2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium
For Prelims: India Mobile Congress, Bharat 6G Alliance, Telecom Technology Development Fund, International Telecommunication Union
For Mains: Bharat 6G Vision and its alignment with Digital India and Viksit Bharat 2047, Challenges in India’s 6G deployment and the roadmap for readiness
Why in News?
At the India Mobile Congress(IMC) 2025, India highlighted its growing leadership in next-generation telecom through the 2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium, marking a key step towards building a self-reliant, innovative, and globally connected 6G ecosystem for Viksit Bharat 2047.
- The IMC is Asia's most prominent technology expos, jointly organized by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) and the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI).
What are the Key Outcomes of 2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium at IMC 2025?
- New Delhi Declaration on 6G: At the Symposium, global research alliances including Bharat 6G, 6G-IA (European organization), ATIS’ Next G Alliance (North American organization), and others issued a Joint Declaration to shape 6G as a global public good.
- The declaration outlines five core principles for 6G networks that are trusted and secure, resilient and reliable, open and interoperable, inclusive and affordable, and sustainable and globally connected.
- The declaration also calls for skills development and global collaboration to build a future-ready, inclusive 6G ecosystem aligned with India’s 6G Vision 2030.
- Economic Vision: The symposium highlighted India’s 6G roadmap aiming for USD 1.2 trillion GDP impact by 2035 and 10% of global 6G patents, along with a threefold growth in satellite communications by 2033.
- The Symposium showcased India’s indigenous 4G stack as a milestone toward technological self-reliance and export readiness.
- Focus on Collaboration and Inclusivity: The symposium urged stronger global collaboration, indigenous R&D, and industry- academia synergy to build an inclusive 6G framework.
- It highlighted India’s shift from a technology consumer to a co-creator and global leader, backed by milestones like the rollout of one lakh indigenous 4G towers.
What is Bharat 6G Vision?
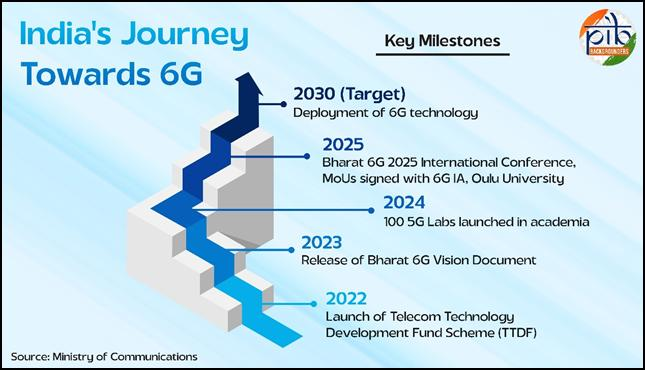
- Bharat 6G Vision: Launched in 2023, Bharat 6G Vision aims to position India as a global leader and co-creator in next-generation wireless communication.
- It aligns with the Viksit Bharat 2047 goals, focusing on affordability, sustainability, and universal access by 2030.
- Features of the Vision:
- Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA): An industry-led, government-facilitated body uniting telecom operators, academia, startups, and R&D institutions.
- It focuses on domains like spectrum, technology, sustainability, applications, and use cases.
- Bharat 6G Alliance signed a Memorandum of Understanding with global alliances including Next G Alliance (USA), 6G-IA (Europe), 6G Forum (South Korea), 6G Flagship (Finland), 6G Brazil, and others to collaborate on research and global standards.
- As of July 2025, the alliance comprises over 80 member organizations.
- It is also working with Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI) and National Association of Software and Services Companies(NASSCOM) to leverage national expertise and ensure resilient, trusted supply chains.
- Bharat 6G Mission:Aims to make India a global co-creator and leader in 6G technologies by 2030.
- Focuses on indigenous innovation, capacity building, and skills development.
- Emphasizes sustainability, security, and inclusivity in telecom development.
- Seeks to ensure that 6G innovation originates in India and benefits both national and global communities.
- Infrastructure: The government funded two advanced testbeds, the 6G THz Testbed and the Advanced Optical Communication Testbed to promote research and innovation in next-generation telecom technologies.
- It also sanctioned 100 5G labs across academic institutions in FY 2023–24 to build a 6G-ready academic and startup ecosystem, and approved 104 research proposals on 6G network systems.
- India’s Initiatives for 6G Ecosystem:
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF): Launched in 2022 to fund R&D in 5G and 6G technologies.
- TTDF supports domestic companies, startups, and academic institutions developing telecom products for affordable rural connectivity.
- As of September 2025, 115 projects worth Rs 310.6 crore have been approved, with durations of 1–5 years.
- Technology Innovation Hub (TIH) at IIIT Bangalor: Set up under National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS), to pioneer Advanced Communication Systems for 5G+ and 6G.
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF): Launched in 2022 to fund R&D in 5G and 6G technologies.
6G (Sixth-Generation)
- It is the successor to 5G cellular technology. 6G will use higher radio frequencies to deliver data with near-zero delay, enabling speeds up to 1,000 times faster than 5G.
- The 6G Technology has been named ‘International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) 2030’ by International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the specialised agency for Information and Communication Technologies of the United Nations.
- 6G will power real-time applications like remote surgery, smart robotics, and immersive virtual experiences, while AI integration will make networks smarter, faster, and more efficient.
What are the Challenges Related to 6G Implementation in India?
- Infrastructure Readiness: India’s current 5G rollout is still expanding, and the shift to 6G will demand dense fiber networks, advanced semiconductors, and indigenous hardware, areas where domestic capability is still limited.
- Limited R&D Ecosystem: Despite initiatives like the Bharat 6G Mission, India’s research output, patents, and private investment in frontier telecom technologies remain modest compared to global leaders like China and US.
- Spectrum and Standards Gap: The allocation and regulation of terahertz (THz) bands for 6G are still evolving globally, leaving India with uncertainty in planning its 6G roadmap.
- Talent and Skill Shortage: There’s a shortage of trained professionals in AI, photonics, and network engineering needed for indigenous 6G innovation.
- Affordability and Digital Divide: High deployment costs could widen the gap between urban and rural connectivity if not supported by inclusive policies.
- Security and Privacy Risks: With ultra-fast data transfer and massive device connectivity, ensuring cybersecurity and data protection becomes more complex.
What Steps are Needed to Ensure Successful Implementation of India’s 6G Vision?
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: Integrate 6G components under Production Linked Initiative (PLI) Schemes for telecom, semiconductors, and electronics to reduce import dependency and enhance domestic production.
- Skill Development and Human Capital: Expand 5G Labs in academic institutions to create a 6G-ready talent pool and promote interdisciplinary courses in AI, IoT, photonics, and network engineering.
- Spectrum Policy and Regulation: Formulate a forward-looking National Spectrum Strategy for THz frequencies and encourage global harmonization through participation in ITU and global standard-setting bodies.
- Inclusive Access and Affordability: Align 6G rollout with Digital India and BharatNet to ensure equitable access in rural and remote regions, avoiding a new digital divide.
Conclusion
India’s 6G journey reflects its shift from a technology adopter to a global innovator. With initiatives like the Bharat 6G Alliance, and strong global partnerships, the country is building a secure, inclusive, and future-ready telecom ecosystem paving the way for a self-reliant and digitally empowered Viksit Bharat by 2047.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. India’s 6G Vision aims to position the country as a global co-creator in next-generation telecom. Discuss. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Bharat 6G Vision 2030?
Launched in 2023, it aims to make India a global leader and co-creator in 6G, focusing on affordability, sustainability, and universal access by 2030.
2. What is the Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF)?
Launched in 2022, TTDF funds R&D and indigenous innovation in 5G and 6G technologies to boost rural connectivity and domestic manufacturing.
3. What is the Bharat 6G Alliance?
An industry-led and government-facilitated body uniting telecom operators, academia, startups, and R&D institutions to drive indigenous innovation and develop global 6G standards.
4. What is IMT-2030?
It is the official name for 6G technology designated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the UN agency for ICT standards.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Internationalisation of Indian Higher Education
For Prelims: National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, Setting up and Operation of Campuses of Foreign Higher Educational Institutions in India Regulations 2023, Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER), Make in India, Digital India, Public-Private Partnerships.
For Mains: Significant Policy Reforms Driving Transformation in India’s Higher Education Sector, Emerging Prospects and Challenges Linked to the Entry of Foreign Universities in India.
Why in News?
17 foreign universities mainly from the UK and Australia, have received approval to set up campuses in India under UGC’s 2023 regulations. This move aligns with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and comes amid growing demand for quality higher education in India.
How is India Advancing Global Partnership in Higher Education?
- NEP 2020 Vision: Guided by the principles of Access, Equity, Quality, Affordability, and Accountability, NEP 2020 aims to establish India as a global education hub.
- It allows top 100 global universities to operate in India, fostering international collaboration, student and faculty mobility, and academic credit transfer to elevate the entire education ecosystem to global standards.
- UGC’s Regulations 2023: To operationalize the NEP 2020's vision, UGC’s (Setting up and Operation of Campuses of Foreign Higher Educational Institutions in India) Regulations 2023 was enacted, permitting top-ranked Foreign Higher Educational Institutions (FHEIs) to establish campuses in India.
- Eligible FHEIs must be ranked within the top 500 QS World University rankings.
- These institutions are mandated to maintain the same academic standards, curricula, and degree equivalence as their parent campuses abroad.
- They are granted operational autonomy, including flexibility in faculty recruitment—both Indian and foreign—and are not bound by existing fee caps applicable to Indian universities.
What Factors are Driving Foreign Universities to Establish Campuses in India?
- Demand Surge for Quality Higher Education: With over half its population under 30 and a Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) below 30%, India presents a vast untapped higher education market.
- Rising incomes, a growing middle class, English proficiency, and demand for global learning make it an attractive destination for foreign universities.
- Supportive Policy Environment: NEP 2020 promotes the internationalisation of education, inviting top global universities to India, while UGC’s 2023 regulations provide a supportive framework for establishing their campuses.
- Declining International Students: Recent data shows a sharp decline in Indian students abroad due to stricter immigration policies, including restrictions on foreign students bringing dependents and other measures to reduce immigration in the UK, US, and Canada.
- Diversification of Revenue: With stagnant domestic enrolments and declining public funding, universities in the UK, Australia, and Canada see India as a strategic market for revenue diversification and financial stability.
- Strategic Global Partnerships: Indian campuses strengthen institutional ties, promote research collaboration and student exchange, and build a talent pipeline for future postgraduate recruits and global alumni networks.
- E.g., UK–India Education and Research Initiative (UKIERI) promotes bilateral student and faculty exchange.
What are the Implications of Internationalising India’s Higher Education?
- Global Competitiveness: Foreign universities introduce global curricula, teaching standards, and quality assurance, elevating India’s academic ecosystem while attracting innovation and research funding.
- Curbing Brain Drain: Highly skilled talented students may now stay in India, reducing the massive annual outflow of billions of dollars spent on studying abroad.
- Systemic Improvement: The presence of foreign universities will drive Indian institutions to innovate, enhance quality and competitiveness, while their governance models and industry-academia linkages can serve as a blueprint for systemic reform.
- Alignment with National Goals: Courses in high-demand fields like AI, Data Science, and Finance will build a skilled workforce aligned with Make in India and Digital India, while fostering a diverse and cosmopolitan academic environment.
- Affordable International Degrees: Earning a foreign degree in India is far more affordable than studying abroad — e.g., Southampton University’s 2026 fees for Undergraduate (UG) courses (Rs 13.86–23.10 lakh) are about half of UK on-campus costs.
What are the Key Challenges in Setting Up Foreign University Campuses in India, and How can They Be Addressed?
|
Challenges |
Way Forward |
|
Autonomy Challenges: Limited autonomy on fees, curriculum, faculty; complex UGC approvals. |
Stable Regulatory Framework: Fast-track single-window clearances; transparent policies on autonomy, taxation, and fund repatriation. |
|
Financial Viability: Balancing affordability with costs; meeting enrollment targets for break-even. |
Sustainable Financial Models: Phased investments; public-private partnerships; allow surplus repatriation with reinvestment clauses. |
|
Competition Challenges: Intense competition from IITs/IIMs; student skepticism on degree value. |
Strategic Academic Partnerships: Joint degrees, credit transfers; collaborative research on India-specific themes. |
|
Quality Assurance Issues: Attracting top faculty; ensuring no dilution of curriculum/pedagogy standards. |
Robust Monitoring & Evaluation: Define success via research, employability, and community impact metrics. |
|
Infrastructure Barriers: Land acquisition, taxation, labour laws, and infrastructure readiness. |
Cultural Integration: Adapt curricula to Indian context and values; promote local skills and knowledge economy. |
Conclusion
India's framework for foreign universities, driven by NEP 2020 and UGC 2023, aims to transform higher education by enhancing quality, curbing brain drain, and fostering global competitiveness. Success hinges on balancing foreign autonomy with national interest, ensuring affordability, and creating sustainable, mutually beneficial academic partnerships for long-term impact.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine how National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and UGC Regulations 2023 facilitate the internationalisation of higher education in India and assess their policy implications |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the policy framework for foreign universities setting up campuses in India?
NEP 2020 and UGC Regulations 2023 permit top-ranked Foreign Higher Educational Institutions (FHEIs) to establish campuses, promoting internationalisation and quality parity.
2. Which eligibility criterion must foreign universities meet under UGC rules?
FHEIs must be ranked within the top 500 globally (overall or subject-wise) or demonstrate exceptional domain expertise as per UGC assessment.
3. How does the entry of foreign universities align with India's national development goals?
It supports goals like 'Make in India' and 'Digital India' by creating a skilled workforce in high-demand fields, curbing brain drain, and fostering research and innovation within the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)
Q2. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)
Reclassification of CPSEs
Why in News?
The Government is planning to revise the classification and performance assessment criteria for Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) by introducing two new ‘Ratna’ categories in addition to the existing Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna statuses.
- The Department of Public Enterprises under the Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises grants Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna status to CPSEs based on their financial performance.
What are the Key Aspects of the CPSEs’ Reclassification?
- New Evaluation Parameters: New evaluation parameters under discussion include corporate governance, succession planning and leadership development, capital expenditure, dividend payout, sustainable business practices, and alignment with Vision 2047.
- Re-evaluation Committee: A 10-member committee led by Cabinet Secretary T.V. Somanathan is conducting the re-evaluation, with its report due before the Union Budget 2026–27.
- Objective of Revision: It aims to modernize the public sector and align it with India’s national economic strategy by developing next-gen CPSEs capable of global competitiveness.
- It focuses on accountability, performance-driven governance, efficiency, and strategic resource alignment toward sectors vital for India’s future economic security.
- Current Ratna Categories: India currently has 14 Maharatna, 26 Navratna, and 74 Miniratna firms. The status enables financial and operational independence in capital spending, joint ventures, and investments.
What are CPSEs?
- About: A Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) is a company, majority-owned and controlled by the Government of India, with at least 51% of its shares held by the Central Government, either directly or indirectly through other CPSEs.
- This definition also extends to include the subsidiary companies of such enterprises.
- Formation: It is an entity that was either incorporated under Indian company law (like the Companies Act, 2013) or established by a specific Act of Parliament.
- Current Classification of CPSEs:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a CPSE?
A Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) is a company with ≥51% government ownership, incorporated under company law or an Act of Parliament, including its subsidiaries.
2. Who is re-evaluating CPSE classification?
A 10-member committee headed by Cabinet Secretary T.V. Somanathan is reviewing CPSE classification and will submit its report before the Union Budget 2026–27.
3. How does the proposed new 'Ratna' differentiation differ from the existing one?
Unlike the existing categories that depend on financial size and turnover, the new tiers will recognize CPSEs based on their strategic importance to national economic goals in critical sectors.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
1. It is a Public Limited Government Company.
2. It is a Non-Banking Financial Company.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage
Why in News?
Google announced that its quantum processor, "Willow," has achieved the first-ever verifiable quantum advantage by utilizing a new algorithm called Quantum Echoes, which ran 13,000 times faster than the world's fastest supercomputers.
- This achievement marks a major step toward real-world quantum applications like Hamiltonian learning.
What is Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage?
- Concept of Quantum Advantage: It refers to the point where a quantum computer outperforms classical supercomputers on specific tasks.
- Google’s Verifiable Quantum Advantage: Google’s Willow quantum processor, featuring up to 105 qubits, successfully ran the Quantum Echoes algorithm, which tracks the forward and backward evolution of entangled quantum states to study quantum chaos and interference.
- This enabled the measurement of the Out-of-Time-Order Correlator (OTOC) - a key indicator of how information gets “scrambled” through entanglement as quantum bits interact.
- The Willow processor achieved the OTOC measurement in just two hours, a task estimated to take 13,000 times longer (equivalent to several years) on a classical supercomputer.
- Unlike earlier demonstrations, the result can be independently verified by other quantum or classical systems, making it the first real-world, measurable quantum advantage
- Practical Applications:
- Hamiltonian Learning: OTOC circuits can aid in Hamiltonian Learning, a quantum technique where a computer simulates the behavior of a physical system (such as a molecule) and compares it with real experimental data to accurately estimate unknown parameters like energy levels or interaction strengths.
- Molecular Structure Estimation: The OTOC method, tested using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, helps analyze proteins, materials, and compounds by studying quantum spin behavior, leading to better insights into molecular geometry.
Quantum Computing Glossary
- Quantum Technology: Quantum computing/technology refers to a class of technologies that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations and achieve capabilities not possible with traditional technology.
- Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at very small scales, such as atoms and subatomic particles.
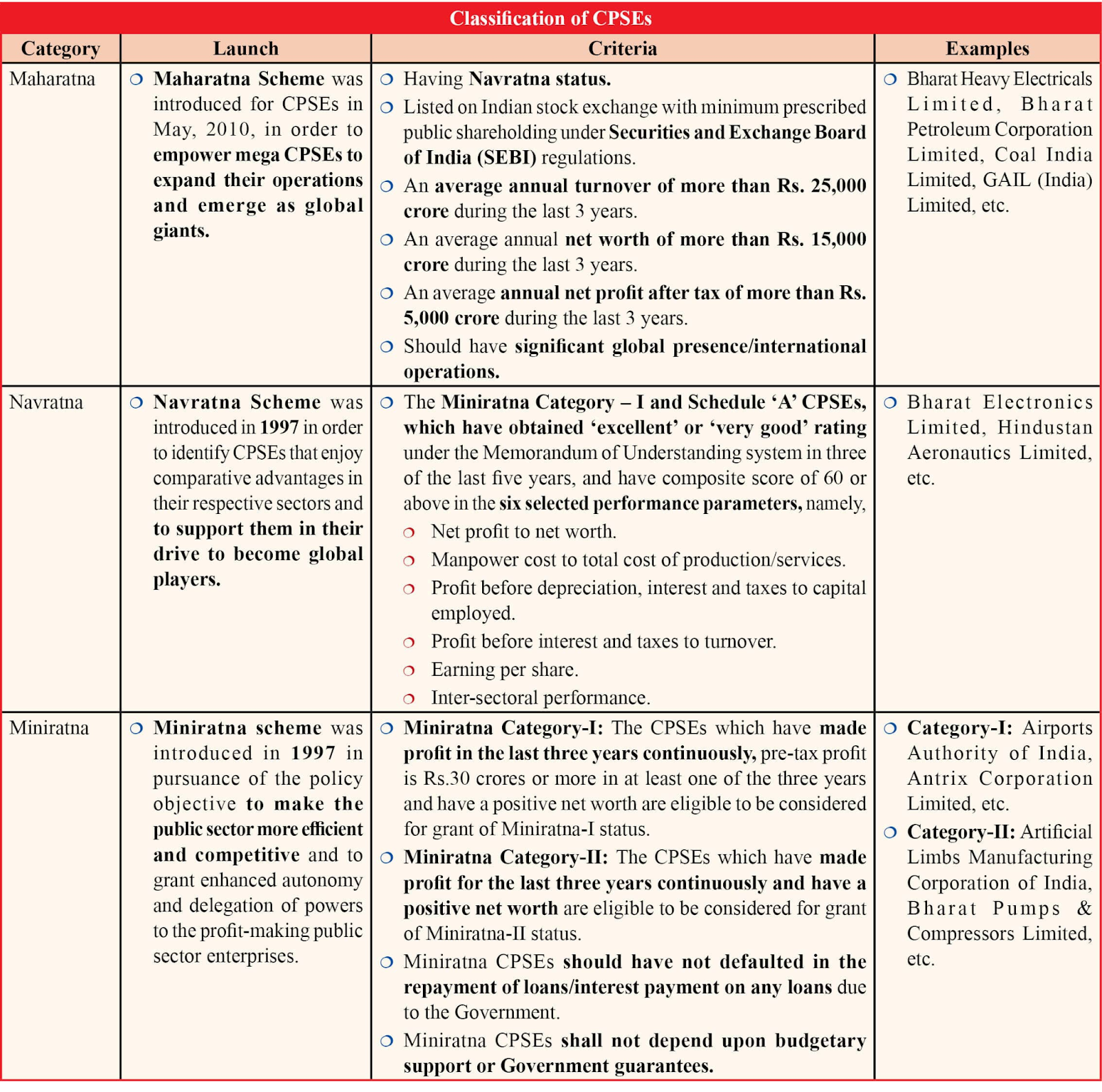
- Qubit (Quantum Bit): The basic unit of quantum information that can exist as 0, 1, or both simultaneously (superposition).
- Superposition: The ability of a quantum system to be in multiple states at once, giving quantum computers massive parallel processing power.
- Entanglement: A quantum link where qubits remain connected, where changing one instantly affects the other, even if they’re far apart.
- Quantum Gate: The building block of quantum circuits, they perform controlled operations on qubits (like classical logic gates).
- Quantum Circuit: A network of quantum gates arranged to perform a specific computation or algorithm.
- Quantum Interference: It is the process of reinforcing correct answers and cancelling wrong ones using the wave-like nature of qubits.
- Quantum Simulation: Using quantum computers to model molecules, materials, or physical systems too complex for classical machines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a verifiable quantum advantage?
It’s when a quantum computer outperforms classical supercomputers on a task, and the result can be independently verified by other quantum or classical systems.
2. What is an Out-of-Time-Order Correlator (OTOC)?
A quantum observable that tracks how information gets “scrambled” among entangled qubits, revealing the level of quantum chaos in a system.
3. What is Hamiltonian Learning and why is it important?
A quantum method where simulated OTOC signals are compared with real data to estimate unknown molecular parameters like energy levels or interactions.
4. What are the practical uses of OTOC-based experiments?
They aid molecular structure analysis, material design, and drug discovery through precise simulation of atomic-scale systems.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term "qubit" is mentioned?
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum Computing
(c) Visible Light Communication Technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)
India Maritime Week (IMW) 2025
India Maritime Week (IMW) 2025, themed “Uniting Oceans, One Maritime Vision,” was inaugurated by the Union Home and Cooperation Minister, showcasing India’s goal to become a global maritime leader by 2047.
- IMW 2025 is a premier five-day event uniting maritime experts, innovators, and leaders from 85 countries.
India’s Maritime Strength
- 11,000 km coastline, 13 coastal states, and a 23.7 lakh sq. km Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) make India a natural maritime power.
- 60% of India’s GDP comes from coastal states, supporting 800 million livelihoods linked to the sea.
- India’s maritime sector handles 95% of the country's trade by volume and 70% by value.
- The Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, guided by the Sagarmala Programme and the vision of MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions), aim to make India a global maritime and trade hub while balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
Maritime India Vision 2030
- It includes over 150 strategic initiatives with Rs 3 - 3.5 lakh crore in investments to modernize ports, shipping, and waterways.
- Under MIV 2030, India’s port capacity has nearly doubled from 1,400 million metric tonnes per annum (MMTPA) in 2013-14 to 2,762 MMTPA in 2024-25 a 92% rise at major ports and 80% at non-major ports.
- The number of Indian seafarers has surged by 200%, reaching 3.2 lakh.
Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047
- India aims to handle one-third of global seaborne trade by 2047, up from 10% currently.
- It targets Rs 80 lakh crore investments to develop green corridors, hydrogen bunkering, and methanol-fueled vessels for sustainability.
| Read more: India's Maritime Sector in Transformation |
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar 2025
The Government of India has announced the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP) 2025, the nation’s highest recognition for outstanding contributions in diverse fields of science, technology, and technology-led innovation.
- Prominent Awardees of 2025: Vigyan Ratna (Posthumous)-Prof. Jayant Vishnu Narlikar – noted astrophysicist.
- Known for co-developing the Hoyle–Narlikar theory of gravity, an alternative to Einstein's general relativity that supports the steady-state model of the universe.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar
- About: The award has been instituted by the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It aims to inspire excellence in Indian science and technology, promote innovation, and acknowledge achievements that contribute to national development.
- Disciplinary Coverage: It covers 13 fields such as Physics, Chemistry, Engineering, Agriculture, Environment, Atomic Energy, Space, etc.
- Categories of Awards: The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is conferred under four categories:
-
Vigyan Ratna (VR): Lifetime achievement recognition.
-
Vigyan Shri (VS): Distinguished contributions.
-
Vigyan Yuva–Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY–SSB): For scientists below 45 years.
-
Vigyan Team (VT): For exceptional collaborative work.
-
| Read More: Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar Awards |
National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM)
The Ministry of Mines has recognized two additional Centres of Excellence(CoEs)- Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru and Centre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET), Hyderabad under the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM).
- Earlier, seven institutes had already been recognized under this initiative.
- CoE will function on a Hub & Spoke model, pooling expertise of academic, R&D, and industry partners.
National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM)
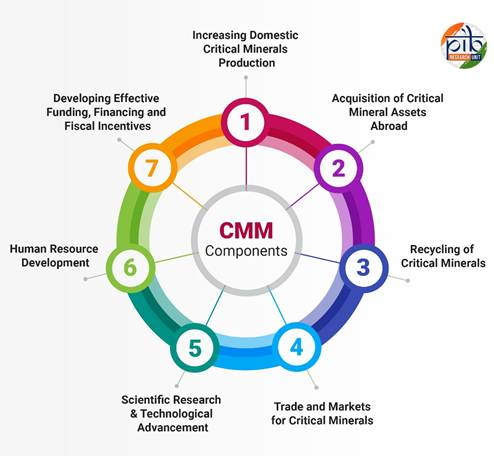
- About: The National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) was announced in the Union Budget 2024–25 to ensure India’s long-term mineral security.
- The mission seeks to strengthen India’s critical mineral supply chain by ensuring steady availability from both domestic and international sources.
- Coverage & Objectives:
- The NCMM covers all stages of the mineral value chain - exploration, mining, beneficiation, processing, and recycling from end-of-life products.
- It aims to secure access to minerals essential for clean energy, electronics, and strategic sectors.
- Key Features:
- Focus will also be on offshore mining of polymetallic nodules rich in cobalt and rare earth elements (REEs).
- Governance:
- The Empowered Committee on Critical Minerals will oversee the mission, with the Ministry of Mines as the nodal authority.
Critical Minerals
- Critical minerals are vital for a country’s economic growth and national security. Their limited global availability poses supply chain risks.
- Key Applications:
- Solar Energy: Minerals like silicon, tellurium, indium, and gallium are crucial for photovoltaic (PV) cells. India’s 64 GW solar capacity depends heavily on them.
- Wind Energy: Rare earth elements such as neodymium and dysprosium are vital for wind turbine magnets.
- Electric Vehicles: Lithium, nickel, and cobalt power lithium-ion batteries under the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP).
- Energy Storage: Advanced batteries for energy storage rely on lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
| Read More: India’s Critical Minerals Roadmap |
Google’s AI C2S-Scale
Google DeepMind’s AI model Cell2Sentence-Scale 27B (C2S-Scale) produced a new, lab-confirmed hypothesis on cancer cell behavior, marking a breakthrough in AI-driven drug discovery and biological research.
C2S-Scale Model
- About: C2S-Scale is a large language model (LLM) built on Google's Gemma-2 architecture, trained to understand gene expression as a language.
- With 27 billion parameters, the model can capture subtle relationships among genes, cells, and tissues, reflecting AI “scaling laws”—where larger models gain emergent abilities that smaller models lack.
- Working: It translates single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data and interprets biological functions as ‘cell sentences’, learning patterns from millions of cells to understand cellular functions.
- Breakthrough: The AI hypothesized that the drug silmitasertib could act as a conditional amplifier, making cancer cells more visible to the immune system only in the presence of low interferon.
- Significance: C2S-Scale enables in-silico (computer-based) screening at unmatched speed and scale, accelerating scientific discovery.
Google DeepMind
- About: It is an Alphabet-owned AI research lab dedicated to achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and applying it to solve complex challenges in science, healthcare, and climate change.
- Achievements: Its notable breakthroughs include AlphaFold for protein structure prediction, AlphaGo for strategic reasoning, and the Gemini large language models.
| Read More: Artificial Intelligence |