-
03 Jul 2025
GS Paper 2
Polity & Governance
Day 16: "Parliament debates, but committees deliberate." Examine the contribution of the committee system to India's legislative process. (150 words)
Approach :
- Briefly introduce the parliamentary committee system.
- Examine the contribution of the committee system.
- Highlight challenges and conclude with a suitable way forward.
Introduction:
Parliament is the supreme law-making body in a democracy, where elected representatives debate issues of public concern. However, due to time constraints, political polarization, and limited subject expertise, parliamentary debates often remain broad. This is where parliamentary committees play a vital role—they deliberate in depth, examine technical details, seek expert opinions, and perform a legislative vetting function
Body
Contribution to the Legislative Process
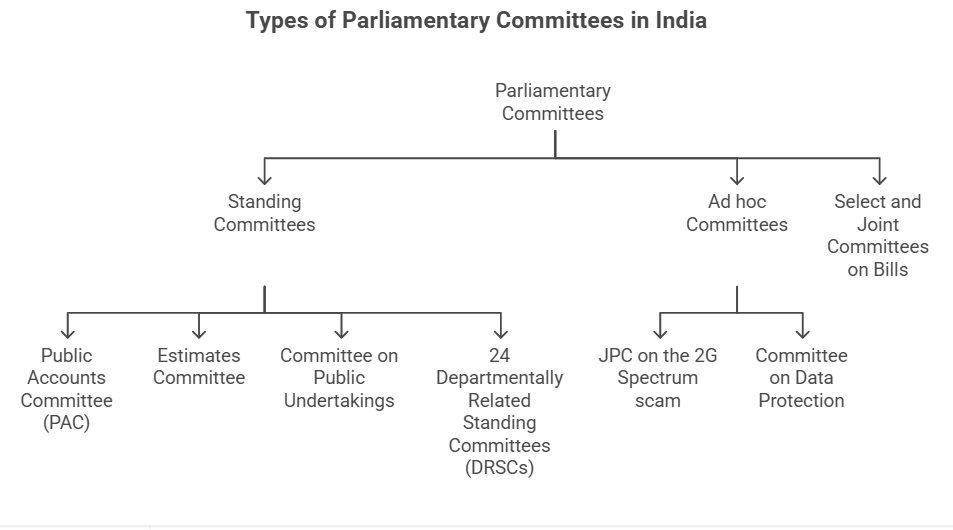
- Detailed Scrutiny of Legislation: Committees examine bills clause by clause, suggesting amendments and improvements.
- The Data Protection Bill was extensively reviewed by the Joint Parliamentary Committee before its reintroduction in Parliament.
- Strengthening Executive Accountability: Financial committees such as the Public Accounts Committee (PAC) scrutinize CAG reports and government spending.
- PAC's probe into the 2G spectrum allocation was critical in exposing irregularities.
- Depoliticized and Informed Deliberations: Committees work beyond the adversarial atmosphere of the House, fostering cross-party consensus and rational debate.
- Expertise and Public Consultation: They call upon subject experts, bureaucrats, and stakeholders, thus enhancing legislative competence.
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Health consulted experts during the COVID-19 pandemic to review government responses.
- Budgetary Oversight: Committees assess demands for grants and policy outcomes, increasing fiscal responsibility.
- The Estimates Committee evaluates how government funds are allocated and spent.
- Year-Round Functioning: Committees operate even when Parliament is not in session, ensuring continuity and sustained policy engagement.
Limitations and Challenges
- Non-binding nature of recommendations.
- Bypassing of committees for key Bills like the Farm Laws (2020), UAPA (2019).
- Low attendance and lack of expertise among members.
- Delayed reports and poor follow-up by the executive.
Conclusion :
Parliamentary committees function as the "think tanks" and "workshops" of legislation, ensuring that political debates translate into policy depth. As former Speaker Somnath Chatterjee aptly noted, “Without committees, Parliament would be reduced to a public forum for speeches, not a forum for law-making.” Strengthening the committee system is key to robust, participatory, and informed law-making in Indian democracy.