Rajasthan
RPSC Exam Syllabus – Mains
- 12 Jan 2026
- 1 min read
Table of Contents
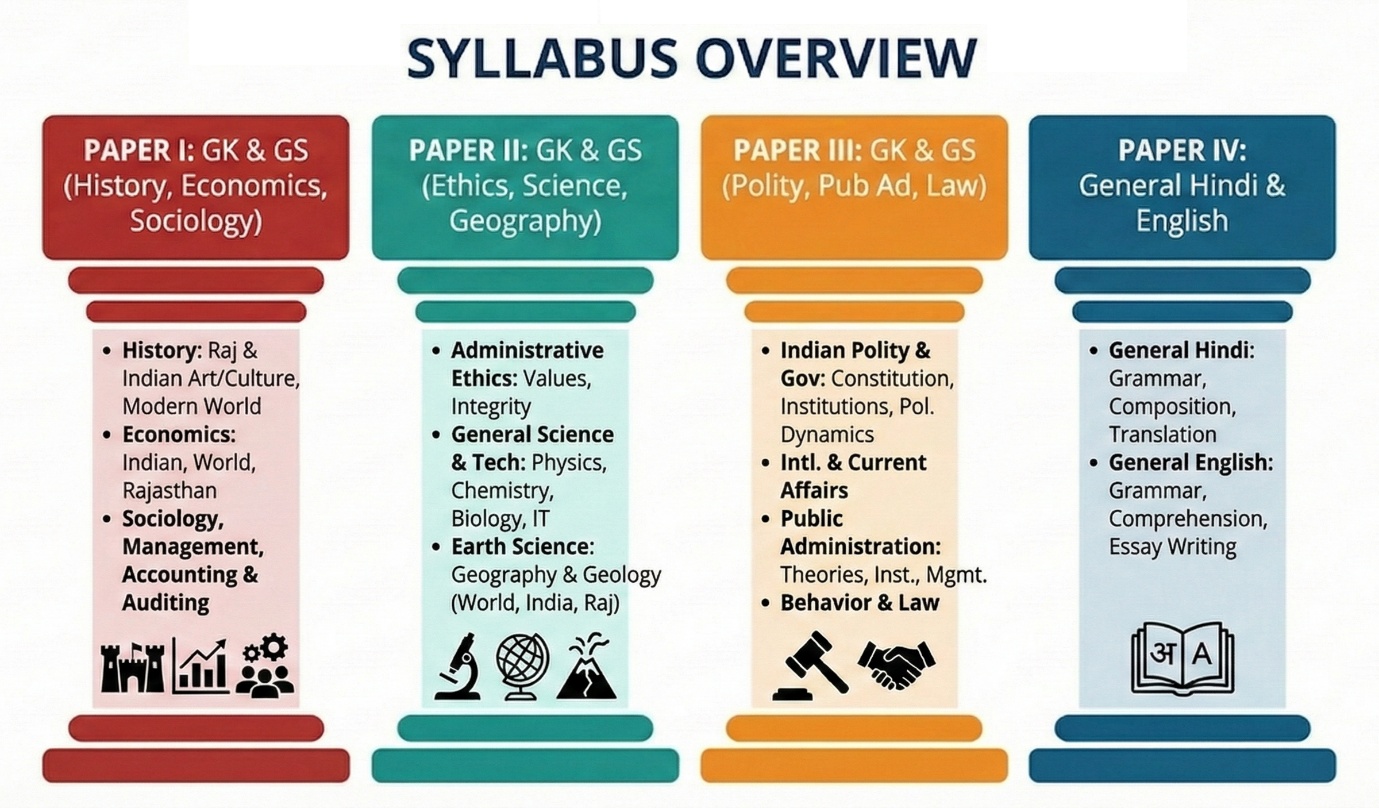
Planning for the RPSC RAS Mains Exam starts with understanding the official syllabus clearly. The RAS Mains Syllabus (updated in January 2026) is divided into four papers covering General Studies, Rajasthan-specific topics, Science & Technology, Polity, Ethics, Law, and Language skills. Below, you’ll find the complete topic-wise RAS Mains syllabus, designed to help you streamline your preparation, focus on high-weightage areas, and build a strong answer-writing strategy as per the latest exam requirements.
Scheme and Syllabus of Examination:
|
The latest syllabus for the Mains Examination is provided below for the reference.
Paper – I: General Knowledge and General Studies
Unit I- HISTORY
Part A - History, Art, Culture, Literature, Tradition and Heritage of Rajasthan
Pre historic culture and various ancient historic sites and their importance; Political and cultural achievements of various rulers of Rajasthan (up to 18th century).
- Revenue and administrative system and changing patterns.
- 19th and 20th century: Revolt of 1857 peasant and tribal movements, political awakening, mass movements and integration of Rajasthan.
- Art and Culture: Performing and fine arts, handicraft, Architecture and monuments, Folk music and folk Dances, Folk Stories and Folk Lores.
- Fairs and festivals
- Tribes and their Traditions.
- Heritage: Major sites of Heritage and tourism in Rajasthan.
- Rajasthani language and important literary work.
- Religious beliefs, Saints and folk deities.
Part B - Indian History & Culture
- Indian heritage: Fine Art, Performing Art, Architecture & Literature from Indus Civilization to British Era.
- Religious Movements and philosophy in Ancient and Medieval India.
- British Policies and their impact: Political, Economic and Administrative unification of the country.
- Indian National Movement- its various stages & streams, important contributors.
- Socio-religious reform movements in 19th and 20th century and Intellectual awakening.
- Post Independent India - Accession of princely states & Linguistic reorganisation of the states. Development of science and technology. Women Empowerment and women reform movement.
Part C - History of Modern World (up to 1991 A.D.)
- Renaissance and Reformation.
- American War of Independence, French Revolution, Industrial Revolution, Russian Revolution.
- Nazism in Germany and Fascism in Italy.
- Impact of World Wars, World during Cold war.
Unit II- ECONOMICS
Part A- Indian Economy
- Growth and development - concept and measurement. Income approach, HDI and other related indices. Climate change and Environmental degradation.
- Agriculture: Productivity and Progress. Land reforms. Agriculture Finance. Agriculture marketing. Food Security. Food Processing. Major Policy initiatives.
- Industry: Policy and Reforms. Globalization, liberalization and privatization. Industrial Finance. Micro, small and medium enterprises: Importance and Policy initiatives.
- Service sector and infrastructure: Energy, Transportation and Communication.
- International trade and Balance of payments. Foreign aid and investment.
- Public Finance- Union Budget: Sources of Revenue and expenditure. Budget deficit and public debt. Fiscal Policy and reforms in India. Centre-state financial relations and Finance Commission.
- Reserve Bank of India and Monetary Management. Banking and financial reforms.
- Social sector: Health and Education, Poverty and Unemployment. Schemes for augmenting employability of labour in India. Welfare Schemes for weaker and
- marginalized sections of the society.
Part B- World Economy
- Global economic Issues: Role of WTO, World bank and IMF.
Part C- Economy of Rajasthan
- Economic growth indicators of Rajasthan - State Domestic Product, Per Capita Income and Inclusive Growth. Viksit Rajasthan 2047. Green Growth and Environmental Sustainability. Position of Rajasthan in the Achievements of Sustainable Goals.
- State Budget - Fiscal Management and Budget Deficits.
- Agricultural Growth: Production and Productivity. Water Resources and Irrigation. Animal Husbandry and Allied Activities. Agricultural Marketing. Government Schemes for Farmer's Welfare.
- Rural Development and Rural Infrastructure. Panchayati Raj Institutions and State Finance Commission.
- Institutional Framework of Industrial Development. Investment Promotion Policy. Importance Of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises and Policy Initiatives for Their Development. Petroleum And Oil Resources in The State.
- Infrastructure Development- Power and Transportation. Public-Private Partnership Projects Externally Aided State Projects.
- Human Resource Development- Health and Education: Unemployment and Poverty. Employment Generation and Poverty Eradication Schemes.
- Good Governance and digital transformation ensuring efficient public services.
- Major Welfare Schemes of State Government For SC/ST/Backward Classes) Minorities / Disable Persons, Destitute, Women, Children and Old Age People.
Unit III- SOCIOLOGY, MANAGEMENT, ACCOUNTING & AUDITING
Part A- Sociology
Sociological thought in Indian Society:
- Concept of Caste & Class, Changing dimensions of Caste and Class in Indian Society.
- Changes in Contemporary Indian Society and Culture: Secularisation, Urbanisation, Modernisation and Globalisation.
- Concepts related to Indian Social system: Doctrine of Karma, Dharma, Purushartha and Ashram system.
- Issues related to Family & Marriage, Elderly people and disabled in present Indian Society. Impact of Cyber-crime and social media on Indian Society.
- Challenges and Issues before Indian Society: Dowry, Divorce, Corruption, Poverty, Prostitution, Unemployment and Drug addiction.
- Problems related to weaker sections of Indian Society (with special reference to Rajasthan): Women, Marginalised groups, Dalits, SC&ST and their Welfare schemes.
Part B- Management
- General Management: Concept of Management, Managerial skills and levels, Management Functions. MBO, Decision making: process, techniques and models
- Organizational behaviour: Nature and Scope, Perception, Motivation- Concepts and Theories, Group Dynamics and Team Building, Organizational Climate and Culture.
- Marketing Management: Concept and Scope, Marketing mix: Product, Pricing, Promotion and Physical Distribution. Service and digital marketing.
- Human Resource Management: Concept and Scope, Human Resource Planning, Recruitment, Selection, Placement and Training, Performance Appraisal System, Modern Trends in Human Resource Management
- Strategic Management: Concept and Scope, Business environment and SWOT analysis, Strategic Formulation and implementation, Strategic control and evaluation.
Part C- Accounting & Auditing
- Theory Base of Accounting: Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAPs) and Accounting Concepts.
- Accounting Standards: Basic Knowledge of Accounting Standards
- Financial Statement of a Company; Techniques of analysis of Financial Statements; Cash Flow Statement; Basic knowledge of Responsibility and Social Accounting.
- Computerised Accounting: Features and Software Packages
- Basic Knowledge of Goods and Services Tax
- Meaning & Objectives of Auditing, Audit Programme, Basic Knowledge of Social, Performance and Efficiency Audit; Elementary knowledge of Government Audit.
Paper –II: General Knowledge and General Studies
Unit I- Administrative Ethics
- Ethics and human Values: Lessons from lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators. Role of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
- Ethical concepts Rit and Rin-Inspiration from Karmavada. Concept of Duty, concept of Good and Virtue
- Ethics in private and public relationships. Philosophical basis of Integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship. Liberal Society: Transparency, media and bureaucracy
- Ethics of Bhagwad Geeta and its role in administration.
- Gandhian Ethics.
- Contribution of Moral thinkers, and Philosophers from India and World.
- Ethical concerns, dilemmas and challenges in administration. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Versus Conscience in administrative decision making
- Basis of Ethical decision making: Social justice, humanitarian concerns, accountability in governance. Instrumental rationality versus value rationality.
- Non-factual Case Studies on the above-mentioned topics.
Unit II- General Science & Technology
- Chemistry in Everyday Life; Atomic Structure; Metal, Non-Metal and Metalloids, Metallurgical Principles and Methods, Important Ores and Alloys; Acid, Base and Salts, Concept of pH and Buffers; Important Drugs (Synthetic and Natural), Antioxidants, Preservatives, Insecticides, Pesticides, Fungicides, Herbicides, Fertilizers, Binders and Sweeteners; Carbon & its Compounds and their Domestic, Industrial Applications; Fuels, Octane Rating; Radioactivity- Concepts and Applications; Green Chemistry and its Applications.
- Physics in Everyday Life; Motion, Work, Power and Energy; Gravitation; Light and its Properties; Heat; Static and Current Electricity; Magnetism, Electro-Magnetism, Sound and Electro-Magnetic Waves, Application of Physics in Medical Diagnostics; Nuclear fission and Fusion; Radiation Safety.
- The Cell; Plant Parts - their Functions and Uses; Plant Nutrition & Growth Regulators with special reference to Agriculture and Horticulture; Sexual and Asexual Reproduction in Plants. Basics of Human Physiology- Digestion, Respiration, Circulation, Excretion, Reproduction and Nervous System. Food and Nutrition; Immunity; Diseases; Public Health Initiatives; Beneficial & Harmful Microbes; Fermentation Technology; Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering-Basic Concepts and their Applications; Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (ELSI) of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs). Recent Advances - Vaccines, CRISPR, mRNA Technology, Artificial Organs.
- Basic Computer Science; Networking; Analog and Digital Telecommunication; Frequency Spectrum; Mobile Telephony, Recent Developments in Information and Communication Technology- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning; Big Data; Cloud and Edge computing; Internet of things; Blockchain and Digital Currency; Virtual and Augmented Reality; OTT Platforms & social media.
- Contribution of Indian Scientists in Science & Technology; Major Indian Scientific Institutions; Scientific and Technological Advancements- Robotics, Nanotechnology, Quantum Computing, etc.; Development of Science & Technology in India and Rajasthan; Government Policies related to Science and Technology; Digital India Initiatives; Cyber Security and Data Privacy.
- Space and Defence Technology- Indian Space Programme; Satellites and their Applications; Various Launch Vehicles; Remote Sensing; Defence Research and Indigenous Technologies; Indian Missile Programme; Drone Technology;
- Chemical and Biological Weapons.
Unit III- Earth Science (Geography & Geology)
Part A- World
- Interior of the Earth and Geological Time Scale.
- Broad Physical Features: Mountains, Plateaus, Plains, Deserts- types and distribution.
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Types, distribution and their impact.
- Climate- Insolation, Atmospheric circulation, Humidity and Precipitation.
- Major Environmental Issues.
Part B- India
- Physiography of India.
- Drainage pattern and important Rivers.
- Climate: Monsoon, Climatic characteristics, Distribution of rainfall and Climatic regions.
- Natural Resources: Types and uses of Water, Natural Vegetation, Soil, Minerals and Power Resources.
- Population: Growth, Distribution and Density, Sex-ratio, Literacy, Urban and Rural Population.
Part C- Rajasthan
- Physiography.
- Important Rivers and Lakes.
- Climatic Characteristics and their classification.
- Natural Vegetation, Wildlife and Biodiversity.
- Soil resources
- Agriculture- Major Crops: Production and Distribution.
- Minerals Resources- Types, distribution and industrial uses.
- Demographic Characteristics.
- Tribes.
- Concept of UNESCO Geo-parks and Geo-heritage sites: Potential in Rajasthan.
- Tourism
Paper-III: General Knowledge and General Studies
Unit I- Indian Polity, Governance, India and International Affairs and Current Affairs
Origin, Structure, and Key Principles of the Constitution of India
- Constituent Assembly, influences, Philosophical Bases, Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles, and Fundamental Duties.
- Basic Structure Doctrine, Amendment Process and major constitutional changes.
- Recent Constitutional Developments and Judicial Pronouncements, Constitutional Morality and Transformative Constitutionalism.
Institutional Framework & Governance Mechanisms
- President, Vice President, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, and Parliament
- Emerging trends in Federalism in India.
- Supreme Court, High Courts, Judicial Review, Judicial Activism, Virtual Court, eCourts and e-Committee.
Dynamics of Indian Polity
- Contemporary shifts in India’s democracy marked by evolving party systems, assertive regionalism, and coalition realignments.
- Shift from identity-based politics to issue-driven and inclusive politics with increasing gender participation, Socio-Political Implications of Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Mobilization.
- Voting behaviour, electoral reforms, and the functioning of elections in India.
- Contemporary Evolving Patterns in Indian Politics.
- Internal Security: Threats, Security Forces and Agencies — Mandate, Roles, and Challenges in Internal Security Management.
State Policies and governance in Rajasthan
- Patterns of political participation, leadership, and electoral behaviour
- Role of political parties and coalition politics in the state.
- Panchayati Raj and Urban local Self-Government – Structure, Issues and Challenges
- New Dynamics and Challenges in Rajasthan’s Politics
- Framing of Public Policy in Rajasthan: institutions, processes, stakeholders, and implementation bottlenecks
- Major E-Governance Initiatives: Achievements and Challenges
India and International Affairs
- Post-Cold War changes, USA’s hegemony, multipolarity, Global political economy, International Terrorism.
- Determinates and attributes of Indian Foreign Policy, India’s relations with major powers and Neighbouring countries, Indian Diaspora and Cultural Diplomacy.
- India's role in regional and global platforms—UN, WTO, EU, ASEAN, BRICS, G-20, QUAD, I2U2, AUKUS, DAKSHIN.
- India’s leadership in climate and green diplomacy (COP Summits, ISA, Mission LiFE).
- Contemporary Strategic Initiatives in India’s Foreign Policy.
Current Affairs & Issues
- Important contemporary events, issues and prominent personalities
- Key public welfare schemes and government initiatives of Rajasthan
- Awards, major literary contributions, and key advancements in science, technology, and ICT.
- Sports policies, key institutions, and significant sports events and achievements of India and Rajasthan.
- Role of Yoga in health, wellness and stress management.
Unit II- Concepts, Issues and Dynamics of Public Administration
Public Administration: Theories and Principles
- Public Administration: Meaning, Nature, Scope and Significance. Evolution of Public Administration as a discipline. Its Role in developing and developed societies. New Public Administration, New Public Management, Good Governance, New Public Service
- Theories and Approaches: Scientific Management, Human Relations, Behavioural, Structural-Functional, Ecological.
- Principles of Organisation: Hierarchy, Unity of Command, Span of Control, Delegation, Centralisation and Decentralisation, Coordination, Authority and Responsibility, Accountability
- Administrative Behaviour: Leadership, Communication, Morale.
Union Government and Administrative Institutions
- Administrative Institutions: UPSC, Election Commission of India, C&AG, Finance Commission, Lokpal, NITI Aayog.
- Personnel Administration: Recruitment, Training, Promotion, Neutrality and Anonymity in Civil Services, Code of Conduct.
- Issues in Administration: Union-State Relations, Minister-Civil Servants Relations, Generalists- Specialists, Administrative Reforms, Social Audit.
- Control over Administration: Legislative, Executive and Judicial.
Comparative Public Administration
- Features of Administrative Systems of U.S.A., U.K., France and China.
State & District Administration
- State Administration: Governor, Chief Minister, Council of Ministers, State Secretariat, Chief Secretary, Role of Directorates. Police Administration, Revenue Board, State Election Commission, State Human Rights Commission, Lokayukta.
- District Administration: District Collector, Law and order Administration, Revenue Administration, Development Administration.
Unit III- Behavior and Law
Part A – Behavior
- Intelligence: Cognitive intelligence, Social and Emotional intelligence, Cultural intelligence, Appreciative intelligence and Spiritual intelligence; Their importance and inculcation at workplace.
- Leadership Profiles: Theories, Types and Styles; Their Challenges and Effectiveness at workplace. Leaders of tomorrow; Their opportunities and challenges.
- Communication at workplace: Models and Networks of communication and their effectiveness; Barries and Distortions of communication; Electronic & Destructive communication- Cyberslacking, Cyberloafing, Moonlighting etc.
- Flourishing at work: Virtues & Strengths, RAISEC Model and Person-Fit-Environment.
- Burnout, Stress and Coping at workplace: Occupational Stress; Sources & Coping styles; Personality and stress; Gender issues at workplace.
Part B-Law
- Contemporary Legal Issues:
- The Right to Information Act, 2005: Sections 1-20
- The Information Technology Act, 2000:
- Section 1
- Section 2- Definitions: Communication device, Computer, Computer Network, Computer Resource, Computer System, Cyber Cafe, Cyber Security, Data, Digital Signature, Electronic Record, Electronic Signature, Information, Private Key, Public Key.
- Sections 65, 66, 66(B-F), 67, 67 (A-C), 71-78
- Intellectual Property Rights: Concepts, types and purpose.
- Crimes against Women and Children:
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005: Sections 1-29, 31
- Sexual Harassment at work place (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013: Sections 1-9, 11-20
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012: Sections 1-15.
- The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007: Sections 1-25
- Important Land Laws in Rajasthan:
- Rajasthan Tenancy Act, 1955:
- Section 1
- Section 5- Definition: Agricultural Year, Agriculture, Agriculturist, Assistant Collector, Board, Collector, Commissioner, Crops, Grove-Holder, Grove land, Holding, Ijara or Theka, Improvement, Land, Land Cultivated Personally, Land Holder, Land less person, Occupied land, Pasture Land, Rent, Revenue, Revenue Appellate Authority, Revenue Court, Revenue Officer, Sayar, Settlement, Sub-divisional officer, Sub-Tenant, Tehsildar, Tenant, Trespasser, Nalbat Sections (14-17A, 31 -37, 38-54A, 206-232, 239- 242
- Rajasthan Land Revenue Act, 1956:
- Section 1, 2
- Section 3-Interpretation: Land Record Officer, Municipality, Nazul Land, Panchayat Circle, Revenue Appellate Authority, Settlement Officer, Village.
- Sections 4-36, 40A, 74-87, 106-137, 142-183
- Rajasthan Tenancy Act, 1955:
- The Bhartiya Nyay Sanhita, 2023:
- Section 1
- Section 2- Definition: Child, Court, Document, Gender, Good faith, Government, Judge, Person, Public, Public Servant, Valuable Security. Sections 189-191, 194-197, 270, 294-296
- The Bharatiya Nagrik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023:
- Section 1
- Section 2- Definition: Audio-Video electronic means, Bail, Bailable offence and non-Bailable offence, Bail-Bond, Bond, Charge, Cognizable offence, Complaint, Electronic communication, Inquiry, Investigation, Non-cognizable offence, Sub division, Summons Case, Warrant Case.
- Sections 3(2)(a), (b), 14-17, 41-43, 126-129, 148-149, 152, 163-167, 173, 174, 187, 194-196
Paper – IV: General Hindi and General English
Unit- I: सामान्य हिंदी
सामान्य हिंदी (कुल अंक: 90), इस प्रश्न-पत्र का उद्देश्य अभ्यर्थी की भाषा-विषयक क्षमता तथा उसके विचारों की सही, स्पष्ट एवं प्रभावपूर्ण अभिव्यक्ति की जाँच करना है।
भाग (A) — (अंक 30)
- उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय: शब्दों में से उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय पृथक करना
- समश्रुत भिन्नार्थक शब्द: वाक्यों में प्रयोग द्वारा अर्थ स्पष्ट करना
- शब्द शुद्धि
- वाक्य शुद्धि
- मुहावरे: मुहावरों का प्रयोग कर अर्थ स्पष्ट करना
- कहावत/लोकोक्ति: प्रयोग द्वारा अर्थ स्पष्ट करना
- पारिभाषिक शब्दावली: प्रशासन से संबंधित अंग्रेजी शब्दों के समानार्थी हिंदी पारिभाषिक शब्द
भाग (B) — (अंक 30)
- संक्षिप्तीकरण: गद्यावतरण का लगभग एक-तिहाई शब्दों में संक्षिप्तीकरण
(गद्यावतरण की शब्द सीमा: लगभग 150 शब्द) - पल्लवन: किसी सूक्ति, काव्य पंक्ति, प्रसिद्ध कथन आदि का भाव-विस्तार
(शब्द सीमा: लगभग 100 शब्द) - अनुवाद: दिए गए अंग्रेजी अनुच्छेद का हिंदी में अनुवाद
(शब्द सीमा: लगभग 50 शब्द)
भाग (C) — (अंक 30)
- पत्र-लेखन: सामान्य कार्यालयी पत्र, कार्यालय आदेश, अर्द्धशासकीय पत्र, अनुस्मारक, प्रतिवेदन (रिपोर्ट)
- प्रारूप-लेखन: अधिसूचना, निविदा सूचना, परिपत्र, प्रेस विज्ञप्ति, कार्यालय ज्ञापन
Unit- II General English (Total marks 70)
Part A- Grammar & Usage (20 Marks)
- Preposition
- The same word used as different part of speech
- Phrasal Verbs & Idioms (application)
- One Word Substitute (application)
- Words often Confused or Misused (application)
Part B- Comprehension, Translation & Precis Writing (30 Marks)
- Comprehension of an Unseen Passage (300 Words approximately), 05 Questions based on the passage and Precis Writing (of the same passage) approximately 100 words.
- Translation of five sentences from Hindi to English.
Part C- Composition & Letter Writing (20 Marks)
- Elaboration of a given theme (Any 1 out of 3, approximately 150 words).
- Writing: Official Letter/Demi-Official/Official Memorandum/Report Writing (approximately 150 words).
Unit- III- Essay (Total Marks 40)
There will be Six thematic areas in the Essay part of the question paper. Candidates will have to write one essay of about 600 words in either Hindi or English language as per their choice. The essay topics will be based on the following Six themes:
- Language, Literature, and Cultural Heritage
- Society, Governance, and Public Affairs
- Science, Technology, Environment, and Sustainable Development
- Economy, Agriculture, Industry, and Commerce
- Current Affairs, Disasters, and National Development Initiatives
- Tourism, Culture, and Contemporary Issues with reference to Rajasthan
Candidates may be required to write an essay on a range of topics arising from these thematic areas. They are expected to maintain strict relevance to the assigned subject, organize their ideas in a coherent manner, and present with precision and brevity. Credit will be accorded for clarity of thought, coherence of structure and effectiveness of expression.
That’s the complete RAS Mains syllabus, structured paper-wise and unit-wise for quick clarity. Use it to build your preparation plan, track topic coverage, and focus on answer writing with consistent revision. Cover Rajasthan-specific sections thoroughly along with core GS areas to improve your overall scoring potential in the exam.
|
Related Resources |
|
|
RPSC RAS Exam Pattern |
|
|
RPSC RAS Previous Year Papers |
|
|
RPSC RAS Exam Strategy |
|
|
Rajasthan State GK |
|
|
Monthly CA Consolidations |
|