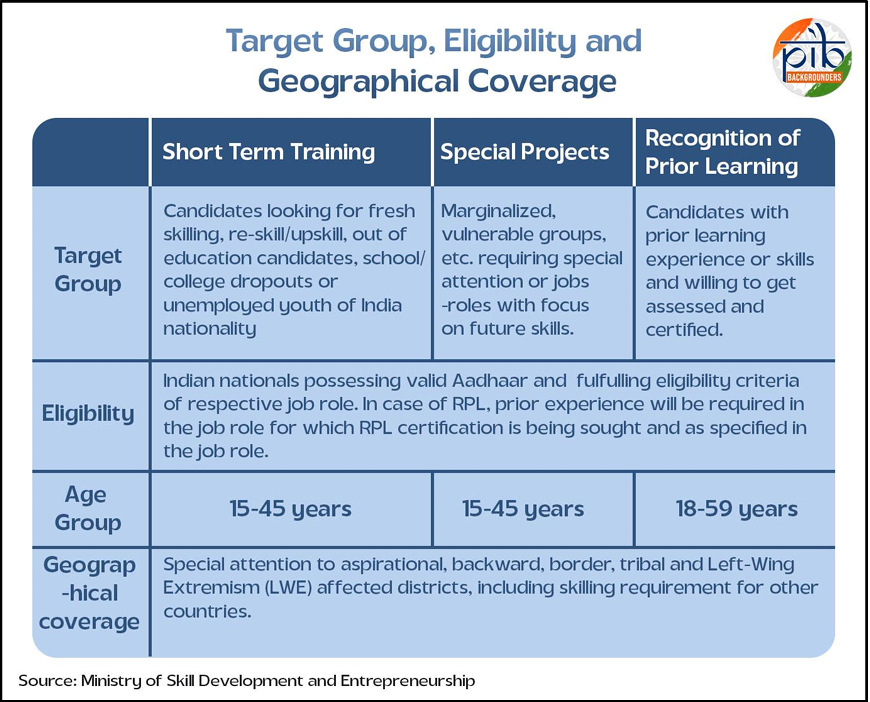
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, National Skills Qualification Framework , Skill India Digital Hub,
For Mains: Skill India Mission (SIM), Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana and its Significance,Skill Development
Why in News?
India’s flagship skilling programme, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), is under scrutiny after the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) blacklisted 178 training partners (TPs) and training centres (TCs) over serious irregularities such as fake trainees, forged documents, and non-existent centres.
What are the Issues Highlighted Regarding PMKVY?
- Widespread Corruption & Fund Misuse: Several Training Partners inflated bills, diverted funds, and manipulated records.
- Many Training Centres existed only on paper, with no real training activity.
- Attendance records were manipulated to show students who never attended the programme.
- Poor Monitoring And Transparency: Oversight has been inconsistent, National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) refused to disclose details of defaulting centres under Right to Information Act 2005 citing confidentiality.
- In many cases, Training Partner and Training Centre identities did not match, weakening accountability.
- State agencies reported lack of clarity on inspections, documentation, and next steps, slowing corrective action.
- Training Disruptions: With 178 TPs/TCs blacklisted (highest in UP, then Delhi, MP, Rajasthan), training in several areas came to a standstill.
- Skill–Industry Mismatch: Training programs often fail to align with current industry requirements due to weak collaboration between training institutions and employers, insufficient labour market forecasting, and inadequate practical exposure for trainees.
- Infrastructure and Accessibility: Many training centres, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, suffer from inadequate facilities, limited access to digital tools, and poor internet connectivity.
- Financial constraints and logistical challenges further restrict participation and outreach.
What is Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)?
- About: PMKVY is the flagship skill-development scheme of the MSDE, launched in July 2015. It aims to provide free short-duration training, certify skills through Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), and enhance youth employability across India.
- Training is delivered through approved Training Centres under a standard quality framework aligned with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- Under the Scheme, every certified candidate is given a reward of Rs. 500 for clearing the exam as encouragement.
- It has trained candidates across sectors like manufacturing, construction, healthcare, IT and retail, and has expanded to future-focused areas such as Artificial Intelligence, Drone Technology, Robotics, Mechatronics and Internet of Things (IoT).
- Inclusivity: Inclusivity was a key pillar of the scheme with 45% of the candidates being women and a significant share coming from Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
- Progress: Over the years, more than 1.63 crore candidates have been trained under PMKVY in diverse sectors, such as manufacturing, construction, healthcare, IT, electronics, retail and more.
- PMKVY 1.0: During its pilot phase in 2015-16, 19.85 lakh candidates were trained.
- PMKVY 2.0 (2016–20): 1.10 Crore candidates were trained/oriented.
- PMKVY 3.0 (2021–22): 7.37 lakh trained.
- PMKVY 4.0 (2022–26): As of July 2025, over 25 lakh candidates have been trained under this phase.
- Innovative initiatives by PMKVY:
- Special Projects: Trained Bru-tribe youth, jail inmates, and women under PANKH to expand skilling access for marginalised groups.
- Traditional Crafts & Upskilling: Supported Namda artisans and weavers in J&K and Nagaland through targeted RPL training.
- Mainstreaming Skilling: Integrated skill development into major national missions like PM Surya Ghar and Vibrant Villages.
- Covid-19 Response: Provided crash-course training to over 1.2 lakh health workers during the pandemic.
- Skill Hub Initiative: Used schools and colleges as vocational training hubs under NEP 2020 (National Education Policy).
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL): Certified informal workers’ existing skills to improve employability.
- Skill India Digital Hub: Introduced the Skill India Digital Hub for digital tracking and Aadhaar-based verification.
- Academic Mobility: Linked PMKVY qualifications with the Academic Bank of Credits for transferable learning credits.
Skill India Mission (SIM)
- About: The SIM provides skilling, reskilling, and upskilling through a nationwide network of training centres.
- In February 2025, the government restructured the mission for 2022–23 to 2025–26, merging PMKVY 4.0, Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and the Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme into a single Central Sector Scheme.
- JSS: Provides vocational training to non-literates, neo-literates, and school dropouts (15–45 years), with a focus on women, SC/ST/OBC, and minorities; More than 26 people lakh trained (2018–24).
- NAPS: Supports apprenticeships by subsidising stipends. It includes basic and on-the-job training.
- 43.47 lakh apprentices engaged across 36 States/UTs through 51,000 establishments as of May 2025.
What Measures Can Enhance the Effective Implementation of PMKVY?
- Strengthen Monitoring & Accountability: Use real-time digital attendance, geo-tagged centres, and biometric verification to curb fake enrolments.
- Link performance ratings of TPs with continuation of funding and empanelment.
- Incentivise TPs based on placement outcomes, not enrolment numbers.
- Support candidates with post-placement tracking, transport allowances, and workplace counselling.
- Promote Regional & Sectoral Customisation: Tailor courses to match local economic needs, such as agro-processing, tourism, or green energy.
- Encourage state-specific Skill Plans to reflect labour supply and demand.
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Scale up the Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH) for training delivery, assessments, credentialing, and job matching.
- Integrate with ABC (Academic Bank of Credits) for portability of qualifications.
- Better Convergence: Link PMKVY with MUDRA, PM-Vishwakarma, and Start-Up India for credit and mentoring. Provide enterprise-management modules to help youth start micro-businesses.
Conclusion
PMKVY can unlock India’s demographic dividend only when skilling becomes demand-driven, industry-linked, and outcome-oriented. Strong oversight, industry-linked placements, digital systems, and inclusive access can help PMKVY translate training into real jobs and stronger livelihoods.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically evaluate Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) transition from enrolment-driven delivery to outcome-based skilling |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana?
PMKVY is the Government’s flagship scheme (2015) offering free short-term skill training and RPL certification to boost youth employability.
2. What is the Skill India Mission?
Skill India Mission is a nationwide effort to skill, reskill, and upskill youth through schemes like PMKVY, Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and the Jan Shikshan Sansthan to build a job-ready workforce.
3. What key challenges under PMKVY were flagged?
Fake centres, fake attendance, fund misuse, weak monitoring, poor transparency, and training disruption after 178 TPs/TCs were blacklisted.
4. What measures improve PMKVY effectiveness?
Biometric/geo-tagged attendance, third-party audits, outcome-linked payments, stronger industry ties, and transparent public dashboards.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)
Immunology Research in India
For Prelims: Biotechnology sector, Vaccine development, Immunological Research, Nobel Prize 2025, Health Sector Initiatives
For Mains: Public Health, Role of Immunology in Public Health and Disease Prevention, Significance of the 2025 Nobel Prize in Medicine, Immunotherapy Applications, India’s Immunology Research Ecosystem and Policy Initiatives
Why in News?
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded for discoveries concerning peripheral immune tolerance. This recognition once again places immunology at the heart of modern biomedical science and public health - an area increasingly relevant for India’s healthcare and research landscape.
What is Immunology?
- About:
- Immunology is the branch of biomedical science that studies the body’s immune system - its organs, cells, and molecules that protect against infection, disease, and foreign substances.
- It explores how the immune system identifies and neutralizes pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
- It also examines how this system sometimes malfunctions, leading to autoimmune diseases, allergies, cancers, or organ transplant rejections.
- Modern immunology forms the backbone of vaccine development, immunotherapies, and pandemic preparedness, directly impacting public health and global disease control.
- Need for Immunology Research:
- Healthcare burden: India faces a dual burden of infectious diseases (communicable) and rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
- Immunology links both domains: e.g., vaccines against infectious diseases, and immune-based therapies for cancers and autoimmune disorders.
- Vaccine and research capability: The pandemic highlighted how immunology underpins rapid vaccine development, public health responses, and hence economic and social resilience.
- Innovation opportunity: With large population size, genetic diversity and unique disease patterns, India has the potential to contribute to global immunology research (e.g., population-specific vaccines, cheaper immunotherapies) if the infrastructure and human-capital are in place.
- Global health leadership: As global health becomes more important, countries that lead in immunology will shape future medical practice, supply chains, biotech and public health policy. India should not remain a consumer but become a producer of knowledge and technology.
- Healthcare burden: India faces a dual burden of infectious diseases (communicable) and rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Immunological Research
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT) – Funds immunology research projects and vaccine development programmes.
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) – Supports translational research in infectious and non-infectious immunological disorders.
- National Vaccine Policy (2011) and Mission COVID Suraksha (2020) – Encourage indigenous vaccine R&D and production.
- BIRAC (Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) – Promotes academia-industry collaboration in biotechnology and immunotherapy.
- National Institute of Immunology (NII) – A premier institute advancing research on immune system mechanisms, diseases, and vaccines.
- National Biopharma Mission – Aims to boost development of affordable biologics and next-generation therapeutics, including immunotherapies.
What are the Key Issues Impacting Immunological Research in India?
- Limited Immunology Education: Immunology and molecular biology receive limited emphasis in medical and undergraduate curricula. Only select institutes such as AIIMS, IISc, and NIBMG provide in-depth courses, creating a shortage of trained immunologists.
- Funding Gaps: Funding gaps persist as research grants are typically short-term (3-5 years), limiting long-term, high-risk immunology projects, with the ecosystem prioritizing quick results over in-depth scientific exploration.
- Fragmented Research Ecosystem: Collaboration between basic scientists, clinicians, and industry remains weak. Discoveries in institutions like IITs or IISERs often fail to progress to clinical validation due to the absence of structured translational frameworks.
- High Treatment Costs: Advanced immunotherapies, including CAR-T cell therapy, remain unaffordable for most Indians (₹30–40 lakh per dose).
- Brain Drain and Infrastructure Constraints: Inadequate high-end labs, limited BSL-3 facilities, and few stable academic positions drive skilled researchers abroad.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Lengthy and overlapping approval processes involving ICMR, DBT, and CDSCO delay immunology research and clinical trials. Lack of a unified biomedical regulatory authority increases compliance burdens and deters innovation.
- Weak Public Health Integration: While vaccination under Ayushman Bharat and NTEP is extensive, immune surveillance and regional immunogenomic data remain underused for predicting outbreaks or tailoring vaccines.
Way Forward
- Curriculum and Human Capital Development: Immunology must be strengthened in medical and life science education through revised National Medical Commission (NMC) guidelines.
- Laboratory-based learning should be incorporated using modern techniques such as Flow Cytometry and ELISA to provide hands-on skills.
- Regional Immunology Teaching Laboratories in major universities across India can serve as national training hubs to develop a strong scientific workforce.
- Research and Infrastructure Investment: 15-20% of life science research funding from agencies like DBT, ICMR, and DST should be allocated specifically to immunology, focusing on areas such as tuberculosis immunity, dengue, autoimmune disorders, and cancer resistance mechanisms.
- The establishment of Regional Immunology Research Centres and Biobanks will facilitate large-scale immunogenetic studies, advancing research in these critical areas.
- Translational Science and Innovation: Public-private partnerships should be encouraged through initiatives like BIRAC’s Translational Immunology Grant to develop low-cost vaccines and biosimilars.
- Policy and Global Integration: Immunological strategies should be embedded in the National Health Policy and Pandemic Preparedness Plan. Enhanced collaboration with WHO and global institutions will ensure India’s leadership in immunology research and application.
Conclusion
India stands at a pivotal moment, where advancing immunology can address both its unique healthcare needs and contribute to global medical progress. By strengthening its research infrastructure and fostering cross-disciplinary collaboration, India has the potential to become a leader in immunological innovation, ensuring that the benefits of these breakthroughs are felt both domestically and worldwide.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q.Discuss the growing significance of immunology in modern medicine and evaluate India’s preparedness to harness its potential for public health and biomedical innovation. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Immunology?
Immunology is the scientific study of the immune system’s structure, functions, and disorders, forming the foundation for vaccines, immunotherapies, and disease prevention.
2. What is Peripheral Immune Tolerance?
It is the mechanism by which regulatory T cells prevent the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues, maintaining immune balance and self-tolerance.
3. Why was the 2025 Nobel Prize awarded in Medicine?
Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi received it for discovering regulatory T cells and their role in maintaining peripheral immune tolerance.
4. How is India promoting immunology research?
Through initiatives like DBT, ICMR, NII, BIRAC, and the National Biopharma Mission, supporting vaccine R&D, immunotherapies, and public-private collaboration in biotechnology.
Diversification of India’s Export Markets
Why in News?
India’s exports are diversifying, with non-US markets like the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia helping balance out losses to the US, reflecting a successful trade diversification strategy.
- Despite a 12% drop in exports to the US, India’s merchandise exports grew 6.7% to USD 36.38 billion, reflecting resilient diversification.
- Export diversification expands a country’s products and markets to reduce dependence on a few partners, enhancing economic stability, trade resilience, and innovation.
What are the Key Trends in India's Export Diversification Strategy?
- Decline in US Exports: India’s exports to the US fell due to reduced demand and trade tensions, as tariffs rose from 10% to 50% between April–August 2025, reducing exports from USD 8.8 billion to 5.5 billion.
- Even tariff-free exports dropped 47% to USD 1.8 billion from USD 3.4 billion, though overall exports remain resilient through alternative markets.
- Rise of Non-US Markets: Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East have become key markets for India, importing pharmaceuticals, textiles, engineering products, and machinery.
- Marine exports rose 60% to China, Vietnam, and Thailand, Basmati rice exports to Iran grew six-fold, and tea exports expanded to the UAE, Iraq, and Germany.
- Government and Policy Initiatives: The Indian government has strategically implemented policies aimed at boosting exports to these non-US regions. Programs like the Foreign Trade Policy 2023 and Market Access Initiative (MAI) focus on strengthening trade ties with new partners, offering incentives, and easing logistics barriers.
What are the Key Factors Driving the Diversification of India’s Exports?
- Regional Free Trade Agreements (FTAs): India’s participation in various regional FTAs has been a crucial factor in diversifying its export base. FTAs with countries like the UAE, Japan, and South Korea have opened new avenues for trade.
- Supply Chain Management: India has emerged as a reliable alternative in China-plus-one strategies, attracting global companies and promoting value addition and diversification beyond traditional markets.
- Government Outreach: Identification of 40 key importing nations across Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that account for three-fourths of global textile and apparel demand. Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes boost competitiveness in manufacturing and exports across high-growth sectors.
- Long-Term Goals: India aims to reduce dependence on the US market and expand its global export footprint through diversification.
- The goal is to build resilient, sustainable trade systems aligned with Viksit Bharat 2047 and the vision of becoming a top 3 global exporter.
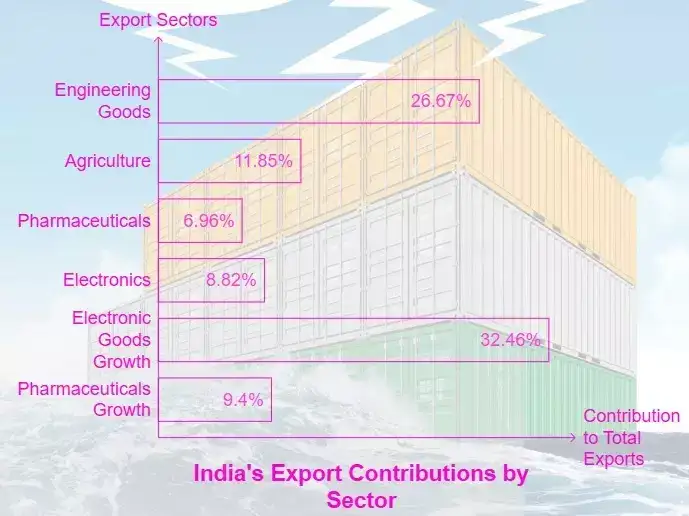
India's Export Basket (FY 2024-25)
- Engineering Goods: Largest contributor at 26.67%, totaling USD 116.67 billion. Key export destinations: US, UAE, Saudi Arabia, UK, Germany. Exports consistently above USD 100 billion since 2021-22.
- Agriculture & Allied Products: Contributed 11.85% to total exports, totaling USD 51.86 billion. Key commodities: spices, coffee, tea, tobacco, rice, fruits & vegetables, marine products.
- Major destinations for spices: China, US, UAE, Bangladesh, Thailand; coffee: Italy, Russia, Germany, UAE, Belgium, USA.
- Pharmaceuticals: India exports medicines to over 200 countries, continuing a trend of steady growth since 2014-15.
- Electronics: Computer hardware & peripherals doubled from USD 0.7 billion to USD 1.4 billion. Major export markets: UAE, US, Netherlands, UK, Italy.
Conclusion
While diversification shows promise, challenges persist — the US market’s high value remains hard to replace, and competition from China is strong. However, opportunities lie in building a resilient export economy and a potential US-India Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) aimed at boosting trade to USD 500 billion by 2030.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How have US tariff hikes impacted India’s export profile, and what strategies has India adopted to mitigate these effects? |
1. Why did India start its export diversification strategy?
India began diversifying exports after the US imposed 50% tariffs on Indian-origin goods, impacting key sectors like textiles, gems, and carpets.
2. Which countries have emerged as new destinations for Indian exports?
UAE, France, Japan, China, Vietnam, and Thailand have become major alternative markets for Indian exports.
3. How is the government facilitating export diversification?
By identifying 40 key importing countries, strengthening global supply chain integration, and promoting deep-tech and manufacturing exports.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)
India Demonstrates 500 km Quantum Key Distribution Network
Why in News?
In a landmark achievement under the National Quantum Mission (NQM), Startup QNu Labs demonstrated India’s first 500 km Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) network over existing optical fiber infrastructure.
- This strengthens India’s quantum capabilities and advances quantum-secure communication and cyber defense.
What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Network?
- About: QKD is a secure communication technology that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and share encryption keys between two parties, ensuring that the data exchanged cannot be intercepted or hacked — even by quantum computers.
- Its core promise is to detect the presence of any third party trying to eavesdrop on the key exchange.
- Core Principle: The strong security of QKD is based on two key quantum principles:
- No-Cloning Theorem: An unknown quantum state cannot be copied, so an eavesdropper cannot duplicate photons without changing them.
- Observer Effect: Measuring quantum particles disturbs them, meaning any attempt to spy on the key creates detectable changes.
- Functioning: QKD uses qubits (quantum bits) transmitted through optical fibers via total internal reflection to securely exchange encryption keys between two users.
- Unlike classical bits, qubits, encoded on photons, are highly sensitive to interference, and any eavesdropping disrupts them, enabling tamper-evident quantum encryption.
- QKD enables distant users to create a shared secret key authenticated by classical cryptography.
- Significance:
- Future-Proof Security: QKD is inherently secure against quantum computers, relying on quantum laws rather than computational difficulty, unlike classical encryption.
- Eavesdropper Detection: It offers provable, information-theoretic security, detecting any intrusion and allowing compromised keys to be discarded.
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: QKD safeguards government, military, financial, and national assets, preventing the “harvest now, decrypt later” threat.
- Digital Sovereignty and Innovation: Indigenous QKD development enhances digital sovereignty, builds trust in digital ecosystems, and drives technological advancement and economic opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)?
QKD is a quantum-secure communication technology that generates encryption keys using quantum mechanics, ensuring tamper-evident and unhackable data exchange.
2. What is the National Quantum Mission (NQM)?
NQM is India’s flagship initiative to promote quantum research, communication, computing, and sensing, aiming to make India a global leader in quantum technologies.
3. How does QKD enhance cybersecurity for India?
By providing future-proof, tamper-evident encryption, QKD protects government, military, and financial networks against quantum and classical cyber threats.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term "qubit" is mentioned? (2022)
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum Computing
(c) Visible Light Communication Technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)
Kazakhstan Poised to Join Abraham Accords
US President Donald Trump announced that Kazakhstan will join the Abraham Accords, expanding the framework that normalises relations between Israel and Muslim-majority nations.
- Abraham Accords: The Abraham Accords are US–brokered agreements (2020) that normalised ties between Israel and several Arab/Muslim-majority countries
- The accords are named after the biblical figure Abraham, considered a common ancestor of Jews and Arabs, symbolizing brotherhood.
- Key Signatories: The key signatories to the Abraham Accords include Israel, UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco (all in 2020), and Sudan (2021).
- The UAE was the first to announce full normalisation, followed by Bahrain. Sudan joined after being removed from the US terror list, while Morocco normalised ties in exchange for US recognition of its Western Sahara claim.
- Significance The Accords shows how the Arab countries are gradually decoupling themselves from the Palestine issue. It enhances regional diplomacy, trade, technology and tourism.
- India’s Interests: India has leveraged the Abraham Accords to strengthen its relationships with both Israel and Arab states at the same time.
- The new strategic platform I2U2 (India, Israel, UAE and the US) grew out of this environment, opening doors for collaboration in energy, water, health, transport, food security and space.
| Read more: Three years of the Abraham Accords |
Mussels as Bioindicators
Mussels are being used as bioindicators to monitor microplastic and chemical pollution in the Saronic Gulf of Greece.
- About: Mussels are bivalve mollusks ( shell-bearing invertebrates with two hinged shells). They are found in both marine (family Mytilidae) and freshwater (family Unionidae) environments.
- They occur worldwide, especially in cooler seas, and are an important component of coastal biodiversity.
- Role as Bioindicators: Mussels are used as bioindicators because they are sessile, filter-feeding organisms that accumulate contaminants like heavy metals, microplastics, and other pollutants in their tissues, providing a record of water quality over time.
- Their wide distribution and ability to reflect the presence of pollutants make them valuable for monitoring both freshwater and marine environments for pollution, including chemical and biological hazards.
| Read more: Invasive Species: Charru Mussel |

.png)
.png)