Sharda River | 17 Jun 2025
Why in News?
Several people drowned after being caught in the strong currents of the Sharda River near Devraghat in the Sitapur district.
Key Points
- About the Sharda River:
- Origin and Course:
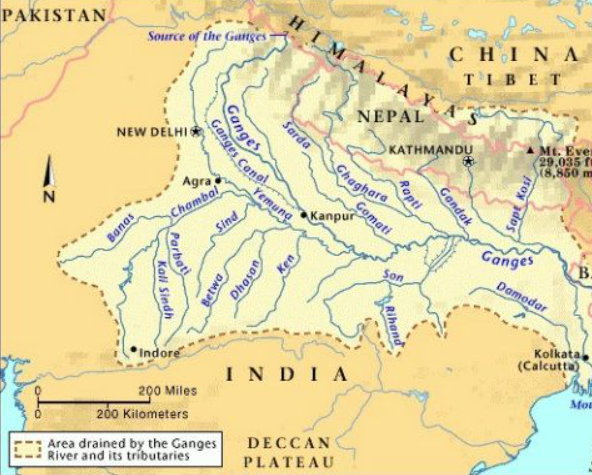
- The Sharda River, also known as the Kali River in its upper reaches, originates in Uttarakhand.
- It rises in the Great Himalayas, on the eastern slopes of the Nanda Devi massif.
- Flowing generally south-southwest, the river forms the boundary between Uttarakhand (India) and western Nepal.
- After descending from the mountains, it enters the Indo-Gangetic Plain at Barmdeo Mandi in Nepal.
- As the river widens above the Sarda Barrage, it is referred to as the Sarda River.
- After crossing into India, the Sarda River flows southeastward through northern Uttar Pradesh.
- It eventually joins the Ghaghara River southwest of Bahraich, covering a total length of approximately 480 km (300 miles).
- Major Tributaries:
- Key tributaries of the Sarda River are Dhauliganga River, Goriganga River, Sarju River.
- Sarda Barrage and Canal System:
- The Sarda Barrage, located near Banbasa in Uttarakhand, plays a significant role in irrigation.
- It serves as the origin of the Sarda Canal, completed in 1930, which is one of northern India’s longest irrigation canals.
- Origin and Course:
Ghaghara River
- Origin and Upper Course:
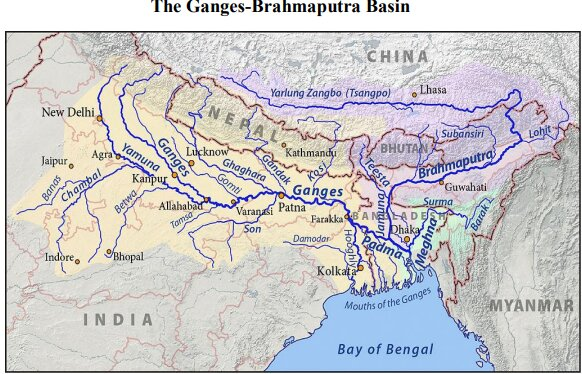
- The Ghaghara River is a major left-bank tributary of the Ganges River.
- It originates as the Karnali River in the high Himalayas of the southern Tibet Autonomous Region in China.
- Flowing southeast through Nepal, it descends from the mountains and cuts across the Siwalik Range.
- Formation of the River:
- After crossing the Siwalik Range, the river splits into two branches.
- These branches reunite south of the India-Nepal border, forming what is known as the Ghaghara River.
- Key Tributaries:
- Major tributaries that join the Ghaghara from the north include Kuwana River, Rapti River, Little Gandak River.
- These tributaries contribute significantly to the river’s volume and have helped shape the extensive alluvial plains of northern Uttar Pradesh.
- In its lower reaches, the Ghaghara is also known by other names Sarju River, Deoha.
- It was referred to as Sarabos by the 2nd-century Greek geographer Ptolemy.