Haryana
Earthquake Hits Jhajjar
- 12 Jul 2025
- 3 min read
Why in News?
A magnitude 4.4 earthquake with its epicenter near Jhajjar in Haryana struck on 10th July 2025, triggering strong tremors across Delhi-NCR, including Noida, Gurugram, Faridabad, and nearby areas.
Key Points
- About the Earthquake: An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the Earth's surface caused by the release of energy in the crust, which spreads outward as seismic waves.
- Cause of Earthquakes: Earthquakes occur when stress along faults in the Earth's crust overcomes friction, causing rocks to suddenly slip and release energy as seismic waves.
- The focus is the point where the energy is released underground, and the epicenter is the surface point directly above it, where shaking is strongest.
- Types of Earthquake Waves: Earthquake waves are of two types: body waves and surface waves.
- Body waves travel through the Earth’s interior and include:
- P-waves: Fastest, travel through solids, liquids, and gases, with back-and-forth motion.
- S-waves: Slower, move only through solids, with up-and-down motion.
- Surface waves travel along the Earth’s surface and are the most destructive, causing major damage.
- Body waves travel through the Earth’s interior and include:
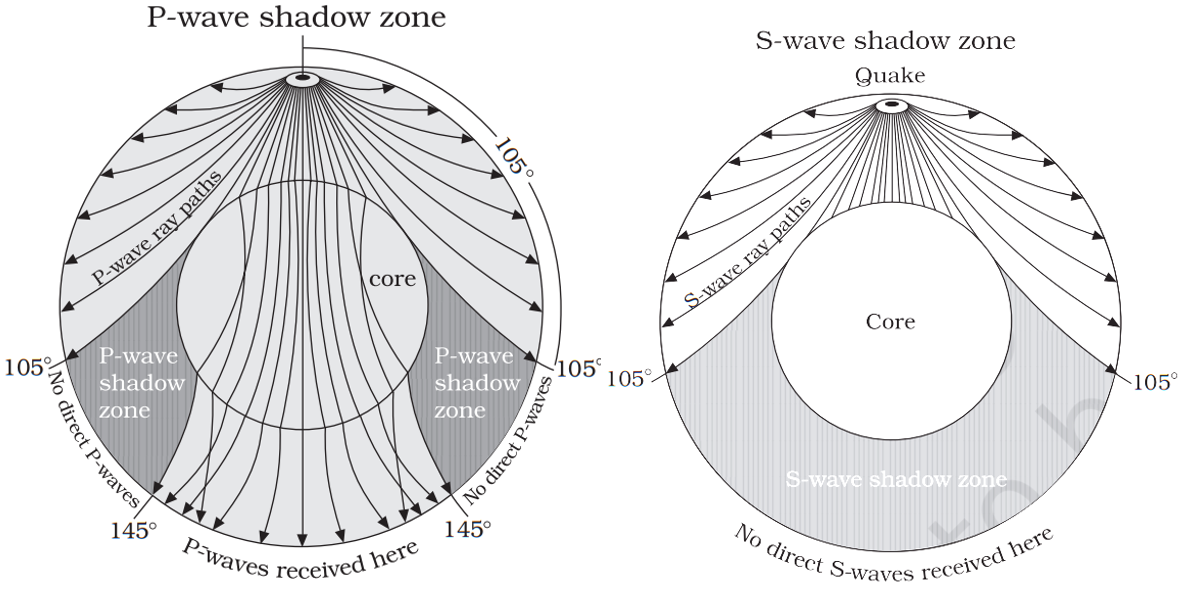
- Seismic Shadow Zones: Shadow zones are areas on Earth’s surface where seismic waves are not detected.
- P-wave shadow zone: Between 105° and 145° from the epicentre.
- S-wave shadow zone: Beyond 105°, as S-waves cannot travel through liquids.
- These zones reveal the Earth’s layered structure, including its liquid outer core.
- Types of Earthquakes:
- Tectonic: Most common; caused by plate movement along faults.
- Volcanic: Linked to volcanic activity in active regions.
- Collapse: Caused by cave or mine roof collapses.
- Explosion: Result of nuclear or chemical blasts.
- Reservoir-induced: Occur near large dams due to water pressure.
- Measuring Earthquakes:
- Richter Scale: Measures magnitude (energy released), ranges from 0 to 10.
- Mercalli Scale: Measures intensity (visible damage), ranges from I to XII.