Indian Economy
GST 2.0 with Next-generation Reforms
- 04 Sep 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Goods and Services Tax (GST), Article 279A, value-added tax ,
For Mains: Evolution and significance of GST in India, Growth & Development
Why in News?
The 56th Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council, unveiled GST 2.0 with next-generation reforms to make the tax regime citizen-centric, boost agriculture, health, manufacturing, and improve ease of doing business.
- The changes in GST rates on services will be implemented with effect from 22nd September 2025.
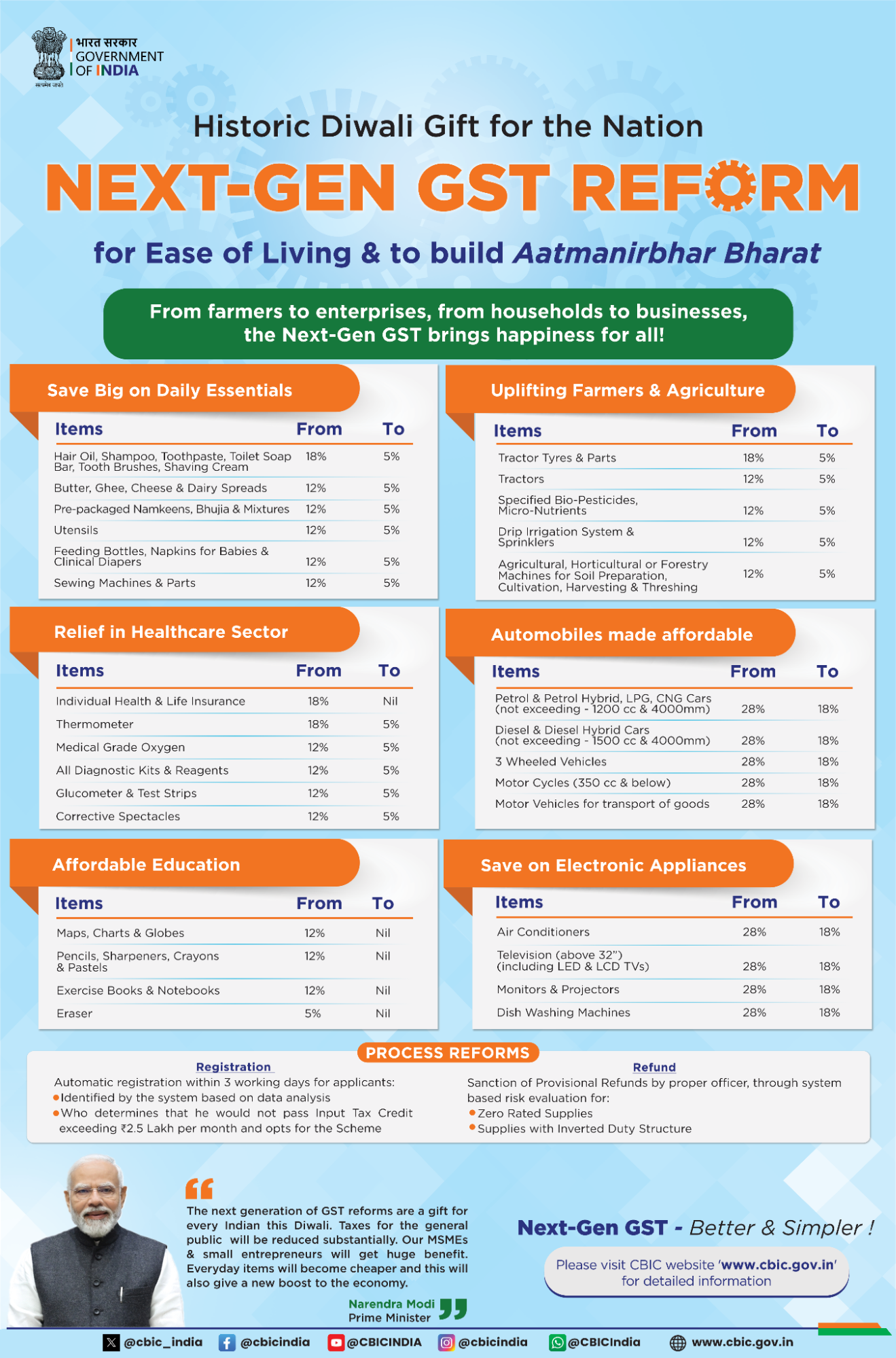
What are the Key Tax Reforms Under GST 2.0?
- Simplified GST Structure: GST 2.0 replaces four GST slabs (5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%) with a two-slab system (5% (merit rate) for essential items and 18% (standard rate) for others), plus a 40% demerit rate for luxury, sin, and demerit goods like tobacco and pan masala.
- Tax Relief for the Essential Goods: Full GST exemption on individual life and health insurance policies. Essential goods such as Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) milk, paneer, and Indian breads now carry nil GST.
- Consumer Goods: GST on small cars, TVs, air conditioners, cement, and auto parts has been reduced from 28% to 18%. GST on renewable energy devices has been reduced from 12% to 5%.
- These cuts are expected to stimulate manufacturing, promote green energy adoption, and boost domestic demand.
- Medical and Health Devices: GST on 33 lifesaving drugs has been reduced from 12% to nil. GST on three critical drugs used for cancer and rare diseases has been reduced from 5% to nil, strengthening healthcare access.
- Support for Agriculture and Rural Sectors: Machinery like tractors, harvesters, and composters: GST reduced from 12% to 5%.
- Fertilizer inputs such as sulphuric acid, nitric acid, and ammonia: GST reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Labour-intensive goods like handicrafts, marble, and leather items: GST reduced from 12% to 5%.
- Trade Facilitation and Dispute Resolution: The Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal (GSTAT) will be operational by December 2025.
- Process reforms for refunds and registration will improve dispute resolution, reduce litigation, and provide predictability for businesses, especially MSMEs.
What is the Goods and Services Tax (GST)?
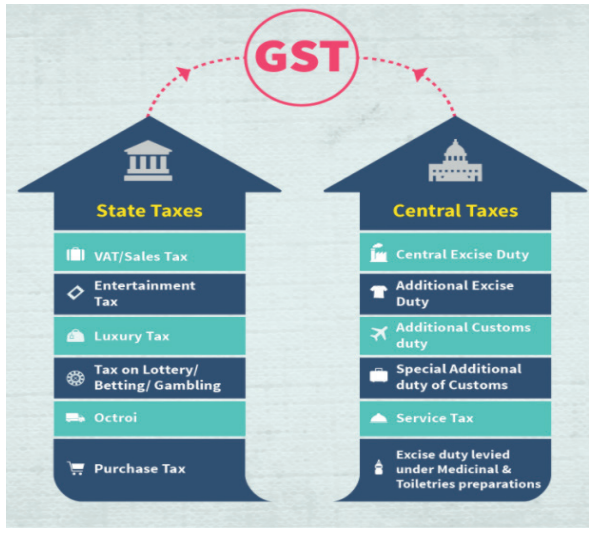
- About: Introduced by the 101st Constitutional Amendment Act, 2017, is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India.
- It is a value-added tax (VAT) that replaced multiple indirect taxes previously levied by the Centre and States.
- Key Features:
- Dual GST Structure: Includes Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST); Integrated GST (IGST) is applicable for inter-state transactions.
- GST Council: It is the primary body for GST policymaking and rate decisions.
- The GST Council, established under Article 279A of the Constitution, is a joint forum of the Centre and States.
- It is chaired by the Union Finance Minister, the Union Minister of State in charge of Revenue or Finance as a Member, and the Minister in charge of Finance, Taxation, or any other Minister nominated by each State Government as Members.
- Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN): help taxpayers in India to prepare, file returns, make payments of indirect tax liabilities and do other compliances.
- Threshold Exemption: Small businesses with turnover below a certain limit are exempt from GST. This makes compliance easier and protects micro enterprises from excessive paperwork.
- Benefits of GST:
- Destination-Based Tax: Collected where goods/services are consumed, benefiting businesses with better cash flow and working capital.
- Ease of Doing Business: Technology-driven, minimal human interface, simplifies compliance, refunds, and registration.
- Boost to Make in India: Makes domestic goods competitive nationally and internationally.
- Exports: Supplies of goods or services, or both, to a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) are treated as zero-rated under GST, with quick refunds, thereby promoting international trade and improving the balance of payments.
- Revenue & Compliance: Expands tax base, increases government revenue, improves transparency, and enhances GDP by 1.5–2%.
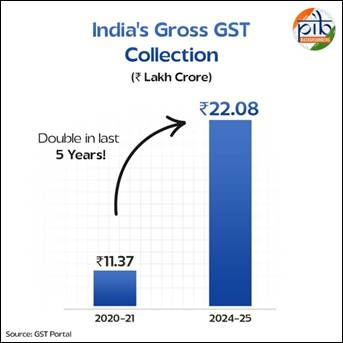
- Achievement of GST: In 2024–25, GST recorded its highest-ever gross collection of Rs 22.08 lakh crore, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 9.4 percent. The average monthly collection stood at Rs 1.84 lakh crore.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine the significance of GST in simplifying India’s indirect tax structure and improving ease of doing business. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of the economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Q. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (2019)