Coping with Type-1 Diabetes | 17 Jun 2022
For Prelims: Type-1 Diabetes, ICMR, World Diabetes Day
For Mains: Diabetes, Healthcare, Initiatives to curb Diabetes, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) issued guidelines regarding diagnosis, treatment, and management for type-1 diabetes.
- This is the first time the ICMR has issued guidelines specifically for type 1 diabetes, which is rarer than type 2.
What do we Need to know about Diabetes?
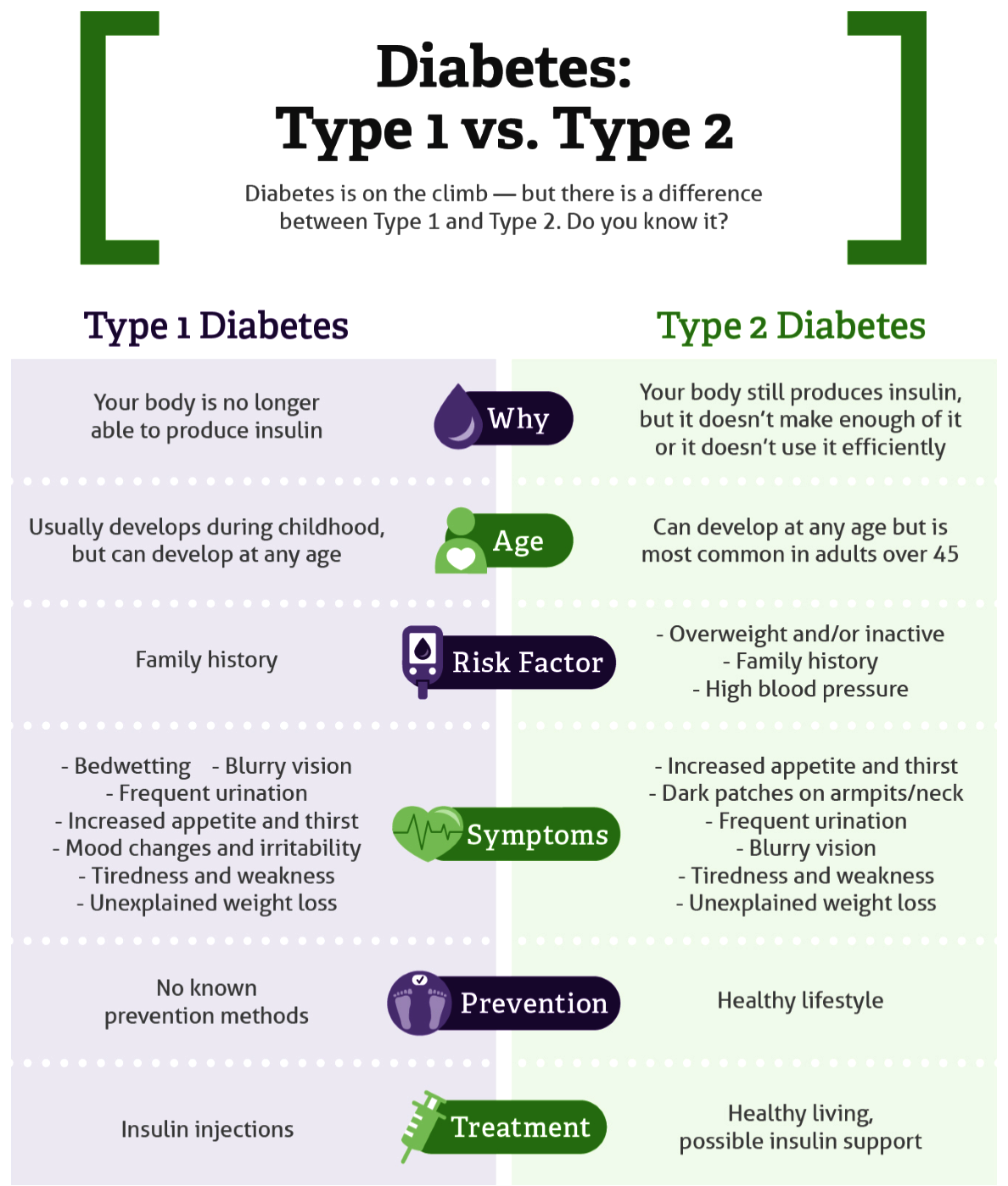
- About: Diabetes is a Non-Communicable Disease (NCD) that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar, or glucose), or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin, it produces.
- Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- It is also known as juvenile diabetes (as it mostly affects children of age 14-16 years), this type occurs when the body fails to produce sufficient insulin.
- It is predominantly diagnosed in children and adolescents. Although the prevalence is less, it is much more severe than type 2.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- It affects the way the body uses insulin. While the body still makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes can occur at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people.
- Gestational Diabetes: This type occurs in women during pregnancy when the body sometimes becomes less sensitive to insulin. Gestational diabetes does not occur in all women and usually resolves after giving birth.
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- Impacts of Diabetes: It affects the five major organs namely, Kidney, Heart, Blood vessels, Nervous System, and Eyes (retina).
- Factors Responsible: Factors that lead to increase in diabetes are an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, harmful use of alcohol, overweight/obesity, tobacco use, etc.
How Rare is Type-1 Diabetes?
- Out of 10 lakh children and adolescents living with type 1 diabetes in the world, India holds the highest numbers.
- Out of 2.5 lakh people living with type 1 diabetes in India, 90,000 to 1 lakh are under the age of 14 years.
- Only 2% of all hospital cases of diabetes in the country are type 1 — but which is being diagnosed more frequently.
What Factors Exacerbate the Condition?
- Genetic Factors: It plays a role in determining whether a person will get type-1 diabetes. The risk of disease in a child is:
- 3% when the mother has it
- 5% when the father has it
- 8% when a sibling has it.
- Presence of Certain Genes: It is also strongly associated with the disease. For example, the prevalence of genes called DR3-DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 is 30-40% in patients with type 1 diabetes as compared to 2.4% in the general population.
- DR3- DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 means the patient is permissive for celiac disease and is capable of developing or having the disease.
What are the Treatments?
- Glucose monitoring: Continuous glucose monitoring devices can help monitor the blood glucose levels throughout 24 hours with the help of a sensor.
- Artificial pancreas: It can automatically deliver insulin when required.
What are Related Initiatives?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS):
- In order to prevent and control major NCDs, this initiative was launched by India in 2010 with focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- World Diabetes Day:
- It is observed on 14th November every year. The 2022 campaign will focus on access to diabetes education. access to diabetes education.
- Global Diabetes Compact:
- WHO launched a Global Diabetes Compact to better fight the disease while marking the centenary of the discovery of insulin.