Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Project Cheetah Wins Innovative Initiative Award
Why in News?
Project Cheetah has been honored with the prestigious 'Innovative Initiative Award' at the 3rd Eco Warrior Awards, which was hosted by the Indian Forest Service (IFS) Association and Indian Mastermind in Delhi.
- The award was presented to Uttam Sharma, the field director of Project Cheetah.
Key Points
- About: The Eco Warrior Awards recognize exceptional efforts in conservation and sustainability.
- The IFS Association specifically chose Project Cheetah for its remarkable achievement in reviving an extinct species in India and for its commitment to involve local communities in the project's success.
- Newsletter: As the project marked its third anniversary, the forest department also released a special newsletter documenting the journey of Project Cheetah from the arrival of the first cheetahs at Kuno National Park in 2022 to the successful births of cubs and ongoing habitat management efforts.
Project Cheetah
- About: Project Cheetah (Cheetah Reintroduction Project) was launched in 2022, with the aim to reintroduce cheetahs to India (declared extinct in 1952) as part of global cheetah conservation efforts.
- Implementing Agencies: National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Madhya Pradesh Forest Department, and Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
- Implementation: Phase 1 involved translocating cheetahs from Namibia (2022) and South Africa (2023) to Kuno National Park, Madhya Pradesh.
- Under Phase-2 of the Project India is considering sourcing cheetahs from Kenya due to similar habitats.
- Cheetahs will be translocated to Kuno National Park and Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh).
- Under Phase-2 of the Project India is considering sourcing cheetahs from Kenya due to similar habitats.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Government to Audit Ladli Behna List
Why in News?
The state government will audit the "Ladli Behna" beneficiary list to remove ineligible names before the monthly assistance increases from Rs 1,250 to Rs 1,500 after Diwali.
- A public appeal will be made, urging women who do not qualify for the scheme to voluntarily withdraw, followed by departmental scrutiny to remove any ineligible entries from the list.
Ladli Behna Yojana
- About: The scheme was launched on 10th June 2023 by the then Chief Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan.
- Under this, married women between 23 and 60 years of age were initially given assistance of Rs 1,000, which was later increased to Rs 1,250 per month.
- Objective: Its main objective is to economically empower the women of Madhya Pradesh.
- Eligibility and Rules:
- The annual income of the woman's family should be less than Rs 2.5 lakh.
- No member of the family holds a government job.
- Apart from this, the family should not have more than 5 acres of land, a tractor, or a four-wheeler.
- Current Status: The scheme currently has over 1.26 crore women enrolled, making it the state's largest direct benefit transfer programme, costing around Rs 1,550 crore per month.
Other Women-Centric Schemes
- Ladli Laxmi Yojana: Launched in 2006, the scheme aims to secure the future of girl children by improving their educational and economic status.
- It also seeks to promote a positive societal mindset towards the birth of a girl child and reduce gender discrimination.
- Eligibility Criteria: The scheme benefits parents who have adopted family planning after having two living children, ensuring population control.
- Families must be registered with an Anganwadi centre and should not be income tax payers to qualify for the scheme.
- Financial Benefits: The state government purchases National Savings Certificates worth Rs 6,000 annually in the girl's name from birth until the total reaches Rs 30,000.
- When the girl turns 21 years old and if she has not married before the age of 18, she receives a lump sum amount of Rs 1 lakh as the final benefit under the scheme.
- Usha Kiran Yojana: The Usha Kiran Yojana, launched by the Government of Madhya Pradesh in 2006, provides protection and legal support to women and children facing domestic violence.
- It functions under the provisions of the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005.
- Core Objectives: The scheme seeks to safeguard victims from physical, sexual, mental, emotional, and economic abuse.
- It aims to ensure justice, dignity, and security for women and children affected by domestic violence.
- Target Beneficiaries: The scheme supports women of all ages, irrespective of marital status.
- It also includes children under 18 years who may be directly or indirectly affected by domestic violence.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh's Student Welfare Initiatives
Why in News?
The Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh, Mohan Yadav, handed over scooter keys to 7832 students.
- Additionally, money was transferred to the accounts of female students under the Sanitation-Hygiene Scheme (Samagra Shiksha) and the Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya Scheme.
Key Points
- Free e-Scooty Scheme:
- Launched: Operational since the academic session 2022-23.
- Eligibility: Students who topped their Class 12 exams in government higher secondary schools.
- The scheme applies to regular candidates who studied in government schools run by the School Education Department or the Tribal Affairs Department.
- Sanitation and Hygiene Scheme (Samagra Shiksha)
- Transfer of Funds: Rs 61 crore
- Beneficiaries: 20,37,439 girls studying from Class 7 to Class 12 in government schools.
- Purpose: To provide Rs 300 annually to girl students for personal health and hygiene under the sanitation and hygiene scheme.
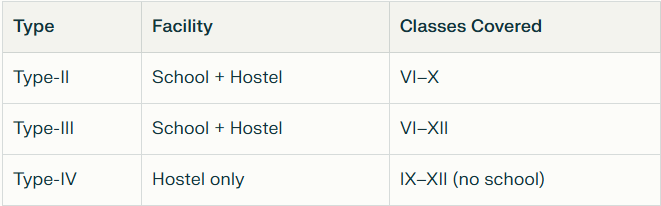
- Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya Type (IV) Scheme:
- Amount Transferred: Rs 7 crore
- Beneficiaries: 20,100 girls
- Purpose: Under the Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya Type (IV) Scheme, girls living in hostels received Rs. 3,400 for TLM (Teaching Learning Material) and stipend.
Samagra Shiksha Scheme
- It was launched by the Ministry of Education in 2018.
- It is an integrated scheme for school education covering the entire gamut from pre-school to class XII.
- It aims to deliver inclusive, equitable, and affordable school education.
- It subsumes the three Schemes of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), and Teacher Education (TE).
- It is being implemented as a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Funding split is 60:40 for most states, but 90:10 for NE/Himalayan states and 100% Centre for UTs.
Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV) Scheme
- Launched in 2004, it aims to provide quality education through residential schools at the upper primary level to girls belonging to the Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), Other Backward Classes (OBC), and minority communities in remote and educationally backward areas.
- The KGBV scheme is implemented in educationally backward blocks (EBB) where the rural female literacy rate is lower than the national average, and the gender literacy gap is higher than the national average.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
CPRI's Regional Testing Laboratory (RTL) at Nashik
Why in News?
The Central Power Research Institute (CPRI), under the Ministry of Power, Government of India, inaugurated its advanced Regional Testing Laboratory (RTL) at Nashik.
- Shri Manohar Lal Khattar, Honorable Minister of Power & Housing and Urban Affairs, officially inaugurated the facility and dedicated it to the nation.
Key Points
- Purpose: The facility aims to serve industries in western India by providing cutting-edge testing services for electrical and power equipment, such as Transformers, Energy Meters, Smart Meters, and Transformer Oil.
- It will reduce turnaround time for testing and certification, improving the quality assurance ecosystem and speeding up procurement cycles for utilities.
- Significance: The establishment of RTL Nashik enhances India's ability to support the power sector’s technological advancement.
- The lab will not only meet industry needs but will also contribute to R&D in power sector equipment testing, advancing India's power infrastructure.
Central Power Research Institute (CPRI)
- The Central Power Research Institute (CPRI) was established in 1960 by the Government of India and became an autonomous society under the Ministry of Power in 1978.
- The headquarters of CPRI is located in Bengaluru, with additional centers situated across the country.
- These include the Switchgear Testing & Development Center in Bhopal, the UHV Research Laboratory (UHVRL) in Hyderabad, the Thermal Research Center in Nagpur, and Regional Testing Laboratories in Noida, Kolkata, Guwahati, and Nashik.
- The institute serves as a National Testing and Certification Authority to ensure the availability of quality equipment for Indian Power Systems.







 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan