Important Facts For Prelims
Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement
- 06 Sep 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Ministry of Earth Sciences has set up a 12 member panel to implement a new law to safeguard its interests in international ocean waters, aligning with the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement (High Seas Treaty) agreement.
What is the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement ?
- About: The BBJN Agreement or High Seas Treaty is a legal framework under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) to safeguard the ecological health of oceans.
- Adopted in 2023, it aims to curb pollution, conserve biodiversity, and ensure sustainable use of marine resources in waters beyond national boundaries.
- Scope of the Treaty:
- Establish Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to regulate activities and conserve ocean ecosystems.
- Regulates extractive activities such as seabed mining & ensures fair distribution of benefits from marine resources and organisms.
- Make EIAs mandatory for major oceanic projects that may harm the high seas, even if carried out within national waters.
- Support developing nations in accessing marine technologies and resources while ensuring conservation.
- Signing and Ratification: As of August 2025, over 140 countries have signed the treaty and 55 have ratified it.
- India has signed the BBNJ Agreement in 2024 but has not yet ratified it.
- Signing shows intent, while ratification legally binds a country to the treaty, with the process differing across nations.
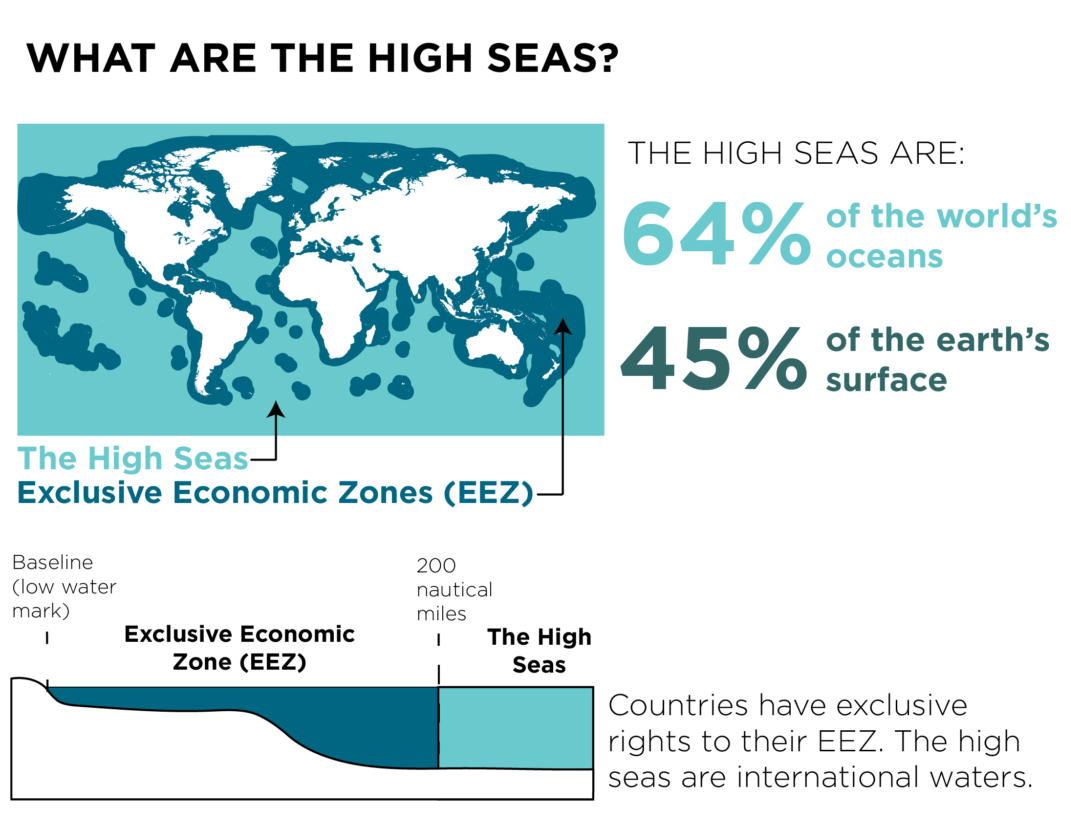
High Seas
- About: High seas refer to regions beyond the national jurisdiction of any country.
- Generally, national jurisdictions extend up to 200 nautical miles (370 km) from a country's coastline, known as the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- No country has jurisdiction or responsibility for resource management in these waters.
- Only about 1% of the high seas are currently protected.
- Significance: The high seas cover 64% of oceans and 50% of Earth’s surface & are vital for marine biodiversity, climate regulation, carbon absorption, solar energy storage, and heat distribution.
- They provide key resources like seafood, raw materials, genetic resources, and medicinal compounds.
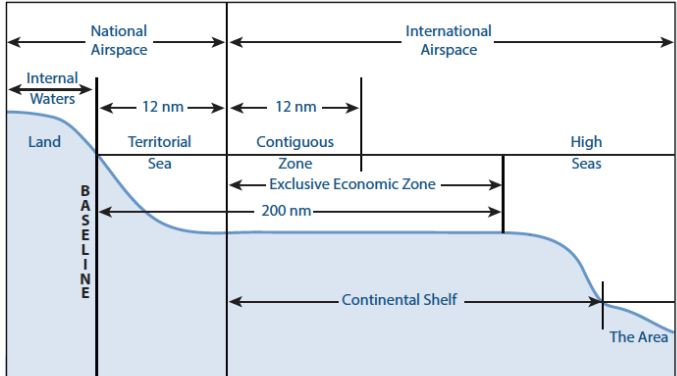
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- UNCLOS, also called Law of the Sea, is an international treaty adopted and signed in 1982, replacing the 1958 Geneva Conventions.
- It provides the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- It divides ocean space into 5 zones- Internal Waters, Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), and High Seas.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)