Indian Economy
Shift From Physical to Digital Gold
- 14 Nov 2023
- 14 min read
For Prelims: Shift From Physical to Digital Gold, Gold Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), Gold Mutual Funds and Sovereign Gold Bonds, Real Estate, Gold Monetisation Scheme.
For Mains: Shift From Physical to Digital Gold, Investment models, Capital Market
Why in News?
- In recent Years, Gold Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), Gold Mutual Funds and Sovereign Gold Bonds have become very popular over Physical gold, which comes with its own challenges, especially regarding its storage and safety.
How is Gold Linked With Indian Households?
- Weightage of Gold with Indian Households:
- As per Jefferies report, 15.5% of Total Indian Household Assets as of March 2023 are in Gold.
- Jefferies, a US based investment banking and capital markets firm, provides insight, expertise and execution to investors, companies and governments in the Americas, Europe and the Middle East and Asia.
- Gold’s share is second only to Real Estate which accounts for 50.7%.
- Bank deposits (14%), Insurance funds (5.9%), Provident & Pension funds (5.8%), Equities (4.7%) and Cash (3.4%) make up the rest.
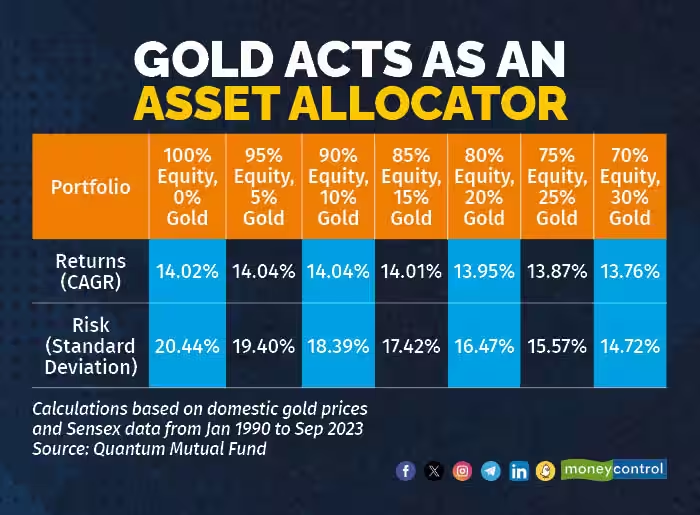
- With a Quantum Mutual Fund study concluding that a 10-15% portfolio allocation to gold is ideal from a risk-return perspective, it seems that Indians, with their affinity for gold, have got it right.
- The 10-15% allocation allows investors to lower risk without impacting overall portfolio returns.
- As per Jefferies report, 15.5% of Total Indian Household Assets as of March 2023 are in Gold.
- Shift from Physical to Digital Avenues:
- Traditionally Indians have saved in gold by buying small jewellery or gold bars and coins which are later converted to larger wearables at opportune times like weddings or liquidated in times of financial needs.
- While bars and coins are very liquid, their purity is not always guaranteed. They have storage costs and come with issues of retailer mark-ups and lower resale value.
- But with changing demographics, greater access to banking facilities, explosion of the digital economy, and increasing awareness about financial investment avenues, consumer preference is slowly moving away from physical gold to digital avenues.
- Due to which Gold ETFs and SGBs as digital gold investment avenues in the country today are seeing growing acceptance.
- Traditionally Indians have saved in gold by buying small jewellery or gold bars and coins which are later converted to larger wearables at opportune times like weddings or liquidated in times of financial needs.
What are Digital Avenues for Gold Investment?
- Gold ETF:
- About: Gold ETF, which aims to track the domestic physical gold price, are passive investment instruments that are based on gold prices and invest in gold bullion.
- Gold ETFs are units representing physical gold which may be in paper or dematerialised form.
- One gold ETF unit is equal to 1 gram of gold and is backed by physical gold of very high purity.
- They combine the flexibility of stock investment and the simplicity of gold investments.
- Gold ETFs are units representing physical gold which may be in paper or dematerialised form.
- Advantages: There is complete transparency on the holdings of an ETF.
- Gold ETFs have much lower expenses as compared to physical gold investments.
- No wealth tax, no security transaction tax, no VAT and no sales tax is levied on ETFs.
- There is no fear of theft as ETFs are safe and secure as units held in the Demat Account of the holder.
- The Shift to Digital Gold: The number of investors in Gold ETFs has increased from close to 4.61 lakh in January 2020 to 48.06 lakh in September 2023.
- About: Gold ETF, which aims to track the domestic physical gold price, are passive investment instruments that are based on gold prices and invest in gold bullion.
- Gold Mutual Funds:
- Gold mutual funds are professionally managed funds that function by pooling money from multiple investors to invest in a variety of gold-related assets, such as gold mining stocks, bullion, and mining companies.
- Like Gold ETFs, they allow investors’ exposure to the gold market without having to invest in physical gold.
- Sovereign Gold Bonds:
- About: The first SGB scheme was launched by the Government in November 2015, under Gold Monetisation Scheme with an objective to reduce the demand for physical gold and shift a part of the domestic savings - used for the purchase of gold - into financial savings.
- Key Details:
| Item | Details |
| Issuance | Issued by the Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Government of India. |
| Eligibility | SGBs will be restricted for sale to resident individuals, HUFs (Hindu Undivided Family), Trusts, Universities and Charitable Institutions. |
| Tenor | The tenor of the SGB will be for a period of eight years with an option of premature redemption after 5th year. |
| Minimum size | Minimum permissible investment will be One gram of gold. |
| Maximum limit | The maximum limit of subscription shall be 4 Kg for individuals, 4 Kg for HUF and 20 Kg for trusts and similar entities per fiscal year (April-March) notified by the Government from time to time. |
| Joint holder | In case of joint holding, the investment limit of 4 Kg will be applied to the first applicant only. |
| Issue price | Price of SGB will be fixed in Indian Rupees on the basis of a simple average of the closing price of gold of 999 purity, published by the India Bullion and Jewellers Association Limited. |
| Interest rate | The investors will be compensated at a fixed rate of 2.50% per annum payable semi-annually on the nominal value (face value or stated value). |
| Collateral | The SGBs can be used as collateral for loans. |
| Tax treatment | The interest on SGBs shall be taxable as per the provision of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The capital gains tax arising on redemption of SGB to an individual is exempted. |
| Tradability | SGBs shall be eligible for trading. |
| SLR eligibility | SGBs obtained by banks through the pledge process will be considered as part of their Statutory Liquidity Ratio requirements. |
- Digital Gold:
- This is one of the types of Digital Gold investment where one can buy gold in small denominations online.
- It allows investors to own a portion of physical gold that is stored in secure vaults.
- This investment also allows an investor exposure to the gold market without having to worry about the challenges that accompany physical gold investments.
- Many digital payment platforms and investment apps facilitate investments in Digital Gold.
What is an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)?
- An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a basket of securities that trade on an exchange, just like a stock.
- ETF reflects the composition of an Index, like BSE Sensex. Its trading value is based on the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the underlying stocks (such as shares) that it represents.
- ETF share prices fluctuate all day as it is bought and sold. This is different from Mutual Funds that only trade once a day after the market closes.
- An ETF can own hundreds or thousands of stocks across various industries, or it could be isolated to one particular industry or sector.
- Bond ETFs are a type of ETFs which may include government bonds, corporate bonds, and state and local bonds—called municipal bonds.
- A bond is an instrument that represents a loan made by an investor to a borrower (typically corporate or governmental).
- Besides being cost efficient, ETFs offer a diversified investment portfolio to investors.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1 Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
- Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
- Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- Bond is an instrument to borrow money. A bond could be issued by a country’s government or by a company to raise funds.
- Bond yield is the return an investor realizes on a bond. The mathematical formula for calculating yield is the annual coupon rate divided by the current market price of the bond.
- Movements in yields depend on trends in interest rates, it can result in capital gains or losses for investors.
- A rise in bond yields in the market will bring the price of the bond down.
- A drop in bond yield would benefit the investor as the price of the bond will rise, generating capital gains.
- Fed tapering is the gradual reduction in the bond buying program of the US Federal Reserve. So, any actions of the United States Federal Reserve impact the bond yield in India. Hence, 1 is correct.
- The actions of the RBI plays a crucial role in determining the yield of government bonds. The sovereign yield curve has a special significance for monetary policy in influencing a wide array of interest rates in the economy. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Inflation and short-term interest rates also influence the yield of government bonds. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q.2 With reference to ‘IFC Masala Bonds’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the statements given below is/ are correct? (2016)
- The International Finance Corporation, which offers these bonds, is an arm of the World Bank.
- They are rupee-denominated bonds and are a source of debt financing for the public and private sector.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- The World Bank Group, which is a vital source of financial and technical assistance to developing countries, consists of five distinct yet complementary organizations, viz.,
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD),
- International Development Association (IDA),
- International Finance Corporation (IFC), hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA),
- International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID).
- Masala Bonds are rupee-denominated borrowings issued by Indian entities in overseas markets. Masala means ‘spices’ and the term was used by International Finance Corporation (IFC) to popularise the culture and cuisine of India on foreign platforms. The objective of Masala Bonds is to fund infrastructure projects in India, fuel internal growth via borrowings and internationalize the Indian currency. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q.3 What is/are the purpose/purposes of Government’s ‘Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme’ and ‘Gold Monetization Scheme’? (2016)
- To bring the idle gold lying with Indian households into the economy.
- To promote FDI in the gold and jewellery sector.
- To reduce India’s dependence on gold imports.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)