Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Governor Inaugurates Miyawaki Forest at ABVMU
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh Governor and Chancellor Anandiben Patel inaugurated a Miyawaki forest at Atal Bihari Vajpayee Medical University (ABVMU) in Lucknow and participated in a sapling plantation drive.
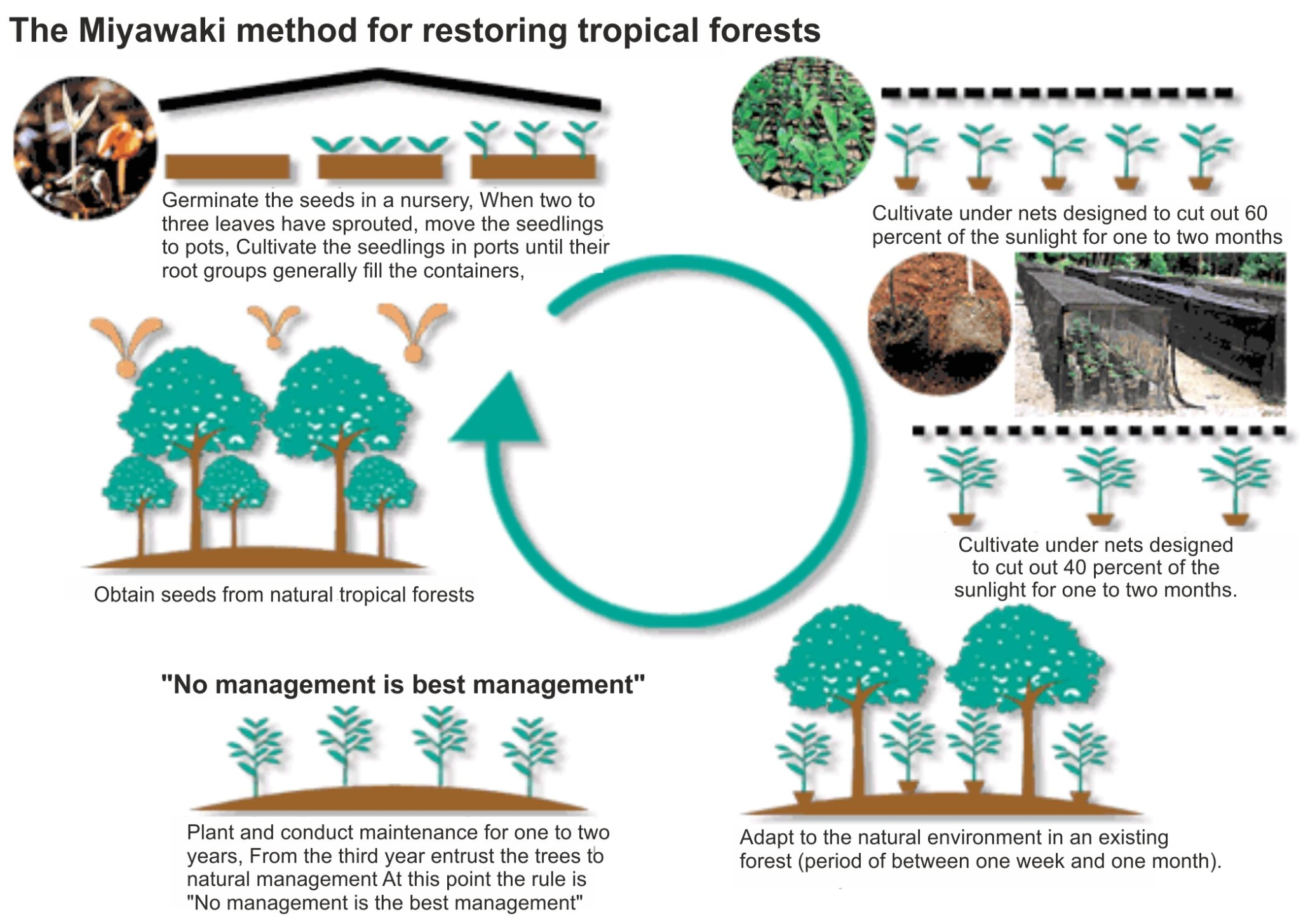
About Miyawaki Plantation Method
- It was named after Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki. This method involves planting two to four different types of indigenous trees within every square metre.
- The methodology was developed in the 1970s, with the basic objective to densify green cover within a small parcel of land.
- In this method, the trees become self-sustaining, and they grow to their full length within three years.
- The plants used in the Miyawaki method are mostly self-sustaining and don’t require regular maintenance like manuring and watering.
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
- Some of the common indigenous plants that are used for these forests include Anjan, Amala, Bel, Arjun, and Gunj.
- These forests encourage new biodiversity and an ecosystem, which in turn increases the fertility of the soil.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Funding for PMAY Urban 2.0 in Uttar Pradesh
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has secured financial approval of Rs 12,031 crore under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) Mission 2.0, aimed at constructing permanent pucca houses for the urban poor.
Key Points
- The scheme is being closely monitored by both state and district-level officials to ensure timely delivery and quality standards.
- Geo-tagging and photographic documentation will be mandatory to allow real-time construction monitoring.
- Houses will be equipped with disaster-resilient features to withstand earthquakes, floods, and other calamities.
- CM Yogi Adityanath has directed officials to ensure strict adherence to quality and transparency.
About Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) 2.0
- Launch Year: 2024 (PMAY-U was originally launched in 2015)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
- Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme
- Interest Subsidy Scheme (ISS) component is Central Sector Scheme
- Eligibility: EWS/LIG/MIG families without pucca house; income up to ₹9 lakh
- Benefits: Subsidy for all-weather pucca houses
- Target: 1 crore urban families (construction, purchase, rental)
- Total Outlay: ₹10 lakh crore (₹2.3 lakh crore Central Assistance)
- Coverage Area: The scheme covers all statutory towns notified in the Census 2011 and towns notified subsequently by State Governments.
- Notified Planning Areas and regions under Urban Development or Industrial Authorities are included under PMAY-U 2.0.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
NHRC Hosts National Symposium on Women’s Safety with University of Lucknow
Why in News?
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), in collaboration with the University of Lucknow, held the National Symposium on ‘Women’s Safety at Work and Public Spaces’, amid growing concerns over gender-based violence in professional and public domains.
Key Points
- NHRC Chairperson Justice V. Ramasubramanian, highlighted the stark contrast between India's cultural reverence for women and the alarming frequency of violence, 51 FIRs every hour.
- He also underlined the long struggle leading to the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013, and called for systemic, enforcement-led, and awareness-driven reforms.
- He urged educators and society to foster gender-sensitive behaviour.
- Institutional Gaps and Policy Suggestions: Symposium noted the gaps in law enforcement, institutional responsiveness, and public awareness, stressing the need for:
- Greater female representation in decision-making bodies.
- Inclusion of the informal sector in women’s safety discourse.
- Promotion of SHE-Box, One Stop Centres, and Pink Police Booths.
- Key Recommendations of Symposium:
- Policy-implementation-awareness triad must be addressed in unison.
- Informal sector workers need tailored outreach and protection.
- Sensitisation must begin at the individual and familial level.
- Inclusive spaces and representation for women must be institutionalised.
- Educational institutions should actively promote gender awareness and conduct training.
About National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- The NHRC of India is an autonomous statutory body established to promote and protect human rights.
- It was constituted on 12th October 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993, which was later amended in 2006 and 2019.
- The Commission was established in conformity with the Paris Principles, which are international standards adopted for promoting and protecting human rights.
- The Paris Principles are the set of international standards adopted for the promotion and protection of human rights in Paris (October, 1991) and endorsed by the General Assembly of the United Nations (UN) on 20th December 1993.
- These principles guide the work of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) across the world.
- Powers of NHRC: NHRC is vested with powers equivalent to those of a civil court as per the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- NHRC Investigation Team: The NHRC has its own investigation team led by a Director General of Police.





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan