International Relations
Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII)
- 29 Jun 2022
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Build Back Better World (B3W), PGII, BRI ,China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), Silk Road Economic Belt, Climate Sustainability Fund, Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka
For Mains: Pillars of PGII, Benefits to India from PGII , Belt Road Initiative
Why in News?
Recently, at the 48th G-7 Summit, the U.S. along with G7 allies unveiled the ambitious Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII).
What is the Background?
- The U.S. along with its allies had announced the launch of the Build Back Better World (B3W) in 2021 with the aim of narrowing the 40 trillion dollar infrastructure gap in the developing world.
- Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment is therefore a relaunch of the B3W plan.
- The PGII is being seen as the G7’s counter to China’s multi-trillion dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) to build connectivity, infrastructure, and trade projects in Asia, Europe, Africa, and Latin America.
What is Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment?
- About:
- PGII is a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low and middle-income countries
- And support the United States and its allies economic and national security interests.
- Under the PGII, G7 will mobilize 600 billion dollars by 2027 to deliver “game-changing” and “transparent” infrastructure projects to developing and middle-income countries.
- U.S. President announced the country’s pledge to channel 200 billion USD in grants, public financing, and private capital over the next five years for the PGII.
- The European Commission President declared Europe’s pledge of mobilizing 300 billion euros for the partnership over the same period.
- PGII is a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low and middle-income countries
- Pillars of PGII:
- First: G7 grouping aims to tackle the climate crisis and ensure global energy security through clean energy supply chains.
- Second: The projects will focus on bolstering digital Information and Communications technology (ICT) networks facilitating technologies such as 5G and 6G internet connectivity and cybersecurity.
- Fibre-optic cable project to link Europe and Latin America.
- Third: The projects aim to advance gender equality and equity.
- Gender Equality: It requires equal enjoyment by women and men of socially-valued goods, opportunities, resources and rewards.
- Gender Equity: It recognizes that each person has different circumstances and allocates the exact resources and opportunities needed to reach an equal outcome.
- Fourth: The project stresses upgrading global health infrastructure.
- The U.S International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), along with the G7 nations and the EU are disbursing a 3.3 million USD technical assistance grant to build a vaccine facility in Senegal.
- The European Commission’s Global Gateway initiative is also undertaking projects supporting the PGII such as mRNA vaccine plants in Latin America.
- Benefits to India:
- U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) will invest up to USD 30 million in Omnivore Agritech and Climate Sustainability Fund.
- Climate Sustainability Fund: It is an impact venture capital fund that invests in entrepreneurs building the future of agriculture, food systems, climate, and the rural economy in India.
- The Fund seeks to invest in companies that increase food security and promote both climate resilience and climate adaptation in India and it will also improve the profitability and agricultural productivity of smallholder farms.
- Omnivore Agritech: It is a technology driven agricultural practice that will increase agricultural prosperity and transform food systems to make farming more resilient and sustainable.
- It includes farmer platforms, precision agriculture, Agri-biotech etc.
- U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) will invest up to USD 30 million in Omnivore Agritech and Climate Sustainability Fund.
How will PGII Counter China’s BRI?
- Projects:
- PGII has laid focus on climate action and clean energy, while China has built large coal-fired plants under BRI along with solar, hydro, and wind energy projects.
- Funding:
- PGII aims to build projects through grants and investments. China builds BRI’s projects by extending large, low-interest loans to countries that have to usually be paid over 10 years.
- While the G7 has pledged 600 billion USD by 2027, It has been estimated that China’s overall funding for BRI by that time could reach 1.2 USD to 1.3 trillion USD with the actual funding being higher. Under the PGII, large private capital will be also mobilized while China’s BRI is majorly state-funded.
- Transparency:
- While G7 leaders emphasized ‘transparency’ as the cornerstone of PGII projects, the BRI has faced criticism for making countries sign confidential tenders for extending massive loans, leaving countries indebted to China.
- For instance, after the BRI’s flagship 62 billion USD China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, Pakistan owes Beijing a large proportion of its foreign debt.
- PGII aims to build projects through grants and investments.
- While G7 leaders emphasized ‘transparency’ as the cornerstone of PGII projects, the BRI has faced criticism for making countries sign confidential tenders for extending massive loans, leaving countries indebted to China.
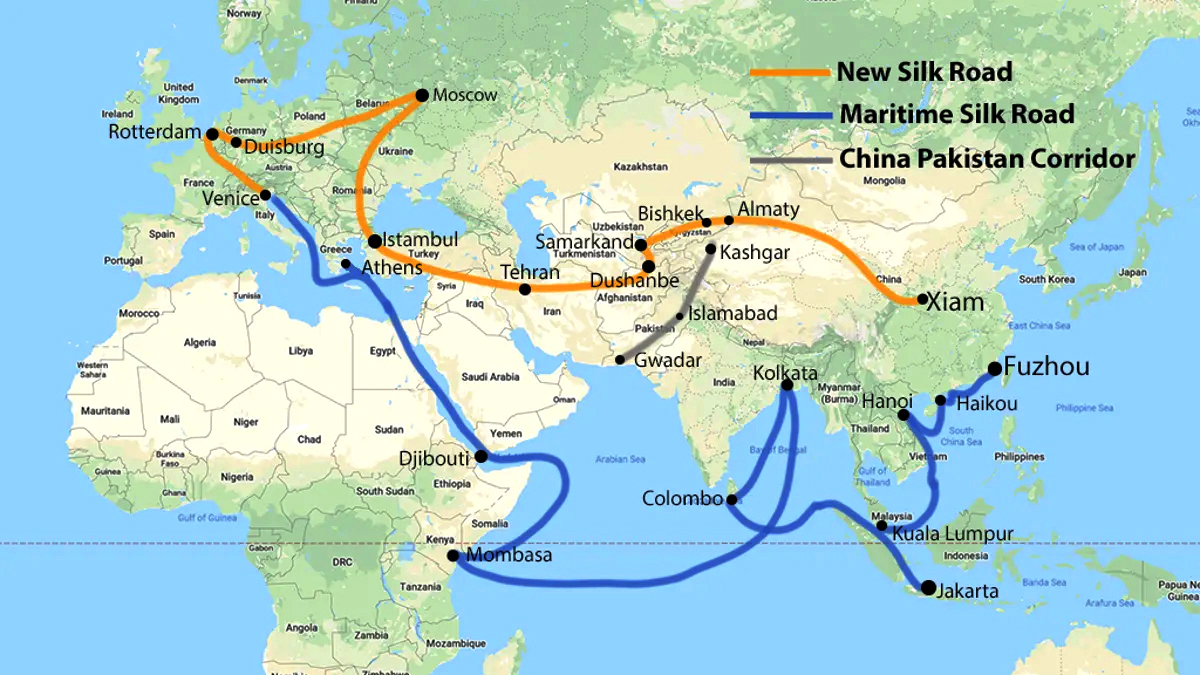
What is the Belt & Road Initiative (BRI)?
- About:
- Belt & Road Initiative (BRI) is an ambitious project that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among multiple countries spread across the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. BRI spans about 150 countries (China’s Claim).
- Initially announced in the year 2013, the project involves building networks of roadways, railways, maritime ports, power grids, oil and gas pipelines, and associated infrastructure projects.
- The project covers two parts.
- Silk Road Economic Belt: It is land-based and is expected to connect China with Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Western Europe.
- 21st Century Maritime Silk Road: It is sea-based and is expected to connect China’s southern coast to the Mediterranean, Africa, South-East Asia, and Central Asia.
- Belt & Road Initiative (BRI) is an ambitious project that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among multiple countries spread across the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. BRI spans about 150 countries (China’s Claim).
- Significance of BRI For China:
- The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is the most emblematic of China’s economic and industrial might, as of its ambitions for global, political and strategic influence.
- As infrastructure spending at home became less sustainable, China has shifted the emphasis to boost the global competitiveness of domestic businesses.
- The large infrastructure investments in the least developed and developing countries have enabled China to leverage its influence around the world, potentially altering the established rules of the global order and challenging western powers.
- BRI will strengthen China’s presence in the Eurasian region and put it in a commanding position over Asia’s heartland.
- Criticism:
- Western critics have attacked the initiative as new colonialism, or the Marshal Plan for the 21st century.
- BRI is also being seen as a part of China’s debt trap policy, wherein China intentionally extends excessive credit to another country with the intention of extracting economic or political concessions from the debtor country.
Why has India not joined BRI?
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is one of the flagship projects of BRI which is seen by India as infringing its sovereignty.
- CPEC can aid Pakistan’s legitimacy in the Kashmir dispute.
- China is building roads and infrastructure in the disputed territory of Gilgit-Baltistan, which is under Pakistan’s control but which India claims as a part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- If the CPEC project gets implemented successfully, this would hamper India’s strategic interests in the South Asian region. It will serve Beijing's strategic ambition to encircle India.
- China’s increasing footprints in the South Asian region is detrimental to India’s strategic hold e.g., construction of the Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka provided China with a critical strategic location in the Indian Ocean.