International Relations
India-Maldives Ties: Tale of A Diplomatic Tussle
- 11 Jan 2024
- 16 min read
This editorial is based on “India-Maldives row: Dangers of hypernationalism on both sides” which was published in The Indian Express on 09/01/2024. The article talks about the recent controversy surrounding the diplomatic relations between India and Maldives following the visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Lakshadweep.
For Prelims: Lakshadweep, India’s Neighbourhood First Policy, Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), Operation Cactus, Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP), ‘India Out’ Campaign, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), String of the Pearls, Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
For Mains: Significance of India-Maldives Relationship, Key Issues in the India-Maldives Relationship, Way Forward.
The visit of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Lakshadweep ignited controversy, further straining the already tense relations between India and the Maldives. The controversy began when three deputy ministers in the Ministry of Youth Affairs from Maldives engaged in negative comments about India and the Prime Minister following his recent visit to Lakshadweep.
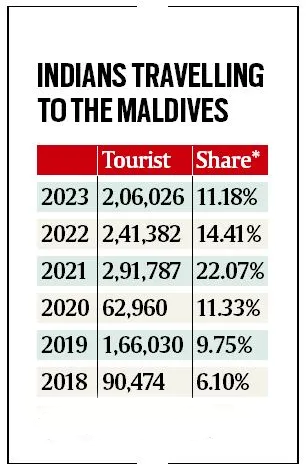
- The comments made by the ministers have sparked criticism in India, with numerous celebrities encouraging people to consider exploring domestic tourist destinations rather than travelling to the Maldives. The incident underscores the dangers of hypernationalism in the region and the need for two South Asian neighbours with much at stake in wide-ranging cooperation.
Why the India-Maldives Relationship is Significant?
- Strategic Significance:
- Focal Point of India’s Neighbourhood First Policy: Maldives’ proximity to the west coast of India and its situation at the hub of commercial sea lanes running through the Indian Ocean imbues it with significant strategic importance to India.
- It is a focal point for the Indian government's priorities under the 'Neighbourhood First Policy.'
- India as a First Responder to the Maldives:
- India's swift response and immediate assistance during the 1988 coup attempt laid the foundation for the development of trust and enduring, friendly bilateral relations with the Maldives. The Indian Armed Forces acted promptly, executing Operation Cactus.
- India was the first to assist Maldives during the 2004 Tsunami as well as the water crisis in Malé in Dec 2014.
- India’s swift dispatch of 30,000 doses of measles vaccine in Jan 2020 to prevent an outbreak in the Maldives, and India’s rapid and comprehensive assistance to the Maldives during the Covid-19 pandemic further reinforced India’s credentials of being the “first responder”.
- India as a Net Security Provider: The importance of India’s strategic role in Maldives is well-recognized, with India being seen as a Net Security Provider.
- A comprehensive Action Plan for Defence was signed in April 2016 to consolidate the defence partnership.
- Both nations are key players in maintaining the safety and security of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), thus contributing to India-led Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) vision.
- Defense cooperation extends to the areas of Joint Exercises - “Ekuverin”, “Dosti”, “Ekatha” and “Operation Shield”.
- Focal Point of India’s Neighbourhood First Policy: Maldives’ proximity to the west coast of India and its situation at the hub of commercial sea lanes running through the Indian Ocean imbues it with significant strategic importance to India.
- Economic and Trade Engagements:
- Tourism Economy:
- Trade Agreements :
- India emerged as Maldives’ 2nd largest trade partner in 2022. The bilateral trade had crossed the USD 300 million mark for the first time in 2021.
- A Bilateral USD Currency Swap Agreement between RBI and Maldives Monetary Authority was signed on 22nd July 2019.
- Indian imports from the Maldives primarily comprise scrap metals while Indian exports to the Maldives include a variety of engineering and industrial products like drugs and pharmaceuticals, cement and agriculture produce.
- Development and Capacity Buiding:
- Infrastructure Projects:
- In August 2021, Afcons, an Indian company, signed a contract for the largest-ever infrastructure project in Maldives which is the Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP).
- The Hanimaadhoo International Airport Development project under an Indian credit line will add a brand-new terminal to cater to 1.3 million passengers a year.
- In 2022, the National College for Policing and Law Enforcement (NCPLE) was inaugurated by India’s External Affairs Minister.
- Healthcare Sector:
- In the healthcare sector, India has provided Rs 52 crore for the development of Indira Gandhi Memorial Hospital besides helping set up a state-of-art cancer facility that will connect over 150 health centres on various islands.
- Educational Programmes:
- In education, India helped set up an institute of technical education in 1996. India has also started a programme to provide training to Maldivian teachers and youth and for vocational training in a USD 5.3 million project.
- India provides the largest number of training opportunities for the Maldivian National Defence Force (MNDF), meeting around 70% of their defence training requirements.
- Infrastructure Projects:
- Cultural Connectivity:
- India and Maldives share ethnic, linguistic, cultural, and religious links steeped in antiquity. According to anthropologists, the origins of Dhivehi (the Maldivian language) harken back to Sanskrit and Pali.
- The Indian expatriate community in the Maldives has an approximate strength of 27,000. The majority of the expatriate teachers in Maldives are Indian nationals.
What are the Key Issues in the India- Maldives Relationship?
- The Ongoing Lakshadweep Issue:
- The controversy ensued when three deputy ministers from the Maldives made derogatory comments about India and the Prime Minister following his recent visit to Lakshadweep.
- They criticized the Indian Prime Minister's visit, alleging that it was intended to pose a challenge to Maldivian tourism, which is well-known for its renowned beachside amenities.
- The Indian government raised the issue with Maldives, after which the Maldives government suspended the ministers.
- This controversy has led many Indians to cancel their holiday bookings in Maldives. The incident underscores the dangers of hypernationalism in the region.
- Maldives tourism industry would be “concerned” about the potential impact of this controversy.
- The India Out Campaign In Maldives:
- The 'India Out' initiative seeks to amplify animosity by instilling scepticism regarding India's investments in the Maldives, the defence partnerships between the two nations, and India's security provisions in the region.
- The recently elected Maldivian government opposes the former administration's 'India First' policy to the extent that the withdrawal of Indian troops was included in Muizzu's election manifesto.
- Sovereignty and Security Dilemma :
- The democratic system in the Maldives is still in its early stages, grappling with regional socio-political instability influenced by major global players.
- The opposition in Maldives strongly feels that the Indian military presence in the Maldives is a threat to the country’s national security and sovereignty.
- Conversely, the government has consistently emphasized that the India Out campaign poses a threat to the national security of the country. It is seen as a factor that could antagonize the partner country providing regional security benefits to the island nation.
- The Trilateral Maritime Security Cooperation meeting between India, the Maldives and Sri Lanka was established in 2011.
- Revocation of Hydrographic Survey Agreement:
- It is worth noting that hydrographic data inherently has a dual nature in that the information collected from the seas can be used for civilian and military purposes.
- Maldives has apprehensions about India’s hydrographic activity being a form of intelligence collection.
- Maldives' recent decision to revoke the agreement with India for joint hydrographic surveys in its waters, causing concern in Indian strategic circles.
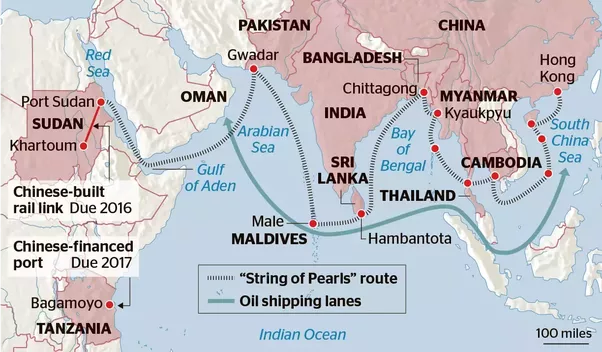
- The China Factor in the Indian Ocean Region :
- The Maldives has emerged as an important ‘pearl’ in China’s “String of Pearls” construct in South Asia.
- Maldives has massive Chinese investment and became a participant in China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- The India-Maldives relationship suffered a setback when Maldives entered into a Free-Trade Agreement (FTA) with China in 2017.
- There are speculation about a Chinese plan to develop a naval base in the Maldives, with past proposals indicating concerns about potential military applications.
- China's oceanographic surveys in the waters of amicable South Asian nations pose potential conflict points due to the presence of Indian hydrographic ships in the region.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Discover and Develop Tourism Destinations in India:
- Discover the Undisclosed Sites: India's coastline is adorned with a mix of well-known and undiscovered beach destinations. It is opportune to explore and cultivate the potential of undisclosed and hidden treasures along India's coast.
- Possible destinations may include places like Goa, Kerala, Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Develop Tourism Facilities: Invest in basic infrastructure such as transportation, roads, and utilities. Develop reliable connectivity to the undisclosed areas to make them easily accessible for tourists.
- The coverage and operations of routes that fall under the Regional Connectivity Scheme – Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (RCS-UDAN) should be enhanced.
- Discover the Undisclosed Sites: India's coastline is adorned with a mix of well-known and undiscovered beach destinations. It is opportune to explore and cultivate the potential of undisclosed and hidden treasures along India's coast.
- Step into the Footsteps of the Gujral Doctrine:
- High-level Diplomatic Engagement: Prioritise regular and constructive diplomatic dialogues to address concerns, build trust, and foster open communication.
- Strengthening Regional Alliances: Building on the positive aspects of the Gujral Doctrine, India should continue strengthening regional alliances and cooperation for mutual benefit.
- Political Engagement with Local People: At present, the ‘India Out’ campaign has support from a limited population but this cannot be taken for granted by the Indian government.
- The strength of bilateral relations hinges on the ability of a partner government to garner public support for its policies.
- Unwavering Support for Capacity Building Programmes: As a development partner, India should provide unwavering support to the Maldives in realizing their aspirations for broad-based socio-economic development and strengthening of democratic and independent institutions in the region.
- Apply Prudence in International Affairs:
- Avoid Needless Provocations: The controversy warns smaller nations like Maldives to exercise prudence in dealing with neighbours, as unnecessary provocations can have detrimental consequences.
- Needless provocations can trigger consequences that could, in the end, hurt the smaller neighbour a lot more.
- Responsive Role of Social Media Warriors:
- It is crucial to acknowledge the significant role played by social media warriors in promoting national interest but engaging in bullying behaviour towards neighbouring countries, particularly Maldives, is counterproductive.
- Such actions have the potential to lose India's diplomatic advantages in favour of China.
- It is crucial to acknowledge the significant role played by social media warriors in promoting national interest but engaging in bullying behaviour towards neighbouring countries, particularly Maldives, is counterproductive.
- Avoid Needless Provocations: The controversy warns smaller nations like Maldives to exercise prudence in dealing with neighbours, as unnecessary provocations can have detrimental consequences.
- Craft a Comprehensive Indian Ocean Strategy to Counter China:
- Maximise Maritime Security: India should participate in efforts to ensure the safety and freedom of navigation in critical sea lanes, contributing to the overall security architecture in the Indian Ocean.
- Maximize Resources: India should keep its commitment to regional security by actively participating in humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations. India can actively engage through QUAD to counter Chinese aggression in the region.
- Project Mausam should provide sufficient space for Maldives to get benefits out of it and boost its economic and infrastructural reliance on India.
Conclusion
Irrespective of the controversy, the enduring regional and geopolitical importance of India ensures that fostering relations with New Delhi remains a paramount priority for the Maldives.
A coordinated synergy between India's 'Neighbourhood First' policy and the Maldives' 'India First' approach is essential for strengthening a mutually beneficial partnership.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the challenges within the bilateral relationship between India and the Maldives and propose measures to address them. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: A
Mains:
Q. Discuss the political developments in the Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause for concern to India? (2013)