Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Geo-Thermal Energy Policy 2025
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand cabinet approved the Uttarakhand Geo-Thermal Energy Policy 2025 to promote scientific and technological research for exploring and developing geothermal resources that are both economically and environmentally sustainable.
Note:
- The cabinet approved the Uttarakhand State Mineral Exploration Trust Rules, 2025 to encourage the formation of state-level mineral trusts.
- It also approved amendments and formalized the Uttarakhand District Mineral Foundation Trust Rules, 2025, replacing the 2017 rules.
Key Points
- About Geo-Thermal Energy Policy 2025:
- The policy aims to utilize geothermal sites for power generation, heating and cooling, water purification and community development.
- The government seeks to enhance Uttarakhand’s energy security, reduce carbon emissions, and contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
- The Energy Department, in collaboration with Uttarakhand Renewable Energy Development Agency (UREDA) and Uttarakhand Jal Vidyut Nigam Limited (UJVNL) will implement the policy across all geothermal projects in the state.
- Project Duration and Allotment Process:
- The government will allot geothermal projects for a maximum of 30 years from the date of commissioning.
- Projects can be awarded to central or state PSUs or private developers through competitive bidding or other specified methods.
- Geological Basis of Geothermal Energy in Uttarakhand:
- Hot springs or geothermal sources in the Himalayan region form when subsurface water reaches geothermal points and emerges through thermal vents.
- Heat generation occurs due to volcanic activity, tectonic movement, and rock formation deep beneath the Earth’s surface.
- When a water source passes near these zones, it absorbs the heat and emerges through thermal vents as hot springs.
- Geothermal sources lie along the Main Central Thrust, a geological fault line where the Indian plate meets the Eurasian plate.
- For Example, Manikaran (Himachal Pradesh), Gaurikund (Uttarakhand)
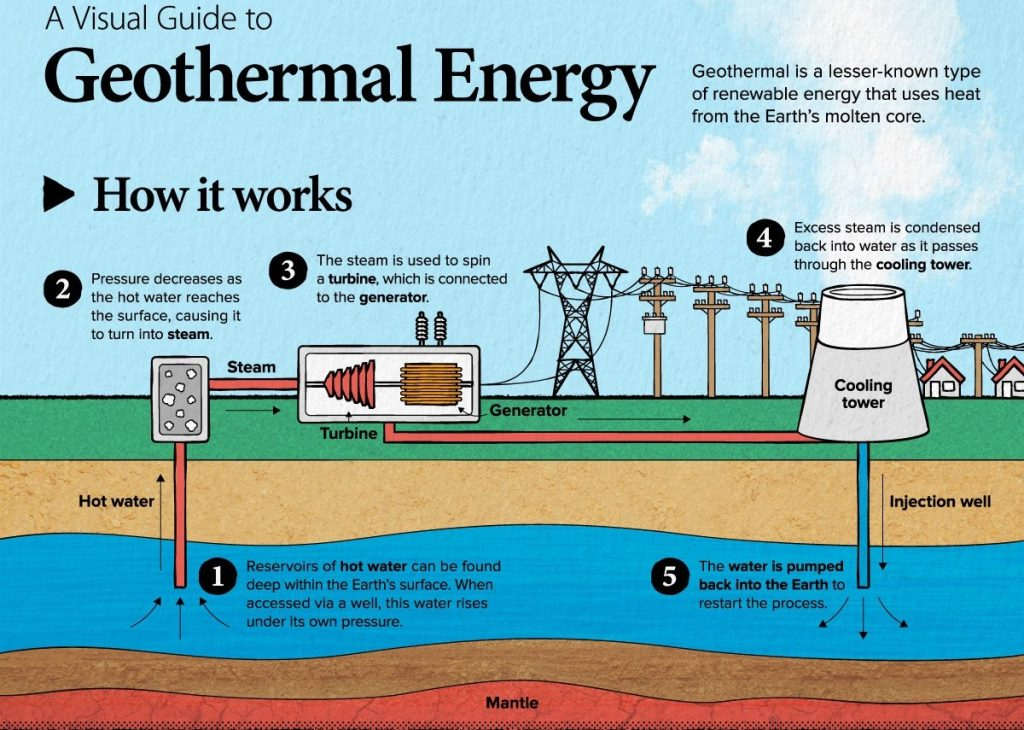
Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal energy is heat from the Earth’s interior, generated by radioactive decay. It is renewable, provides baseload power, available 24/7 as the Earth continuously produces heat.
- India has 381 thermally anomalous sites identified by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) with a potential to generate 10,600 MW, enough to power 10 million households.
- Key projects include a 20 kW pilot plant in Manuguru, Telangana and ONGC's 1 MW project in Puga Valley, Ladakh.
- India has established agreements with countries like Iceland (2007), Saudi Arabia (2019), and the Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP) with the US (2023) for geothermal energy collaboration.
- Geothermal Features:
- Geysers: These are geothermal features that periodically eject water and steam due to underground heating.
- Geysers require large amounts of groundwater to fill underground cavities in volcanic areas. When heated by nearby magma, the water flashes into steam, causing an eruption of hot water and steam.
- Example: Yellowstone National Park (US)
- Fumaroles: These are openings in the Earth’s crust where volcanic gases and steam are released.
- Fumaroles occur when magma passes through the water table, heating the water and causing steam to rise, carrying volcanic gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) to the surface.
- Often found near "dying volcanoes" where magma deep underground has solidified and cooled.
- Example: Barren Island (Andaman and Nicobar Islands)
- Mudpots: These are the bubbling pools of mud that form in geothermal areas.
- Formed when limited geothermal water mixes with mud and clay.
- Example: Yellowstone National Park (US)
- Geysers: These are geothermal features that periodically eject water and steam due to underground heating.





-UPPCS-English%20(web).png)
-UPPCS-English%20(mobile).png)







.jpg)









.png)







 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan