-
16 Jun 2025
GS Paper 1
Indian Heritage & Culture
Day 1: Discuss the significance of conferring classical status on languages like Pāli and Prakrit for India’s linguistic diversity and civilizational identity. (150 words)
Approach :
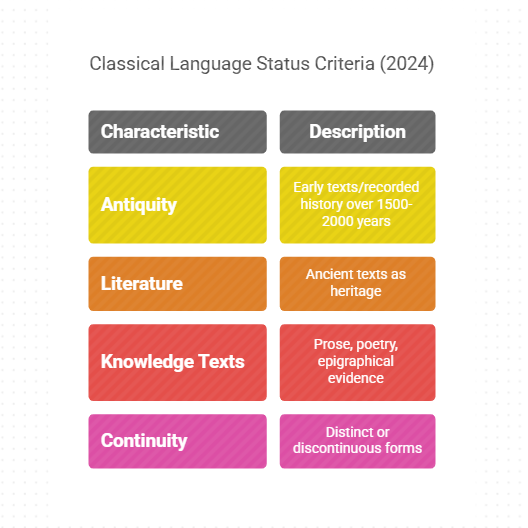
- Begin with a brief description of the Classical Language.
- Outline the criteria for classical status.
- Explain the significance of conferring Classical Status to Pāli and Prakrit.
- Conclude with contemporary relevance.
Introduction
Recently, the government of India conferred the status of Classical Language to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages. The Classical Languages serve as a custodian of India’s profound and ancient cultural heritage, embodying the essence of each community’s historical and cultural milestones.
Body :
Significance for Linguistic Diversity
- Preservation of Vernacular Intellectual Traditions :
- Pāli and Prakrit represent non-Sanskritic literary traditions, offering a glimpse into the language of the masses during ancient times.
- Pāli Canon (Tipiṭaka), composed around the 3rd century BCE, is the foundational scripture of Theravāda Buddhism, containing philosophical discourses, monastic codes, and ethical teachings.
- Prakrit literature, like Gāhā Sattasaī (1st century BCE), reflects themes of love, nature, and daily life, indicating a rich secular tradition.
- Linguistic Inclusivity
- Recognition of these languages protects India’s multilingual heritage, moving beyond a Sanskrit-dominated narrative.
- It validates the linguistic expressions of Buddhist and Jain communities, many of whom still use Pāli and Prakrit in religious contexts.
- Jain Agamas, composed in Ardha-Māgadhī Prakrit, are central to Jain philosophy and ritual.
- Academic and Cultural Revival
- Classical status encourages scholarly research, translation of ancient texts, and integration into academic curricula.
- Institutes like Nav Nalanda Mahavihara and Jain Vishva Bharati are engaged in the revival of these languages.
Significance for Civilizational Identity
- Spiritual Pluralism
- Both languages are pillars of India’s diverse philosophical traditions—Pāli for Buddhism and Prakrit for Jainism—promoting values like non-violence, detachment, and compassion.
- Cultural Continuity and National Identity
- Ashokan inscriptions in Prakrit script provide invaluable evidence of Dhamma propagation and administrative policy.
- These languages bridge the ancient and modern, ensuring the continuity of civilizational wisdom.
- Global Revival of Indian Thought: The recognition of Pāli and Prakrit languages fosters renewed global interest in Indian philosophical traditions.
- Leaders like the Dalai Lama actively promote the Pāli Canon, highlighting its contemporary ethical and spiritual relevance.
- Pāli connects India to Buddhist-majority nations like Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Thailand, strengthening cultural diplomacy.
Conclusion
Granting classical status to Pāli and Prakrit is not just about language preservation—it is about reviving civilizational consciousness, promoting inclusive linguistic identity, and showcasing India's plural spiritual heritage to the world.