-
01 Feb 2023
GS Paper 1
Geography
Day 73
Question 1: Discuss the types of natural vegetation in India. Do you think the Mangroves are promising vegetation? Illustrate. (250 Words)
Question 2: Discuss the major factors of soil formation. What steps can be taken to mitigate soil degradation in India? (250 Words)Answer 1
Approach
- Write an introduction about natural vegetation in India.
- Discuss the benefits of mangroves which reflect the promising nature of mangroves.
- Write a holistic and appropriate conclusion.
Introduction
- India is a large and diverse country with a wide range of climatic and geographical conditions, which has resulted in a rich and varied landscape of natural vegetation.
- From the lush tropical evergreen forests of the Western Ghats to the arid and sparsely populated thorn forests of the Thar Desert, India's natural vegetation covers a wide range of habitats and ecosystems.
- These ecosystems support a diverse range of plant and animal species, and play an important role in maintaining the ecological balance of the region.
- The natural vegetation of India is also an important source of livelihood for local communities, who rely on the forest for timber, fuel, and non-timber forest products.
Body
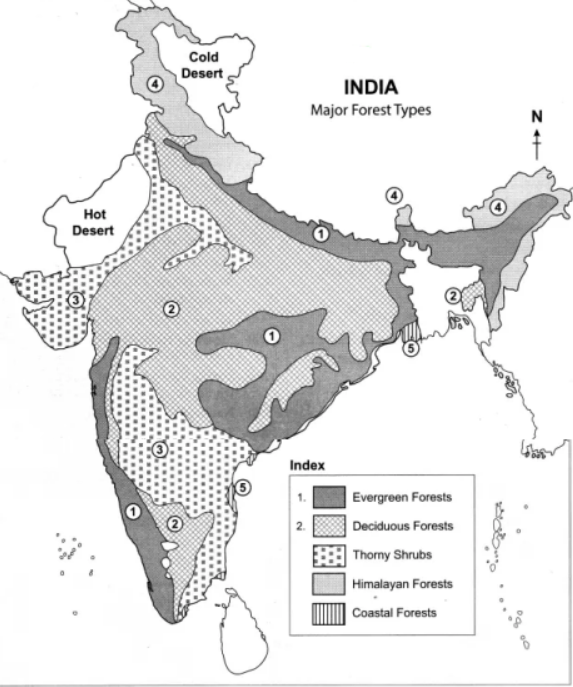
- India is home to several types of natural vegetation, including:
- Tropical Evergreen Forest: Found in areas with high rainfall and humidity, such as the Western Ghats and northeastern India. This forest is characterized by tall trees with a dense canopy and a rich undergrowth of shrubs and ferns.
- Tropical Deciduous Forest: Found in areas with a dry season and found in central and northern India. Trees in this forest shed their leaves during the dry season and regrow them during the rainy season.
- Tropical Thorn Forest: Found in arid and semi-arid regions, such as the Thar Desert. This forest is characterized by drought-resistant trees and shrubs with deep roots to tap into underground water sources.
- Montane Forest: Found in the mountain regions of the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats, and the Himalayas. This forest is characterized by tall trees with a dense canopy and a rich undergrowth of shrubs and ferns.
- Mangroves: Found in the coastal areas of India and are characterized by salt-tolerant trees and shrubs. Mangroves serve as a habitat for various species of fish, crustaceans, and birds, and protect coastal areas from erosion and storm surges.
- Littoral and Swamp Forest: Found along the coasts and in low-lying areas with stagnant or slow-moving water, such as the Sundarbans. This forest is characterized by tall trees adapted to growing in waterlogged soil.
- Mangroves are considered promising vegetation. They provide numerous ecological, economic and social benefits such as:
- Biodiversity: Mangroves are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else in the world.
- Coastal protection: Mangroves help to protect coastlines from storm surges, erosion and tsunamis.
- Carbon sequestration: Mangroves are able to store large amounts of carbon, making them important in mitigating climate change.
- Fisheries: Mangroves serve as important nursery habitats for many commercially important fish species.
- Livelihoods: Mangroves provide livelihoods for local communities through fishing, tourism and non-timber forest products.
Conclusion
India is a country with a rich and diverse landscape of natural vegetation, which supports a wide range of plant and animal species and plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of the region. The different types of vegetation in India, including tropical evergreen forests, tropical deciduous forests, tropical thorn forests, montane forests, mangroves, and littoral and swamp forests, are all important sources of livelihood for local communities. Mangroves, in particular, are considered promising vegetation, providing numerous ecological, economic, and social benefits such as biodiversity, coastal protection, carbon sequestration, fisheries, and livelihoods.
Answer 2
Approach
- Start your answer with writing about major factors of soil formation.
- Discuss the measures that conserve soil from being degraded.
- Write a holistic and appropriate conclusion.
Introduction
- Soil formation is a complex and ongoing process that is influenced by a variety of physical, chemical, and biological factors.
- These factors interact to create the rich and diverse array of soils found across the world, each with its own unique characteristics and properties.
- Understanding the major factors of soil formation is essential for understanding the functioning of ecosystems and the productivity of agricultural lands.
- Some of the key factors that play a role in soil formation include the type of parent material, climate, topography, organisms, time, and human activities.
- By examining the interplay between these factors, we can gain a deeper understanding of the processes that shape the soil and the crucial role it plays in supporting life on Earth.
Body
- Soil formation is a complex process that is influenced by several factors, including:
- Parent material: The type of rock or mineral from which the soil originates plays a major role in determining its characteristics and fertility.
- Climate: The climate of an area, including temperature, precipitation, and wind, affects the rate and type of soil formation.
- Topography: The physical features of an area, such as slope, elevation, and drainage, affect the movement of water and sediment, which in turn affects soil formation.
- Organisms: Soil-forming organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, play a crucial role in breaking down and transforming parent material into soil.
- Time: Soil formation is a slow process that takes place over thousands of years, as physical and biological processes interact to transform parent material into soil.
- Human activities: Human activities, such as deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization, can greatly affect soil formation by altering the balance of physical and biological processes.
- Soil degradation is a serious issue in India and can have severe impacts on agricultural productivity, biodiversity, and human well-being. To mitigate soil degradation, the following steps can be taken:
- Conservation tillage: Adopting conservation tillage practices, such as reduced tillage or no-till farming, can help to reduce soil erosion and improve soil structure.
- Crop rotation: Implementing crop rotation systems can help to reduce soil degradation by preventing the buildup of pests and pathogens, improving soil fertility, and reducing the risk of soil erosion.
- Cover crops: Using cover crops can help to prevent soil erosion and improve soil health by adding organic matter and protecting the soil from the effects of rainfall and wind.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes can help to reduce soil degradation by improving soil structure, fertility, and water-holding capacity.
- Soil conservation measures: Implementing soil conservation measures, such as terracing, contour farming, and building check dams, can help to reduce soil erosion and improve soil health.
- Sustainable land use practices: Adopting sustainable land use practices, such as reducing overgrazing and deforestation, can help to reduce soil degradation and improve soil health.
- Sustainable water management: Implementing sustainable water management practices, such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation systems, can help to reduce soil degradation and improve soil fertility.
- Soil health management: Implementing soil health management practices, such as regular soil testing and the use of organic fertilizers, can help to improve soil fertility and reduce soil degradation.
Conclusion
Soil degradation is a major challenge in India and can have serious impacts on agricultural productivity, biodiversity, and human well-being. Addressing soil degradation requires a multi-faceted approach that involves the implementation of conservation tillage practices, crop rotation systems, cover crops, agroforestry, soil conservation measures, sustainable land use practices, sustainable water management, and soil health management. By taking these steps, we can help to mitigate soil degradation in India and improve the health and productivity of agricultural lands, which is essential for ensuring food security and human well-being in the future.