Chhattisgarh
Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR)
- 21 May 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Chhattisgarh’s Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR) has recorded a remarkable resurgence in wildlife activity, highlighting the reserve’s transformation into a thriving ecological sanctuary.
Key Points
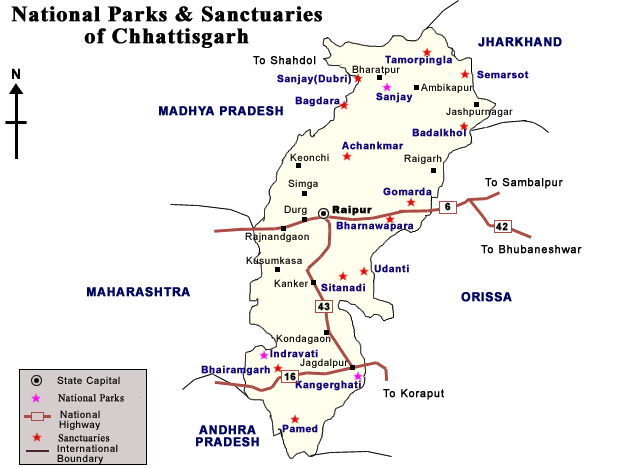
- Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR):
- About:
- It is located in the Gariaband and Dhamtari districts of Chhattisgarh. It was formed by combining the Udanti and Sitanadi Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- It is the source of three major rivers—Mahanadi, Sitanadi, and Udanti—which sustain both Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
- The reserve’s dense forests act like natural sponges, storing rainwater and supporting biodiversity as well as agriculture.
- Ecological Diversity:
- It contains various types of forest crops mixed with Sal forest.
- The Asiatic Wild Buffalo is a key endangered species found in the reserve.
- Apart from the tiger, other endangered and rare species include the Indian Wolf, Leopard, Sloth Bear, and Mouse Deer.
- Strategic Wildlife Corridor:
- USTR functions as a key tiger corridor, connecting Maharashtra’s Gadchiroli forests and Chhattisgarh’s Indravati Tiger Reserve with Odisha’s Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary.
- This linkage supports genetic diversity and long-range animal movement across state borders.
- About:
- Protection Measures by the State Government:
- Community-Centric Conservation Model:
- Local communities are playing a crucial role through participatory initiatives such as Charwaha Sammelans and the recognition of Community Forest Resource (CFR) rights.
- These measures have fostered trust, leading to active local involvement in curbing poaching, illegal logging, and forest fires.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation:
- The ‘Elephant Alert App’ has become an effective tool for early warning and tracking elephant movement, thereby reducing human-wildlife conflict.
- Community-Centric Conservation Model:
Note: In 2022, Chhattisgarh became the second state after Odisha to have recognised CFR rights inside a national park i.e., Kanger Ghati National Park.
Indravati National Park
- About:
- It is situated in the Bijapur district of Chhattisgarh.
- It was established in 1981 and declared a tiger reserve in 1983 under India’s Project Tiger.
- It is named after the Indravati River, which flows from east to west and forms the reserve's northern boundary with Maharashtra.
- Vegetation:
- Comprises three major forest types:
- Moist Mixed Deciduous Forest with Teak
- Moist Mixed Deciduous Forest without Teak
- Southern Dry Mixed Deciduous Forest.
- Comprises three major forest types:
- Flora:
- Common tree species include teak, achar, karra, kullu, shisham, semal, haldu, arjun, bel, and jamun.
- Fauna:
- Hosts one of the last populations of rare wild buffalo.
- Other species include Nilgai, Black Buck, Sambar, Gaur, Tiger, Leopard, Chital, Sloth Bears, etc.
Community Forest Resource (CFR)
- About CFR:
- CFR area is common forest land that has been traditionally protected and conserved for sustainable use by a particular community.
- The community uses it to access resources available within the traditional and customary boundary of the village and for seasonal use of landscape in the case of pastoralist communities.
- Each CFR area has a customary boundary with identifiable landmarks recognised by the community and its neighbouring villages.
- Community Forest Resource (CFR) Rights:
- CFR rights under Section 3(1)(i) of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 (commonly referred to as the Forest Rights Act) provides for recognition of the right to “protect, regenerate or conserve or manage” the community forest resource.



.jpg)