Important Government Schemes
National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- 06 May 2025
- 7 min read
Key Points
|
Overview of National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- About: The National Supercomputing Mission (NSM), launched in 2015, is a Government of India flagship initiative to boost High-Performance Computing (HPC), strengthen technological capabilities, and advance R&D across key sectors.
- The mission is jointly led by DST and MeitY, and implemented by C-DAC, Pune and IISc, Bengaluru.
- Objective: The mission aims to empower academic and R&D institutions across India by installing supercomputers of varying capacities.
- Access is provided via the National Knowledge Network (NKN), a government-backed high-speed network connecting research and academic institutions.
- Skill Development: The mission promotes HPC skill development to meet the demands of advanced computational research.
- Five dedicated HPC training centres have been set up at Pune, Kharagpur, Chennai, Palakkad, and Goa to train students and researchers in supercomputing.
- Significance:
- The mission plays a crucial role in advancing scientific research across diverse fields such as drug discovery, climate modeling, disaster management, and material science.
- It will enhance capacity building by training professionals in HPC and AI, while also supporting start-ups and MSMEs in innovation and product development.
Note
- FLOPs, or Floating-Point Operations per Second, is a commonly used metric to measure the computational performance – processing power and efficiency – especially in the field of HPC and AI.
- Floating-point operations are a certain kind of mathematical calculation using real numbers with fractional parts.
NSM Infrastructure Development Plan
- The NSM aims to achieve self-reliance in supercomputing, promote R&D and problem-solving across scientific and societal domains, and build a globally competitive HPC ecosystem through a three-phase infrastructure development plan.
- Phase 1: Set up six supercomputers with components assembled in India to begin building domestic capabilities.
- Phase 2: Moved towards local manufacturing and software development, achieving 40% indigenous value.
- Phase 3: Aims for full indigenization by designing and manufacturing all key components in India and establishing a national HPC facility.
What is Trinetra?
- About & Objective:
- Under the NSM, the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) has developed "Trinetra".
- It is an indigenous high-speed communication network designed to enhance data transfer and communication between computing nodes.
- This development marks a critical step toward self-reliance in HPC infrastructure, enabling India to compete globally in the field of high-speed computing networks.
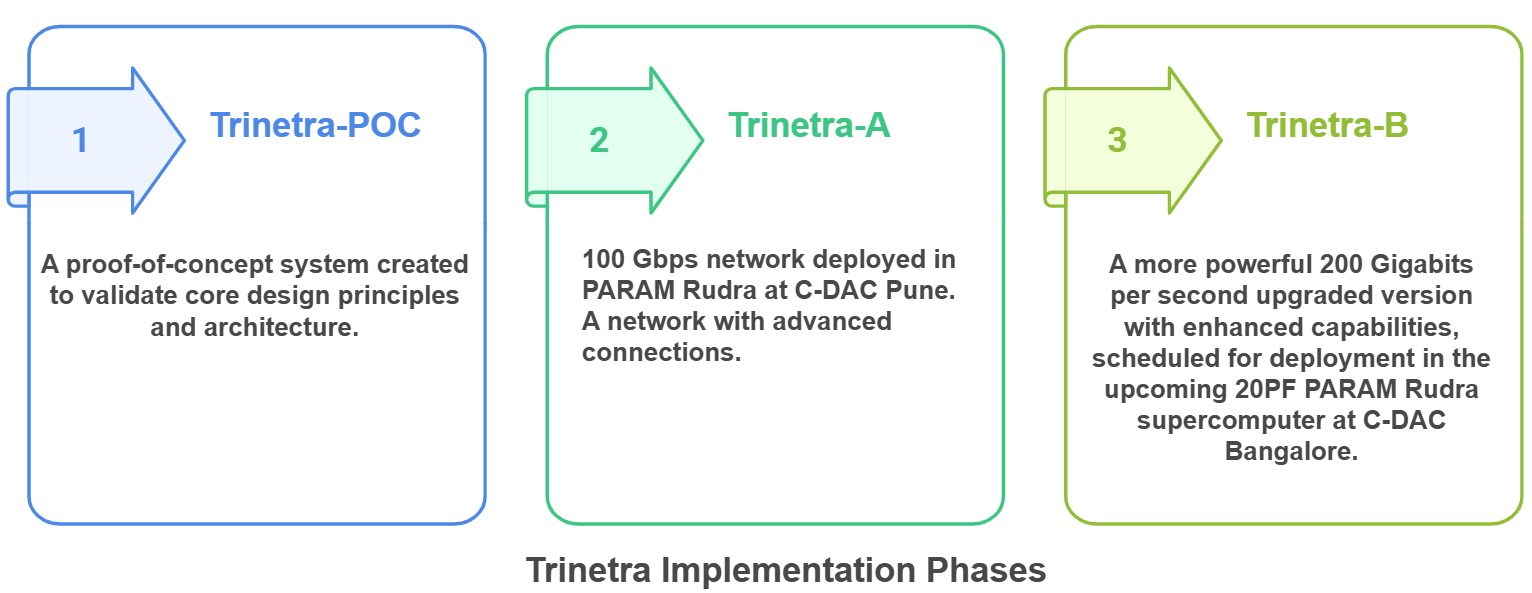
- Phases:
- Trinetra is being implemented in three progressive phases: Trinetra-POC, Trinetra-A and Trinetra-B.
PARAM Rudra Supercomputers
- About: In 2024, three advanced PARAM Rudra supercomputers were officially commissioned for scientific research at Pune, Delhi, and Kolkata.
- PARAM Rudra supercomputers are built using indigenously designed and manufactured HPC servers, known as "Rudra”, along with an indigenously developed system software stack.
- Rudra servers are the first made-in-India servers that match international high-performance computing (HPC) standards.
- Purpose: To facilitate advanced research in physics, earth sciences, and cosmology.
Other Key Installations under NSM
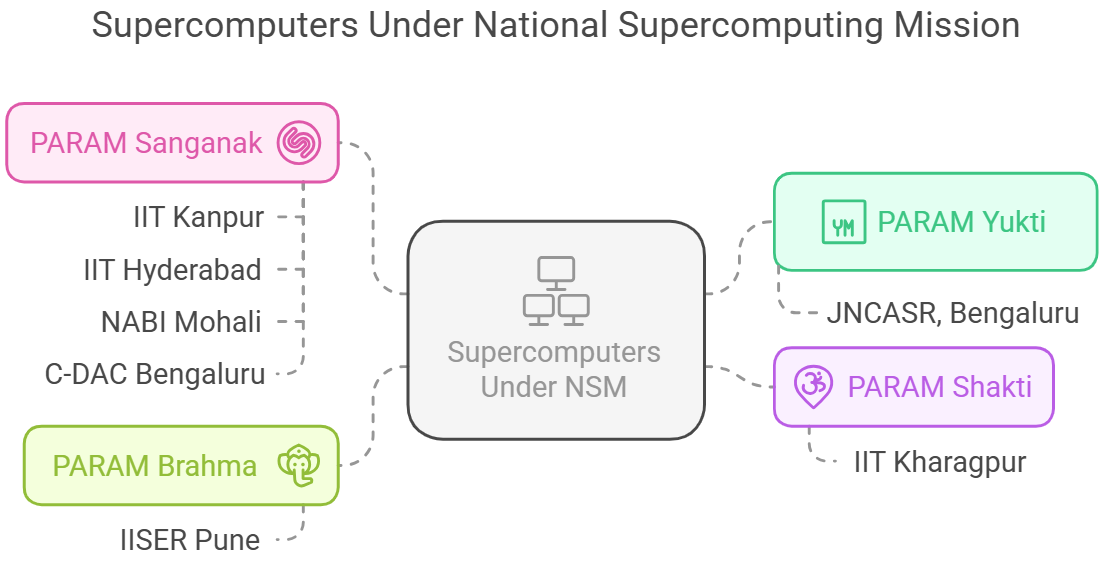
- PARAM Shivay (2019):
- First supercomputer of India under NSM
- Installed at IIT-BHU, Varanasi
- PARAM Pravega (2022):
- Installed at IISc Bengaluru
- It is the largest academic supercomputer in India and one of the most powerful supercomputers in the country.
AIRAWAT (India's AI Supercomputing Platform)
- About & Objective:
- The Government has initiated a project AI Research Analytics and Knowledge Dissemination Platform (AIRAWAT) for providing a common compute platform for AI research and knowledge assimilation.
- Global Recognition:
- AIRAWAT, ranked 75th in the Top 500 Global Supercomputing List at the International Supercomputing Conference (ISC 2023) in Germany, firmly positions India among the world’s leading AI supercomputing nations.
Current Status & Future Prospects of NSM
- As of March 2025, 34 supercomputers deployed across premier and regional institutions with a combined capacity of 35 Petaflops (PF).
- The institutions involved include IISc, IITs, C-DAC, and several others from Tier-II and Tier-III cities.
- System utilization rates are high, with over 85% usage and many systems exceeding 95% efficiency.
- In 2024-25, around 45 petaflops of additional computing infrastructure is planned to be developed using indigenously designed servers and technologies.
Role of India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) in NSM
- The India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) is playing a crucial role in boosting the NSM by enabling domestic production of critical components like processors, memory chips, and accelerators.
- Until now, India relied heavily on imports for these advanced semiconductor technologies.
- ISM aims to make supercomputers more affordable, energy-efficient, and customized to India’s scientific and industrial needs.
- This synergy will help NSM achieve its goal of self-reliance and position India as a global leader in supercomputing.