Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Revives 50 Rivers
The Uttar Pradesh government has successfully rejuvenated 50 rivers spanning 3,363 km through a collaborative effort involving state initiatives and local participation.
Key Points
- About the Project: The initiative was implemented across 1,011 gram panchayats in rural areas.
- The efforts were driven by the Namami Gange programme and sustained through the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA).
- Impact:
- Environmental and Agricultural: The restoration of rivers and construction of 3,388 ponds in rural areas enhanced groundwater levels and water storage capacity,
- It will reduce water scarcity and support agriculture and livestock needs for local farmers.
- Sustainability and Soil Conservation: The government planted along riverbank sites to prevent erosion and reinforce embankments, and identified new projects for river restoration and watershed development.
- Socio-Cultural and Employment Benefits: River revival efforts have restored cultural sites, boosted water conservation awareness, encouraged community participation, and generated rural jobs through MNREGA, aiding local development.
- Environmental and Agricultural: The restoration of rivers and construction of 3,388 ponds in rural areas enhanced groundwater levels and water storage capacity,
Namami Gange Programme
- Launched: It was launched in 2014–15 as a flagship integrated conservation mission by the Government of India.
- Objective: Twin goals of pollution abatement and rejuvenation of River Ganga and its tributaries. Focus on restoring "Nirmal Dhara" (unpolluted flow) and "Aviral Dhara" (continuous flow).
- Coverage: The Ganga Basin spans 11 states, covering 27% of India's land area and supporting 47% of the population.
- Key Components:
- Nirmal Ganga: Pollution control via sewage treatment and waste management.
- Aviral Ganga: Ecological flow restoration and afforestation.
- Jan Ganga: Community awareness and engagement.
- Gyan Ganga: Research, policy support, and river basin planning.
- Recent Initiatives:
- New STPs and drain interception in Varanasi and Bhadohi (over ₹400 crore investment).
- Development of biodiversity parks in 7 districts and priority wetlands in 3 states including UP.
- Launch of a national framework for safe reuse of treated water.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MNREGA)
- It was passed in 2005 and is a rights-based employment guarantee scheme aimed at rural livelihood security.
- Core Objective: To provide 100 days of guaranteed wage employment in a financial year to every rural household whose adult members are willing to do unskilled manual work.
- Key Features:
- Eligibility: Indian citizen, 18 years or older, part of a rural household, and willing to engage in unskilled manual work.
- Decentralized Planning: Planning and implementation are entrusted to Gram Sabhas and Panchayati Raj Institutions, ensuring grassroots participation.
- Unemployment Allowance: If work is not provided within 15 days of application, a compensation (¼ wage for first 30 days, ½ thereafter) must be paid.
- Worksite Norms: Employment must be within a 5 km radius; basic facilities such as drinking water, shade, and first aid must be ensured.
- Time-bound Payments: Wages must be paid weekly and within 15 days, else compensation is applicable.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Kaushal Mela 2025
Why in News?
The city of Lucknow hosted the Kaushal Mela 2025 on the occasion of World Youth Skills Day at Indira Gandhi Pratishthan.
- It focuses on promoting vocational training, skill development, and self-reliance among the youth of Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- Uttar Pradesh Government’s Skilling Initiative:
- Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM):
- Target Group: The mission provides free, employment-oriented training for youths aged 14 to 35.
- Objective: The state government aims to create employment opportunities based on skills.
- Annual Training: Every year, 3 lakh youths are trained across more than 2,800 training centers.
- Total Training: As of March 2025, 14,13,716 youths have been trained since the mission's inception in FY 2017-18.
- Employment Facilitation: The mission has successfully facilitated employment for 5,66,483 youths.
- Partnerships: The mission has partnered with 24 major industrial establishments as training providers and 8 placement agencies to boost job opportunities.
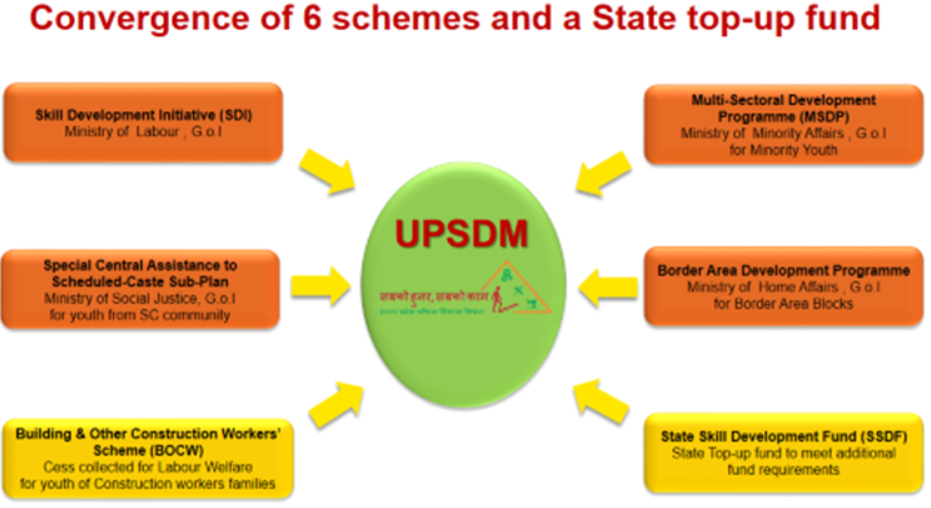
- It is India’s first integrated model that runs five Central Government and one State Government skill development schemes in a standardized and coordinated manner.
- Skill Development Initiative (SDI): A GoI-funded scheme by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, offering MES courses to youth aged 14–35 from all categories with a focus on 30% women and 75% placement.
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled-Caste Sub-Plan: A Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment scheme targeting SC youth (14–35 years), offering MES and QP-NOS courses with 30% women participation, fully funded by GoI.
- Multi-Sectoral Development Programme (MSDP): Run by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, this GoI-funded scheme provides MES training to minority youth in selected districts of UP, ensuring 33% women participation and 75% placement.
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): A Home Ministry scheme for youth in border areas (19 blocks) of UP, offering MES and QP-NOS training with 50% women participation, fully funded by GoI.
- Building & Other Construction Workers’ Scheme (BOCW): A GoUP-funded scheme offering MES and QP-NOS training to registered construction workers and their families aged 14–50 years.
- State Skill Development Fund (SSDF): A UP state top-up fund providing MES and QP-NOS training to youth aged 14–35, targeting 20% minorities and 30% women, with a 60% placement goal.
- Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM):
- A State Skill Development Fund (SSDF) has been instituted to provide top-up funding and ensure effective scheme integration.
- According to common minimum norms, 70% placement of certified candidates is mandatory, with wage employment forming at least 50%.‘
ITI Chalo Abhiyan
- It was launched on 12th May 2025, to increase admissions in ITIs across Uttar Pradesh.
- It aims to strengthen technical education and enhance employability among youth, aligned with Make in India and Digital India.
- Implemented through coordinated efforts of District Magistrates, school authorities, and village heads.
- 149 Government ITIs have partnered with Tata Technologies to offer 11 industry-aligned long-term courses.
- The mission raises awareness in schools and rural areas, bridging the education-employment gap to make UP a skill development hub.







-UPPCS-English%20(web).png)
-UPPCS-English%20(mobile).png)







.jpg)









.png)





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan

