Perspective: Declining Mortality Rates | 10 Oct 2022
For Prelims: Sample Registration System (SRS), Registrar General of India (RGI), Mortality Rates.
For Mains: Findings of the Report, Factors Exacerbate Mortality Rates, Steps that can be taken.
Why in News?
As per the recently released Sample Registration System (SRS) Statistical Report, 2020 by the Registrar General of India (RGI), the country has been witnessing a progressive reduction in IMR (Infant Mortality Rate), U5MR (Under 5 Mortality Rate) and NMR (Neonatal Mortality Rate) since 2014 towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) targets by 2030.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Under 5 Mortality Rate: U5MR for the country has shown a significant decline of 3 points (Annual Decline Rate: 8.6%) from 2019 (32 per 1000 live births in 2020 against 35 per 1000 live births in 2019). It varies from 36 in rural areas to 21 in urban areas.
- U5MR for females is higher (33) than for males (31). There has been a decline of 4 points in male U5MR and 3 points in female U5MR during the corresponding period.
- The highest decline of U5MR is observed in the states of Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka.
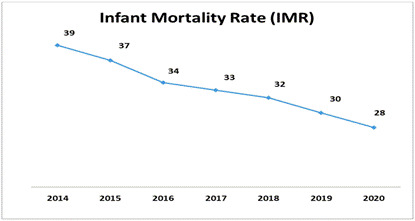
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): IMR also registered 2-point decline to 28 per 1000 live births in 2020 from 30 per 1000 live births in 2019 (Annual Decline Rate: 6.7%).
- The Rural-Urban difference has narrowed to 12 points (Urban 19, Rural-31).
- No gender differential has been observed in 2020 (Male -28, Female - 28).
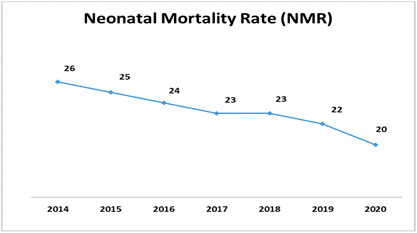
- Neonatal Mortality Rate: It has also declined by 2 points from 22 per 1000 live births in 2019 to 20 per 1000 live births in 2020 (Annual Decline Rate: 9.1%). It ranges from 12 in urban areas to 23 in rural areas.
- Status of SDG Targets:
- Six States/ UT have already attained SDG target of NMR (<=12 by 2030): Kerala (4), Delhi (9), Tamil Nadu (9), Maharashtra (11), Jammu & Kashmir (12) and Punjab (12).
- Eleven States/UTs have already attained SDGs target of U5MR (<=25 by 2030): Kerala (8), Tamil Nadu (13), Delhi (14), Maharashtra (18), J&K (17), Karnataka (21), Punjab (22), West Bengal (22), Telangana (23), Gujarat (24), and Himachal Pradesh (24).
What is Sample Registration System?
- The SRS is a demographic survey for providing reliable annual estimates of infant mortality rate, birth rate, death rate and other fertility and mortality indicators at the national and sub-national levels.
- It was initiated on a pilot basis by the Registrar General of India in a few states in 1964-65, it became fully operational during 1969-70.
- The field investigation consists of a continuous enumeration of births and deaths in selected sample units by resident part-time enumerators, generally Anganwadi workers & teachers, and an independent survey every six months by SRS supervisors. The data obtained by these two independent functionaries are matched.
What is the Registrar General of India?
- Registrar General of India was founded in 1961 by the Government of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It arranges, conducts and analyses the results of the demographic surveys of India including Census of India and Linguistic Survey of India.
- The position of Registrar is usually held by a civil servant holding the rank of Joint Secretary.
What has been a Game Changer during this Time?
- As observed, for the last few years the National Rural Health Mission and the National Health Mission (NHM) has been a game changer for the country in terms of mortality reductions for U5MR or infant mortality or neonatal mobility and maternal mortality rate also.
- About NHM:
- NHM was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission (Launched in 2005) and the National Urban Health Mission (Launched in 2013).
- The main programmatic components include Health System Strengthening in rural and urban areas for - Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), and Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases.
- The NHM envisages the achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality healthcare services that are accountable and responsive to people's needs.
- About NHM:
- Support to States & Union Territories (UT):
- Health Facilities:
- NHM support is provided to States/UTs for setting up new facilities as per norms and upgradation of existing facilities for bridging the infrastructure gaps based on the requirement posed by them.
- Health Services:
- NHM support is also provided for the provision of a range of free services related to maternal health, child health, adolescent health, family planning, universal immunisation programme, and for major diseases such as Tuberculosis, vector-borne diseases like Malaria, Dengue and Kala Azar, Leprosy etc.
- Health Facilities:
What are the Major Initiatives Supported Under NHM?
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK).
- Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK).
- Implementation of Free Drugs and Free Diagnostics Service Initiatives.
- PM National Dialysis Programme.
- Implementation of National Quality Assurance Framework in all public health facilities.
- Mobile Medical Units (MMUs) & Tele-consultation services are also being implemented to improve access to healthcare particularly in rural areas.
- Ayushman Bharat.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY).
What Factors Exacerbate Mortality Rates?
- Malnutrition: According to the National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5) the incidence of anaemia in under-5 children (from 58.6 to 67%), women (53.1 to 57%) and men (22.7 to 25%) has worsened in all States of India (20%-40% incidence is considered moderate).
- Non-institutional Deliveries: Whether the child is born at home or in a facility also determines the infant's survival rate. Infection risks are high in the case of a non-institutional birth.
- Although the share of India's institutional deliveries increased to 88.6% in 2019-2021 (NFHS-5) from 40.8 % in 2005-06 (NFHS 3), it is still much lesser when compared to the developed countries.
- Lack of Immunity and Low vaccine Compliance level: Pneumonia, Prematurity, low birth weight, Diarrhoeal diseases, Neonatal infections, Birth asphyxia, etc. are also the reasons that lead to infant deaths.
- Lack of Education: Maternal education increases the chances of mothers being aware of different health issues and thus taking the correct and appropriate steps toward preventing such issues.
- Age of the Mother: At the time of birth, the age of the mother plays an important role. For example, there exists an inverse relationship between the age of mothers and the incidence of anaemia in children. There are evidence related to the fact that the children of younger mothers are more anaemic.
What can be the Way Forward?
- Infrastructure & Quality Improvement: Infrastructure and quality of hospitals also play a crucial role to reduce further the mortality rates. Quality improvement seeks to achieve predictable results and improve outcomes in terms of healthcare developments.
- Urban-Rural Disparities: There is a need to bring out the systemic changes that are feasible in every part of the country, from the urban to the rural areas that can reduce the socio-economic stress in these areas.
- Political Will: The availability of funds (from Centre) as well as its judicious use by the States is vital in effective implementation of the framed policies and overhauling of the required health infrastructure.
- Integrated Approach: Concerned ministries can collaborate with each other to ensure better coordination, convergence and holistic integration of different schemes.
- Need to Focus on all the Indicators: There is an urgent requirement to look at the situations from the facets of each and every indicator and monitor them very carefully so that the world does not lose any mother or child unnecessarily.
- Private Player Participation: The involvement of private players is not an urgent requirement but their sincere engagement and complementing role to the state can ease the burden of the government. The role of the state in delivering health to its people cannot be overemphasised.
What are the Key Terms?
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): It is defined as the ‘number of deaths of children under the age of 1 year per 1000 live births for a given year.
- The country’s average IMR stands at 32 per 1,000 live births which include an average 36 deaths for rural and 23 for urban areas.
- Under 5 Mortality Rate (U5MR): The under-five mortality rate refers to the probability of dying before age of 5 years per 1,000 newborns.
- Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR): It is defined as the 'number of deaths during the first 28 completed days of life per 1,000 live births in a given year or period'.
UPSC Civil services Examination, Previous Year’s Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘’Empowering women is the key to control the population growth.’’ Discuss. (2019)