Important Facts For Prelims
Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage
- 28 Oct 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Google announced that its quantum processor, "Willow," has achieved the first-ever verifiable quantum advantage by utilizing a new algorithm called Quantum Echoes, which ran 13,000 times faster than the world's fastest supercomputers.
- This achievement marks a major step toward real-world quantum applications like Hamiltonian learning.
What is Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage?
- Concept of Quantum Advantage: It refers to the point where a quantum computer outperforms classical supercomputers on specific tasks.
- Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage: Google’s Willow quantum processor, featuring up to 105 qubits, successfully ran the Quantum Echoes algorithm, which tracks the forward and backward evolution of entangled quantum states to study quantum chaos and interference.
- This enabled the measurement of the Out-of-Time-Order Correlator (OTOC) - a key indicator of how information gets “scrambled” through entanglement as quantum bits interact.
- The Willow processor achieved the OTOC measurement in just two hours, a task estimated to take 13,000 times longer (equivalent to several years) on a classical supercomputer.
- Unlike earlier demonstrations, the result can be independently verified by other quantum or classical systems, making it the first real-world, measurable quantum advantage
- Practical Applications:
- Hamiltonian Learning: OTOC circuits can aid in Hamiltonian Learning, a quantum technique where a computer simulates the behavior of a physical system (such as a molecule) and compares it with real experimental data to accurately estimate unknown parameters like energy levels or interaction strengths.
- Molecular Structure Estimation: The OTOC method, tested using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, helps analyze proteins, materials, and compounds by studying quantum spin behavior, leading to better insights into molecular geometry.
Quantum Computing Glossary
- Quantum Technology: Quantum computing/technology refers to a class of technologies that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations and achieve capabilities not possible with traditional technology.
- Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at very small scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles.
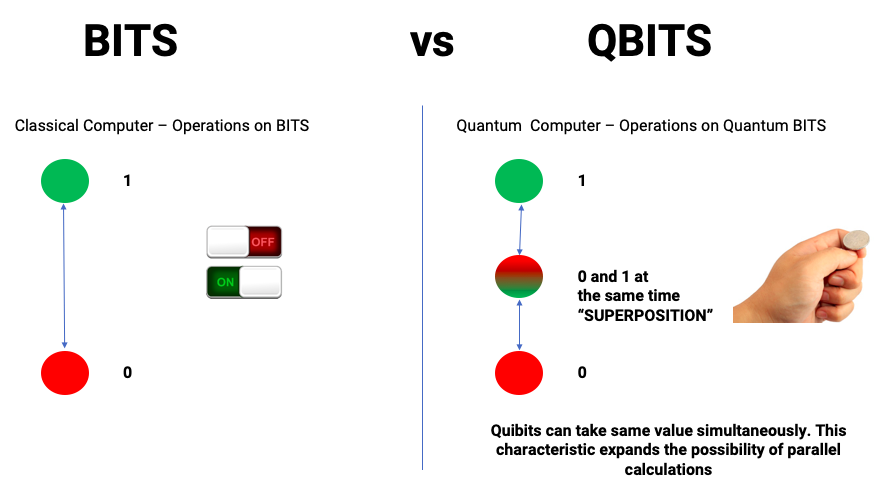
- Qubit (Quantum Bit): The basic unit of quantum information that can exist as 0, 1, or both simultaneously (superposition).
- Superposition: The ability of a quantum system to be in multiple states at once, giving quantum computers massive parallel processing power.
- Entanglement: A quantum link where qubits remain connected, where changing one instantly affects the other, even if they’re far apart.
- Quantum Gate: The building block of quantum circuits, they perform controlled operations on qubits (like classical logic gates).
- Quantum Circuit: A network of quantum gates arranged to perform a specific computation or algorithm.
- Quantum Interference: It is the process of reinforcing correct answers and cancelling wrong ones using the wave-like nature of qubits.
- Quantum Simulation: Using quantum computers to model molecules, materials, or physical systems too complex for classical machines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a verifiable quantum advantage?
It’s when a quantum computer outperforms classical supercomputers on a task, and the result can be independently verified by other quantum or classical systems.
2. What is an Out-of-Time-Order Correlator (OTOC)?
A quantum observable that tracks how information gets “scrambled” among entangled qubits, revealing the level of quantum chaos in a system.
3. What is Hamiltonian Learning and why is it important?
A quantum method where simulated OTOC signals are compared with real data to estimate unknown molecular parameters like energy levels or interactions.
4. What are the practical uses of OTOC-based experiments?
They aid molecular structure analysis, material design, and drug discovery through precise simulation of atomic-scale systems.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term "qubit" is mentioned?
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum Computing
(c) Visible Light Communication Technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)