Facts for UPSC Mains
Diversification of India’s Export Markets
- 08 Nov 2025
- 7 min read
Why in News?
India’s exports are diversifying, with non-US markets like the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia helping balance out losses to the US, reflecting a successful trade diversification strategy.
- Despite a 12% drop in exports to the US, India’s merchandise exports grew 6.7% to USD 36.38 billion, reflecting resilient diversification.
- Export diversification expands a country’s products and markets to reduce dependence on a few partners, enhancing economic stability, trade resilience, and innovation.
What are the Key Trends in India's Export Diversification Strategy?
- Decline in US Exports: India’s exports to the US fell due to reduced demand and trade tensions, as tariffs rose from 10% to 50% between April–August 2025, reducing exports from USD 8.8 billion to 5.5 billion.
- Even tariff-free exports dropped 47% to USD 1.8 billion from USD 3.4 billion, though overall exports remain resilient through alternative markets.
- Rise of Non-US Markets: Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East have become key markets for India, importing pharmaceuticals, textiles, engineering products, and machinery.
- Marine exports rose 60% to China, Vietnam, and Thailand, Basmati rice exports to Iran grew six-fold, and tea exports expanded to the UAE, Iraq, and Germany.
- Government and Policy Initiatives: The Indian government has strategically implemented policies aimed at boosting exports to these non-US regions. Programs like the Foreign Trade Policy 2023 and Market Access Initiative (MAI) focus on strengthening trade ties with new partners, offering incentives, and easing logistics barriers.
What are the Key Factors Driving the Diversification of India’s Exports?
- Regional Free Trade Agreements (FTAs): India’s participation in various regional FTAs has been a crucial factor in diversifying its export base. FTAs with countries like the UAE, Japan, and South Korea have opened new avenues for trade.
- Supply Chain Management: India has emerged as a reliable alternative in China-plus-one strategies, attracting global companies and promoting value addition and diversification beyond traditional markets.
- Government Outreach: Identification of 40 key importing nations across Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that account for three-fourths of global textile and apparel demand. Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes boost competitiveness in manufacturing and exports across high-growth sectors.
- Long-Term Goals: India aims to reduce dependence on the US market and expand its global export footprint through diversification.
- The goal is to build resilient, sustainable trade systems aligned with Viksit Bharat 2047 and the vision of becoming a top 3 global exporter.
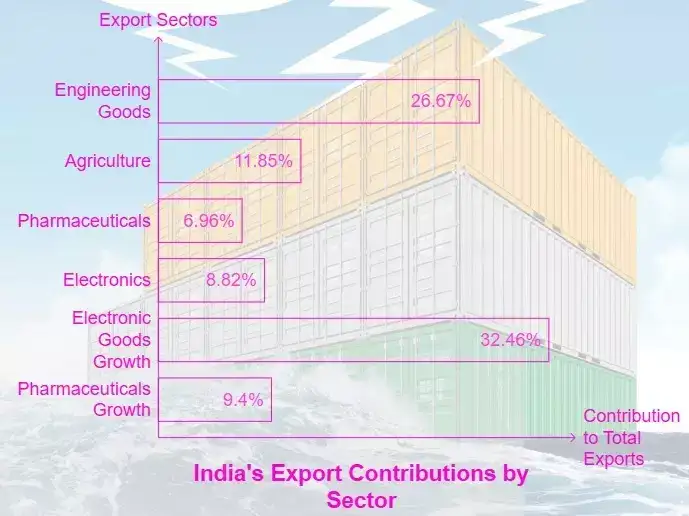
India's Export Basket (FY 2024-25)
- Engineering Goods: Largest contributor at 26.67%, totaling USD 116.67 billion. Key export destinations: US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, UK, Germany. Exports consistently above USD 100 billion since 2021-22.
- Agriculture & Allied Products: Contributed 11.85% to total exports, totaling USD 51.86 billion. Key commodities: spices, coffee, tea, tobacco, rice, fruits & vegetables, marine products.
- Major destinations for spices: China, US, UAE, Bangladesh, Thailand; coffee: Italy, Russia, Germany, UAE, Belgium, USA.
- Pharmaceuticals: India exports medicines to over 200 countries, continuing a trend of steady growth since 2014-15.
- Electronics: Computer hardware & peripherals doubled from USD 0.7 billion to USD 1.4 billion. Major export markets: UAE, US, Netherlands, UK, Italy.
Conclusion
While diversification shows promise, challenges persist — the US market’s high value remains hard to replace, and competition from China is strong. However, opportunities lie in building a resilient export economy and a potential US-India Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) aimed at boosting trade to USD 500 billion by 2030.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How have US tariff hikes impacted India’s export profile, and what strategies has India adopted to mitigate these effects? |
1. Why did India start its export diversification strategy?
India began diversifying exports after the US imposed 50% tariffs on Indian-origin goods, impacting key sectors like textiles, gems, and carpets.
2. Which countries have emerged as new destinations for Indian exports?
UAE, France, Japan, China, Vietnam, and Thailand have become major alternative markets for Indian exports.
3. How is the government facilitating export diversification?
By identifying 40 key importing countries, strengthening global supply chain integration, and promoting deep-tech and manufacturing exports.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)