a total of 28 RRBs left in the fourth phase .
- Merger of banks in Madhya Pradesh:
- From 1 May 2025, Madhya Pradesh Gramin Bank and Madhyanchal Gramin Bank have merged into a single rural bank, sponsored by Bank of India with its headquarters in Indore.
- The move aims to strengthen rural banking and streamline operations.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) were established in the year 1975 under the provisions of the Ordinance promulgated on September 26, 1975 and the Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976.
- RRBs are financial institutions which ensure adequate credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- RRBs enhance the co-operative features and the capacity of a commercial bank to mobilise business and financial resources while being familiar with rural problems.
- Regional Rural Banks are operated in collaboration with the Government of India, State Governments and sponsor banks.
- The shareholding of the Government of India, sponsor banks and the respective states in these banks is 50%, 35% and 15% respectively.
- Regional Rural Banks are regulated by the ‘National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development ' (NABARD).
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Krishi Sakhi in UP
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has decided to train women as 'Krishi Sakhi' to promote natural farming.
Key Points
- About Krishi Sakhi Scheme :
- This initiative formally recognises the role of women in agriculture, and is a strong step towards making them economically and socially self-reliant.
- Selection Process & Role:
- Those women will be selected as 'Krishi Sakhi' who will:
- Be a local resident .
- Be associated with Self-Help Groups (SHGs) or be active in agricultural work .
- Have a minimum of primary education (literacy is compulsory).
- Their role includes:
- Raising awareness among farmers about natural farming benefits.
- Receiving and sharing training on organic inputs and seed treatment.
- Monitoring agricultural clusters and reporting farmer issues to Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
- Promoting collective farming through women’s groups.
- Training and Honorarium:
- These women will be given regular training by Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) on topics like natural farming, organic product production, experimental methods, disease control .
- During the training they will be provided with field demonstrations , visual aids, and toolkits .
- Two Bio-input Research Centres will be established in each district .
- 'Krishi Sakhis' will be paid an honorarium of Rs 5,000 per month, which will become a source of fixed income for rural women .
- Additionally, performance-based incentives may also be given in some areas.
Natural Farming
- Natural farming is a chemical-free agricultural method based on locally available resources.
- It promotes traditional indigenous methods that free producers from dependence on external inputs.
- The major focuses of natural farming are on-farm biomass recycling with biomass mulching, on-farm use of indigenous cow dung and urine, pest management through diversity, on-farm vegetable mixing and exclusion of all synthetic chemical inputs directly or indirectly.
- Since no synthetic chemicals are used in natural farming, it is less hazardous to health .
- These foods have high nutritional content and provide better health benefits.
- Natural Farming aims to make farming viable and aspirational by reducing costs and risks, increasing the net income of farmers as a result of uniform yield and income from intercropping .
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Autobiography of Anandiben Patel
Why in News?
The autobiographical book 'Chunautiyaan Mujhe Pasand Hain' of Governor Anandiben Patel was released by the Vice President of India at Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow .
Key Points
- About the Book:
- This book depicts his struggles and achievements in politics, administration and social life .
- The book mentions her journey from being a simple worker to becoming the first woman Chief Minister of Gujarat and then Governor of Uttar Pradesh.
- It presents examples of women's leadership, struggle and empowerment .
- Anandiben Patel:
- Anandiben Patel is currently the Governor of Uttar Pradesh and is known as an influential woman leader in Indian politics .
- She was born on 21 November 1941 in a Patidar family in Kharod village of Mehsana district of Gujarat.
- She launched the e-Zameen programme, which computerised land records and digitised farmers' thumb impressions and photographs .
Governor
- About:
- The Governor is the executive head of the state. Traditionally, he should not belong to the state where he is appointed, so that he can remain free from local politics.
- Apart from this, while appointing a Governor, it is necessary for the President to consult the Chief Minister regarding the affairs of the state so that constitutional order is ensured in the state.
- The Governor is neither directly elected by the people nor is he indirectly elected under the constitutional process like the President.
- He is appointed by order of the President under his seal.
- He holds office at the pleasure of the President and can be removed by the President at any time.
- The Governor is the executive head of the state. Traditionally, he should not belong to the state where he is appointed, so that he can remain free from local politics.
- Terms of Governor's Office:
- The Raj Bhavan (official corporation) will be available to him without rent.
- He shall be entitled to all emoluments , privileges and allowances as may be determined by the Parliament.
- If the person is appointed as the Governor of two or more States, these emoluments and allowances will be provided jointly by the States as per the norms set by the President .
- His financial achievements and allowances during his tenure cannot be underestimated.
- Privilege:
- Under Article 361, he enjoys personal immunity from legal liability for his official acts .
- During his term of office, he enjoys immunity from trial in criminal proceedings (even if involving personal action).
- He cannot be arrested and put in jail.
- However, civil legal proceedings can be initiated against them for personal activities after giving two months' notice .

























.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


