Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Clean Plant Programme
Why in News?
At India’s first international Agri Hackathon in Pune, the Union government unveiled the ‘Clean Plant Programme’, aimed at providing disease-free horticultural plants to farmers, beginning with Maharashtra.
- The initiative aims to boost agricultural productivity by offering healthy plants for crops like grapes, oranges, and pomegranates.
Key Points
- About the Agri Hackathon:
- International Agri Hackathon served as the largest platform for fostering dialogue and accelerating innovation in agriculture.
- The event was jointly organised by the Department of Agriculture, Government of Maharashtra, along with other institutions of Pune.
- Objective:
- It addresses the challenges posed by a growing population, climate change, and agricultural uncertainties, envisioning a future where agriculture can transform lives.
- It seeks to harness the potential of innovation to build sustainable and scalable agricultural solutions.
- About the Clean Plant Programme:
- The programme will be launched with an investment of Rs 300 crore, with a focus on Maharashtra, where the programme will start in Pune (Grapes), Nagpur (Oranges), and Solapur (Pomegranates).
- Maharashtra has emerged as the horticulture hub of India, driven by consistent government efforts and the innovative spirit of its farmers.
- Key Features of the Programme:
- Disease-Free Plants: Farmers will receive plants that are free from diseases, increasing productivity and reducing crop loss.
- Financial Support for Nurseries: The government will provide funding for large and medium-sized nurseries to support the production of disease-free seedlings.
- Large nurseries will receive Rs 3 crore, while medium-sized ones will receive Rs 1.5 crore.
- Production of Seedlings: The initiative aims to produce 8 crore disease-free seedlings annually, benefiting farmers across the nation.
- India aims to collaborate with countries like Israel and the Netherlands to enhance the Programme’s impact.
- The programme will be launched with an investment of Rs 300 crore, with a focus on Maharashtra, where the programme will start in Pune (Grapes), Nagpur (Oranges), and Solapur (Pomegranates).
- Lab to Land Initiative:
- To bridge the gap between research and practice, the government has launched the ‘Lab to Land’ initiative to directly connect agricultural scientists with farmers.
- Under this 16,000 agricultural scientists across the country will work closely with farmers and agriculture departments to transfer critical knowledge on seed production, disease diagnosis, and agricultural best practices.
Status of Horticulture Sector in India
- As of 2023, India is the 2nd largest producer of fruits and vegetables.
- The Indian horticulture sector contributes about 33% to the agriculture Gross Value Added (GVA) making a very significant contribution to the Indian economy.
- Government Initiatives Related to Horticulture:
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Water Conservation Efforts in Rajasthan
Why in News?
On World Environment Day (5th June 2025), Rajasthan launched a two-week water conservation campaign focusing on restoring traditional water sources, building harvesting structures, recharging groundwater, and repairing dams and canals.
Key Points
- About the Campaign:
- The Chief Minister inaugurated the water conservation campaign at the Rajasthan International Centre, urging public participation and highlighting the moral responsibility to combat climate change.
- A shramdaan programme was held at Ramgarh Dam near Jaipur for its restoration, along with the launch of new water conservation projects on the Chambal River banks in Keshoraipatan, Bundi district.
- Conservation Projects:
- Key Activities:
- Foundation stones will be laid for water conservation projects worth Rs 345 crore.
- The campaign will feature the cleaning of traditional water sources, shramdaan camps (voluntary labour), and tree plantation drives.
- MoUs for Climate and Environmental Initiatives:
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the State Pollution Control Board and the Centre for Science and Environment, New Delhi, to prepare the Climate Change Adaptation Plan 2030.
- Additional MoUs were signed to implement an Emission Trading Scheme and establish an Early Warning System for Alwar and Bhiwadi.
- Key Activities:
- Traditional Water Wisdom in Rajasthan:
- People in Rajasthan have historically used unique methods like stepwells, johads, ponds, and wells to conserve water.
- The state government has committed to constructing at least 125 water conservation structures in each district to revive these traditional practices.
Water Harvesting Systems of Rajasthan
|
Water Harvesting System |
Description |
|
Baoli |
Stepwell structure with arches, carved motifs, and rooms. Integral to urban water storage in low-rainfall areas. |
|
Jhalara |
Rectangular stepwells with tiered steps on three or four sides, designed to collect water from reservoirs or lakes. |
|
Taanka |
Cylindrical underground pit paved to collect rainwater from rooftops or catchment areas. |
|
Khadin (Dhora) |
Long earthen embankments across hill slopes collecting surface runoff for agriculture. |
|
Kundi |
Consists of a deep, circular or rectangular pit, which is crucial in arid and semi-arid areas where water is scarce and rainfall is unpredictable. |
West Bengal Switch to Hindi
India’s First Indigenous Polar Research Vessel
Why in News?
Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE) Kolkata, a Government of India undertaking, has signed an MoU with Norway’s Kongsberg firm to develop India’s first indigenously built Polar Research Vessel (PRV).
Key Points
- About the Polar Research Vessel (PRV):
- A PRV is a ship that supports research in the polar regions (around the North and South Poles) and ocean areas, tailored to the needs of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research.
- PRV will support India’s polar and ocean research missions, strengthening its existing three research stations: Bharati and Maitri in Antarctica, and Himadri in the Arctic.
- The vessel will be equipped with advanced scientific instruments to explore marine ecosystems and deep-sea biodiversity in polar and southern ocean realms.
- The project will reinforce India’s commitment to MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security Across the Regions).
- Under Sagarmala 2.0, India aims to become a global maritime leader by bridging infrastructure gaps and enhancing shipbuilding, repair, and recycling.
- The collaboration with Norway also aligns with India’s ‘Make in India’ and Atmanirbhar Bharat goals by boosting indigenous shipbuilding capability.
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR)
- It was established as an autonomous Research and Development Institution of the Ministry of Earth Sciences on the 25th May 1998.
- Earlier known as the National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR), NCPOR is India’s premier R&D institution responsible for the country’s research activities in the Polar and Southern Ocean realms.
- It is the nodal agency for planning, promotion, coordination and execution of the entire gamut of polar and southern ocean scientific research in the country as well as for the associated logistics activities.
MAHASAGAR
- About:
- It is India’s strategic initiative launched in 2025 to expand its security, trade, and development cooperation beyond the Indian Ocean Region to include the broader Global South—covering Africa, ASEAN, Latin America, and Pacific Island Nations.
- MAHASAGAR builds on the 2015 SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) doctrine, which focuses on maritime security, sustainable development, and regional collaboration in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Key Focus Areas:
- Trade & Connectivity: Strengthens maritime and economic linkages across the Global South.
- Maritime Security: Enhances domain awareness and ensures free and secure sea lanes.
- Disaster Resilience & Humanitarian Aid: Promotes rapid response mechanisms and regional support systems.
- Economic & Cultural Engagement: Deepens partnerships with island and coastal nations through shared heritage, capacity building, and mutual growth.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Namami Gange Mission
Why in News?
On World Environment Day 2025 (5th June, 2025), a special event under the Namami Gange Mission was held in Bulandshahr, Uttar Pradesh, focusing on ecological restoration, sustainable practices, and modern technology for river conservation.
Note: The Ganga rejuvenation programme was recognised as one of the world’s top 10 ecosystem restoration initiatives at the UN Biodiversity Conference in Montreal.
Key Points
- Key Highlights of the Event:
- Sewage and Pollution Control Measures:
- Sewage Treatment Plants across the Ganga basin are preventing untreated wastewater from entering the river.
- Strict action against polluters was emphasized, along with the critical role of community river guardians (Ganga Praharis).
- Promotion of Natural Farming:
- Natural farming was promoted to reduce chemical fertilizer use, improve soil health, and prevent runoff into rivers.
- Traditional bio-inputs were recommended to support sustainable agriculture and water conservation.
- Role of Technological Integration:
- Modern tools like drones and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) surveys are being used to identify pollution hotspots and track drains entering the river.
- A mobile library, Pustak Parikrama, was launched by the National Book Trust (NBT) to promote environmental awareness across rural and semi-urban areas.
- Ecological Restoration Actions:
- Fish fingerlings and turtles were released at Basi Ghat to restore aquatic life.
- The rescue centre for Gangetic dolphins and freshwater turtles plays a crucial role in conservation of endangered species.
- Tree Plantation and Afforestation:
- Several trees were planted under the “Ek Ped, Maa Ke Naam” initiative, reinforcing afforestation’s role in ecological balance.
- Sewage and Pollution Control Measures:
Namami Gange Programme
- About: It is a flagship programme for the rejuvenation of the Ganga River and its tributaries by reducing pollution, improving water quality, and restoring the river’s ecosystem.
- Implementation: Its implementation has been divided into Entry-Level Activities (for immediate visible impact), Medium-Term Activities (to be implemented within 5 years of time frame) and Long-Term Activities (to be implemented within 10 years).
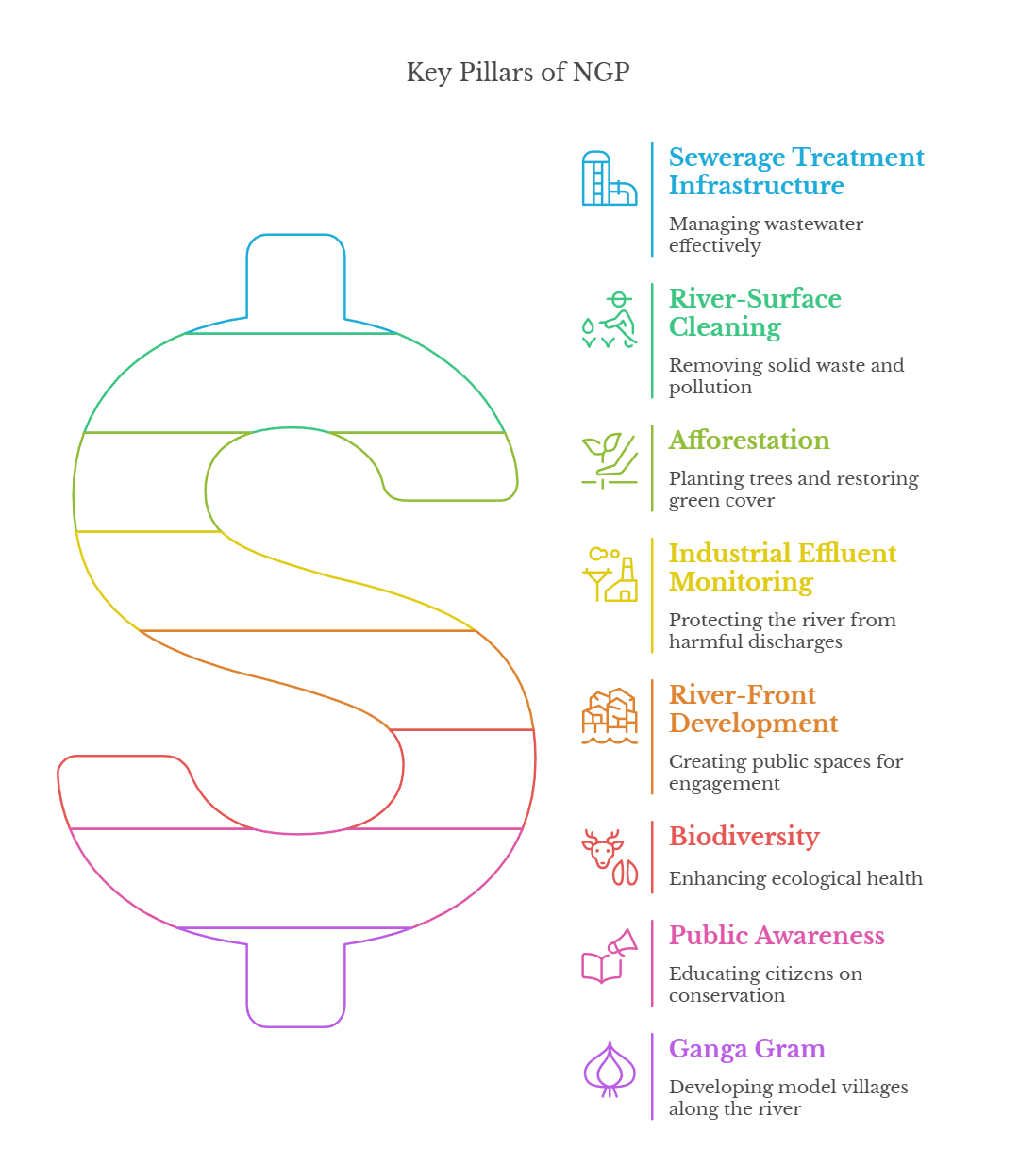
- 8 Pillars of NGP:
- Key Interventions:
- Pollution Abatement (Nirmal Ganga): Setting up sewage treatment plants (STPs), reducing industrial and domestic waste discharge.
- Improving Ecology and Flow (Aviral Ganga): Restoring natural flow and biodiversity, implementing water conservation measures.
- Strengthening People-River Connect (Jan Ganga): Promoting community participation and awareness, involving local stakeholders in conservation efforts.
- Facilitating Research and Policy (Gyan Ganga): Supporting scientific research and studies, formulating evidence-based policies.
Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam’ Campaign
- About: It aims to honor mothers by encouraging tree planting in their names, combining environmental conservation with a tribute to motherhood, symbolizing how mothers, like trees, nurture and sustain life.
- It was launched by the Prime Minister on World Environment Day, 5th June, 2024.
- Objective: To promote environmental preservation, increase forest cover, and support sustainable development while honoring mothers.
- World Record Achievement: On 22nd September 2024, 128 Infantry Battalion & Ecological Task Force of the Territorial Army planted over 5 lakh saplings in one hour in Jaisalmer.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
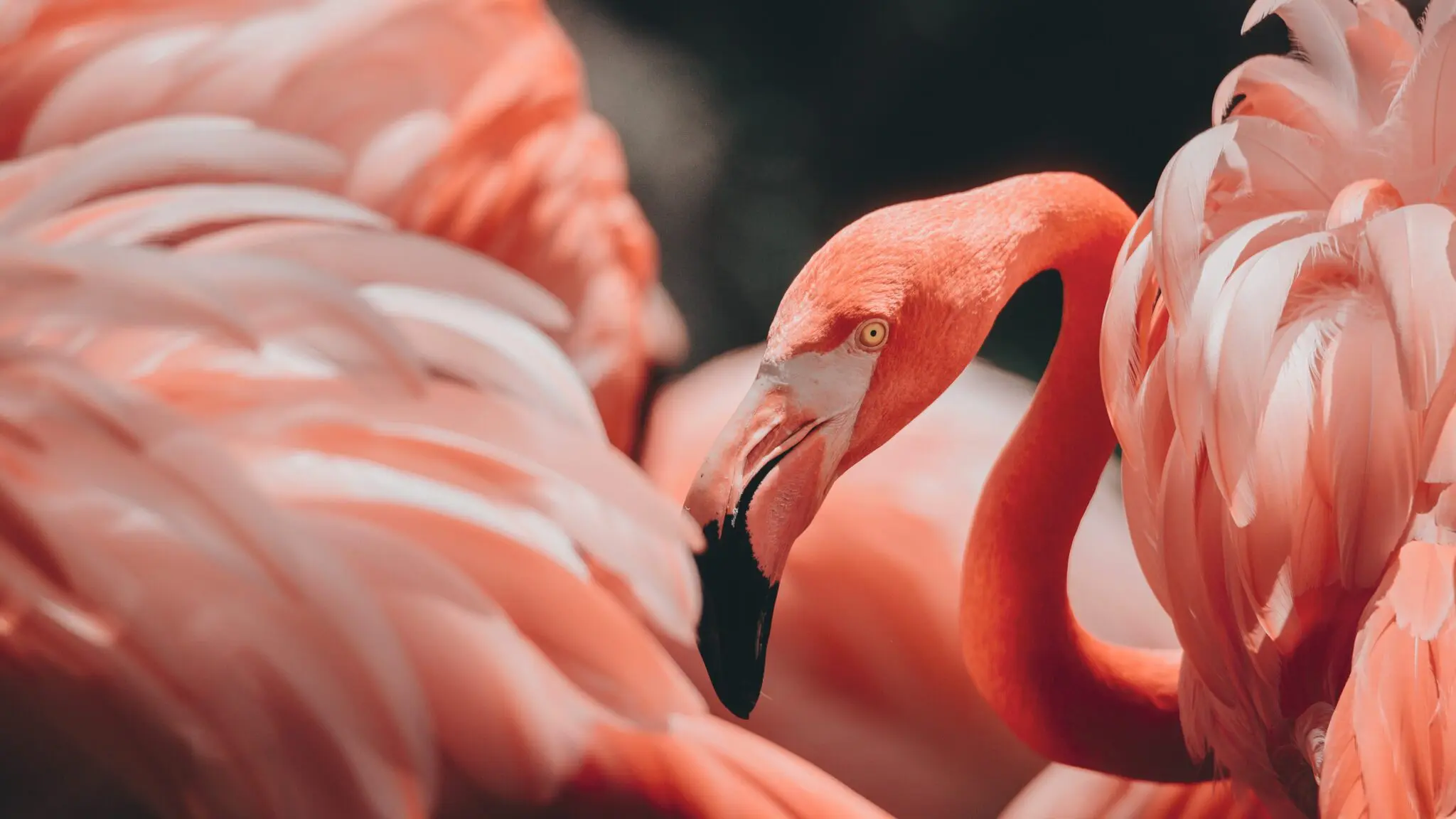
Flamingos at Rajasthan’s Sambhar Lake
Why in News?
Flamingos traditionally migrate to Sambhar Lake between November and March, but in 2025, they stayed significantly longer owing to abundant food supply and changing climate conditions that created a more favorable habitat.
Key Points
- Significant Rise in Bird Population:
- A census conducted in January 2025 recorded over 1.04 lakh migratory birds at Sambhar Lake, including large numbers of Lesser and Greater Flamingos—a substantial increase from 7,147 birds in 2024.
- This reflects better environmental conditions, which have enhanced the lake’s role as a crucial resting and feeding ground for migratory species.
- India hosts over 250 migratory bird species annually, with hotspots including Chilika Lake, Khichan, and Bharatpur.
- A census conducted in January 2025 recorded over 1.04 lakh migratory birds at Sambhar Lake, including large numbers of Lesser and Greater Flamingos—a substantial increase from 7,147 birds in 2024.
- Ecological Importance of Sambhar Lake:
- Sambhar Lake is a critical stopover along the Central Asian Flyway, one of the world’s major bird migration routes.
- It is a saline wetland, located in the Nagaur and Jaipur districts of Rajasthan, bordered by the Aravalli hills.
- It is the source of most of Rajasthan's salt production.
- It was designated a Ramsar site in 1990 due to its ecological significance.
Flamingos
- About: It belongs to the family Phoenicopteridae.
- There are six species of flamingo namely the Greater flamingo (state bird of Gujarat), Chilean flamingo, Lesser flamingo, Caribbean flamingo, Andean flamingo, and Puna flamingo that inhabit lakes, mudflats, and shallow lagoons in the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Europe.
- Distinctive Appearance: Known for their vibrant pink feathers, flamingos have long legs and necks, webbed feet, and a distinctive downward-curving bill adapted for filter-feeding.
- Flamingos' habitats and food sources change by location and season, causing their colors to range from dark or bright pink to orange, red, or pure white.
- Adaptations: Flamingos have adapted to extreme environments with high salinity and temperatures, where their predators are limited.
- Ecological Role: They play a crucial ecological role by maintaining the health of their habitats through their feeding activities, which affect nutrient cycling and algae populations.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List:
- Vulnerable: Andean flamingo (Pink Flamingo)
- Near Threatened: Lesser flamingo, Puna flamingo, and Chilean flamingo
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife Protection Act,1972: Schedule II
- IUCN Red List:






















.jpg)









.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



