Nature-based Solutions and their Importance | 27 Dec 2025
For Prelims: UNFCCC, Amazon Rainforest, Mangroves, Air Pollution, Biodiversity, IUCN, CBD, UNCCD, Carbon Sequestration, Wetland, Green Corridor, UNEP, Green Bonds.
For Mains: Key facts regarding nature-based solutions, their strategic importance for India, Challenges associated with their implementation and way forward.
Why in News?
Brazil's hosting of UNFCCC COP30 in Belem (inside Amazon rainforest) has brought attention to nature-based solutions (NbS) as critical instruments for tackling global climate change.
- It can serve a fundamental role in accelerating partnership for Enhancing Nature-based Solutions for an Accelerated Climate Transformation (ENACT).
Summary
- COP30 and ENACT position Nature-based Solutions at the core of climate action, linking mitigation, adaptation, and biodiversity.
- Success depends on bridging finance gaps, mainstreaming NbS in policy and corporate governance, and fostering inclusive partnerships.
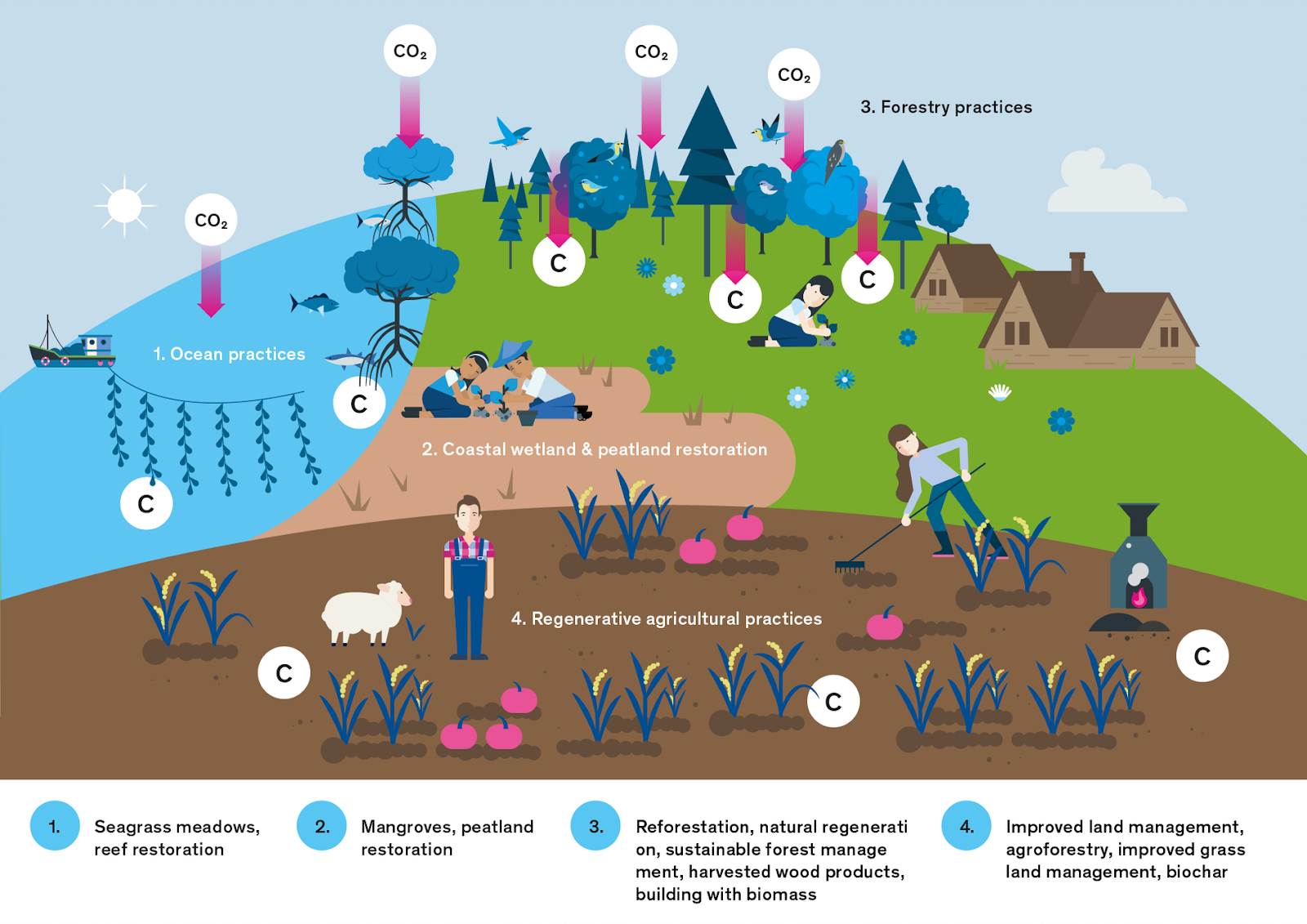
What are Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
- About: NbS are actions to protect, sustainably manage, and restore natural or modified ecosystems that address societal challenges effectively and adaptively, while simultaneously providing benefits for human well-being and biodiversity.
- Restoring mangroves instead of building concrete sea walls provides natural storm surge protection, as seen when India’s Pichavaram forest (Tamil Nadu) reduced 2004 tsunami damage.
- Core Principles of NbS (as defined by the IUCN):
- Address a societal challenge (e.g., climate change, flooding, water security, food security, air pollution, urban heat).
- Provide benefits for human well-being and biodiversity.
- Be designed and implemented with the full engagement and consent of local communities and indigenous peoples.
- Promote equity and balance trade-offs between short-term needs and long-term benefits.
- Maintain biological and cultural diversity.
- Be applied at a landscape scale (not just an isolated patch).
- Be integrated into policy and planning across sectors (not a one-off project).
- Be managed adaptively and generate evidence for effectiveness.
- Key Types & Examples:
|
Ecosystem Type |
NbS Intervention |
Climate Impact |
|
Terrestrial |
Afforestation & Reforestation (e.g., Miyawaki Method in urban areas). |
Carbon sequestration and soil moisture retention. |
|
Marine/Coastal |
Mangrove Restoration (e.g., India's MISHTI Scheme). |
Coastal protection against cyclones and "Blue Carbon" storage. |
|
Agricultural |
Agroforestry & Natural Farming (e.g., ZBNF, PM Pranam). |
Improving soil carbon, reducing chemical runoff, and ensuring food security. |
|
Urban |
Blue-Green Infrastructure (e.g., Restoring urban wetlands like Ennore or Deepor Beel). |
Reducing urban flooding and cooling local temperatures. |
- Government Initiatives for Promoting NbS:
- National Mission for a Green India (GIM),
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA),
- National Water Mission.
- National Afforestation Programme (NAP),
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) 2.0, Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats and Tangible Incomes (MISHTI).
- Mission Amrit Sarovar.
Enhancing Nature-based Solutions for an Accelerated Climate Transformation (ENACT)
- About: ENACT is a global partnership designed to accelerate action on climate change, land degradation, and biodiversity loss by championing and scaling up NbS.
- Governance & Origin: It was launched at UNFCCC COP27 in Sharm el-Sheikh by the Egyptian Presidency with Germany and IUCN. IUCN hosts ENACT’s secretariat and leads its implementation.
- Primary Function: Acts as a collaborative hub for both state and non-state actors to align efforts, build political support, and advocate for evidence-based NbS policies across the three Rio Conventions (UNFCCC, CBD, UNCCD).
- Quantifiable Global Goals (Outcomes):
- Human Resilience: Enhance protection for over 1 billion vulnerable people, with a dedicated focus on at least 500 million women and girls.
- Ecosystem Integrity: Secure up to 2.4 billion hectares (ha) via a combined strategy of protection (45M ha), sustainable management (2B ha), and restoration (350M ha).
- Climate Mitigation: Significantly boost global carbon sequestration by protecting, conserving, and restoring carbon-rich ecosystems across terrestrial, freshwater, and marine realms.
What is the Strategic Importance of Nature-based Solutions (NbS) for India?
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forest conservation and wetland protection provide essential carbon sequestration and water regulation in India, countering deforestation’s 12–15% contribution to emissions. Restoration efforts can create significant carbon sinks, while urban green spaces reduce temperatures by 2–4°C.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Mangrove and floodplain restoration deliver cost-effective protection against floods and storms in India, where damages exceed USD 7.5 billion annually. These measures significantly reduce damage costs and flood volumes.
- Water Security and Quality: Riparian buffers and watershed protection filter pollutants and secure water supplies for India’s 600 million people facing water stress. They reduce flows and improve water quality effectively.
- Urban Health and Well-being: Urban green corridors improve health and connect habitats in India, where over 52 crore people reside in urban areas. They reduce pollution and stress levels significantly.
What are the Challenges in the Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
- Critical Financing Gap: Meeting global biodiversity and climate goals requires annual investment of USD 384 billion by 2025 (UNEP), with current private sector finance for NbS critically low at ~18% of total.
- Flawed Economic Paradigm: A core challenge is treating nature as a costless input. Humanity's demand exceeds Earth's regenerative capacity by ~70%, drawing down ecological capital.
- Corporate Governance Gap: Frameworks like the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) are gaining traction (700+ adopters), but biodiversity is often not a material board-level priority, revealing a disconnect between policy and strategic integration.
- Sectoral & Regional Disparities: TNFD adoption is uneven; high-impact sectors (Energy, Infrastructure) and European firms lead in integration, while Technology/IT sectors and emerging economies like India show varied commitment, often focusing on climate over broader biodiversity.
What are the Pathways to Strengthen Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
- Close the Critical Financing Gap: Catalyze private investment via frameworks like the TNFD and innovative instruments (e.g., green bonds).
- Mainstream NbS into Policy Making: Integrate NbS into core sectoral policies (urban planning, agriculture, infrastructure). Elevate biodiversity from a voluntary concern to a material, board-level strategic priority for corporations.
- Mainstreaming "Inclusive Governance": Adopt a "Rights-based Approach" by making Gram Sabhas the primary decision-makers for NbS projects. This ensures that traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) is integrated and social safeguards are upheld.
- Urban-Rural Integration (The Landscape Approach): Move beyond "isolated patches" to Blue-Green Corridors. For example, restoring the Aravalli Green Wall to tackle desertification and Delhi’s air pollution simultaneously.
- Technology & Monitoring: Utilize the Bhuvan Portal (ISRO) and AI-driven dashboards to track the survival rates of plantations and carbon sequestration levels in real-time, ensuring accountability in schemes like MISHTI and Nagar Van Yojana.
Conclusion
"Hosting COP30 in the Amazon has placed Nature-based Solutions (NbS) at the heart of climate action. Initiatives like ENACT offer a science-backed pathway, but success depends on scaling finance, embedding NbS in governance, and fostering inclusive partnerships. As we move forward, 'Nature is not a luxury, but a vital infrastructure. Investing in NbS is an investment in our collective climate insurance.'"
|
Drishti Mains Question: Nature-based solutions are increasingly viewed as a bridge between climate mitigation, adaptation, and biodiversity conservation. Discuss with examples. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Nature-based Solutions (NbS)?
NbS are actions to protect, manage, and restore ecosystems to address climate change, disasters, food, and water security, while delivering biodiversity and human well-being benefits.
2. What is the ENACT Partnership?
ENACT is a global partnership launched at COP27, hosted by IUCN, to scale up NbS and align climate, biodiversity, and land-degradation actions across the Rio Conventions.
3. What are the key global targets under ENACT?
Protect 1 billion vulnerable people, secure 2.4 billion hectares of ecosystems, and enhance carbon sequestration through restoration of carbon-rich terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the role of UN-Habitat in the United Nations programme working towards a better urban future, which of the statements is/are correct? (2017)
- UN-Habitat has been mandated by the United Nations General Assembly to promote socially and environmentally sustainable towns and cities to provide adequate shelter for all.
- Its partners are either governments or local urban authorities only.
- UN-Habitat contributes to the overall objective of the United Nations system to reduce poverty and to promote access to safe drinking water and basic sanitation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods, highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (2016)
Q. Do government schemes for up-lifting vulnerable and backward communities by protecting required social resources for them, lead to their exclusion in establishing businesses in urban economies? (2014)