MoEFCC Reverses Decision to Merge Autonomous Bodies
For Prelims: Forest Survey of India, National Tiger Conservation Authority, Wildlife Crime Control Bureau, Central Zoo Authority, Project Tiger, Project Elephant, Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
For Mains: Environmental Conservation Organizations and Related Concerns.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) reversed its decision to establish integrated regional offices by merging key environmental bodies under its umbrella.
What was the Initial Proposal of the MoEFCC?
- Proposal:
- The initial plan, announced during the Covid-19 lockdown, aimed to bring together the Forest Survey of India (FSI), the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB), and the Central Zoo Authority (CZA) under a unified structure.
- This move was intended to streamline operations and create a single point of authority for these organizations.
- The initial plan, announced during the Covid-19 lockdown, aimed to bring together the Forest Survey of India (FSI), the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB), and the Central Zoo Authority (CZA) under a unified structure.
- Criticisms:
- It would undermine the independence and authority of these bodies, which have different mandates and roles in environmental governance.
- It would create administrative confusion and chaos, as these bodies have different reporting structures and jurisdictions.
- It would compromise the quality and credibility of their work, as they would be subject to political interference and pressure from the MoEFCC.
- It would dilute the focus and expertise of these bodies, which have specialised functions and skills in their respective domains.
- Reversal of Decision:
- The recent notification from the MoEFCC not only scrapped the merger plan but suggests rearranging the current regional offices, and this plan is also facing criticism.
- For instance, the Bengaluru regional office would have had jurisdiction of three states and a Union Territory with different geography and environment: Karnataka, Kerala, Goa, and Lakshadweep.
- Concerns were also raised over the recent plan to merge Project Tiger and Project Elephant, potentially affecting the autonomy and importance of these initiatives.
- The recent notification from the MoEFCC not only scrapped the merger plan but suggests rearranging the current regional offices, and this plan is also facing criticism.
|
Environment Bodies |
Features |
|
Forest Survey of India(FSI): |
|
|
National Tiger Conservation Authority: |
|
|
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau: |
|
|
Central Zoo Authority: |
|
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam
(d) Sundarbans
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. “Policy contradictions among various competing sectors and stakeholders have resulted in inadequate ‘protection and prevention of degradation’ to environment.” Comment with relevant illustrations. (2018)
Indian Himalayan Region
For Prelims: Himalayan region, Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin, Biodiversity, Glacier retreat, Earthquakes, Landslides, Flash flood, Glacial lake outburst floods.
For Mains: Challenges Associated with Indian Himalayan Region
Why in News?
The Himalayan region, renowned for its breathtaking landscapes and cultural heritage, faces a pressing need to address sanitation issues that have long been overshadowed by concerns over illegal construction and surging tourist influx.
- A recent analysis conducted by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), highlighted the dire state of sanitation systems in Himalayan states.
What are the Major Highlights of the Analysis?
- Water Supply and Wastewater Generation: According to Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin guidelines, each hill town receives approximately 150 liters per capita of water supply.
- Alarmingly, 65-70% of this water supply is converted into wastewater.
- Grey Water Management Challenges: In Uttarakhand, merely 31.7% of households are connected to sewerage systems, leaving the majority reliant on on-site sanitation facilities.
- Both households and small hotels frequently resort to using soak pits to manage grey water, generated from bathrooms and kitchens.
- The presence of unlined open drains in some towns leads to the unregulated flow of grey water, exacerbating its infiltration into the ground.
- Implications for Soil and Landslides: The Himalayan region's soil makeup, including clayey, loamy, and metamorphosed schist, phyllite, and gneiss rocks, is inherently delicate.
- The excessive seepage of water and wastewater into the ground, as observed in the analysis, can render the soil softer and trigger vulnerability to landslides.
What are the Other Challenges Associated with the Indian Himalayan Region?
- About:
- The Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) is spread across 13 Indian States/Union Territories (namely Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Assam and West Bengal), stretching across 2500 km.
- Nearly 50 million people reside in this region, which is characterized by a diverse demographic, and versatile economic, environmental, social and political systems.
- With its towering peaks, majestic landscapes, rich biodiversity and cultural heritage, the IHR has long drawn visitors and pilgrims from the Indian sub-continent and across the world.
- Challenges:
- Environmental Degradation and Deforestation: The IHR faces extensive deforestation, which disrupts the delicate ecological balance.
- Rampant construction for infrastructure and urbanization leads to habitat loss, soil erosion, and disrupted water flow.
- Climate Change and Disasters: The IHR is highly sensitive to climate change. Rising temperatures lead to glacier retreat, altering the timing and availability of water resources for downstream communities.
- Erratic weather patterns, increased intensity of rainfall, and prolonged dry spells further impact ecosystems and local communities.
- The region is also highly susceptible to natural disasters like earthquakes, landslides, and flash floods.
- Poorly planned development, lack of disaster-resilient infrastructure, and inadequate early warning systems amplify the impact of such events.
- Cultural and Indigenous Knowledge Erosion: The IHR is home to diverse indigenous communities with unique knowledge and practices that have sustained them for generations.
- However, modernization can lead to the erosion of these cultural traditions, which often contain valuable insights for sustainable resource management.
- Environmental Degradation and Deforestation: The IHR faces extensive deforestation, which disrupts the delicate ecological balance.
Way Forward
- Nature-Based Tourism: Develop sustainable and responsible tourism practices that generate income for local communities while minimizing negative impacts on the environment.
- This could involve promoting eco-tourism, enforcing carrying capacity limits, and raising awareness among tourists.
- Glacial Water Capture: Develop innovative methods to capture and store meltwater from glaciers during the summer months.
- This water can then be released gradually during dry periods, supporting both agricultural needs and downstream ecosystems.
- Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation: Develop comprehensive disaster management plans that address the unique risks of the region, including landslides, avalanches, and glacial lake outburst floods. Invest in early warning systems, evacuation plans, and community training.
- Greywater Recycling for Agricultural Enrichment: There is a need to Implement a greywater recycling system in IHR that collects and treats household greywater for agricultural use.
- The treated greywater could then be directed to local farms for irrigation, providing a sustainable source of water and nutrients to enhance crop growth.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation Zones: Designate specific areas as bio-cultural conservation zones, where both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices are preserved. This can help maintain the intricate relationship between local communities and their environment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. When you travel in Himalayas, you will see the following: (2012)
- Deep gorges
- U-turn river courses
- Parallel mountain ranges
- Steep gradients causing land sliding
Which of the above can be said to be the evidence for Himalayas being young fold mountains?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Bring out the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in Western Ghats. (2013)
Q. Describe the various causes and the effects of landslides. Mention the important components of the National Landslide Risk Management Strategy. (2021)
Sixth Anniversary of the Minamata Convention
For Prelims: Minamata Disease, United Nations Environment Programme, World Health Organization,Global Environment Facility, planetGOLD program, Methylmercury
For Mains: Sources of Mercury Pollution, Minamata Convention.
Why in News?
The sixth anniversary of the Minamata Convention on Mercury is a reminder of global efforts to combat the toxic effects of mercury.
- On this occasion, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reflects on the ongoing campaign to eradicate the use of mercury in small-scale gold mining.
- This practice, despite its economic significance, poses severe risks to both miners and the environment due to the hazardous properties of mercury.
What is the Minamata Convention?
- The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty to protect human health and the environment from the adverse effects of mercury and its compounds.
- It was agreed at the fifth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee in Geneva, Switzerland 2013.
- Controlling the anthropogenic releases of mercury throughout its lifecycle is one of the key obligations under the Convention.
What is Mercury Pollution?
- About Mercury:
- Mercury is a naturally occurring element found in the Earth's crust. It is considered by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the top ten chemicals or groups of chemicals of major public health concern.
- Major Applications of Mercury:
- Thermometers and Barometers:
- Mercury's high coefficient of thermal expansion and easy visibility make it suitable for use in traditional thermometers and barometers.
- Chemical and Mining Processes:
- Mercury has been used in various chemical and mining processes, including the production of chlorine and mining of gold.
- Electronics and Electrical Switches:
- Mercury-wetted switches are used in various electrical applications because mercury's conductivity and low resistance make it suitable for creating a reliable electrical connection.
- Thermometers and Barometers:
- Sources of Mercury Pollution:
- Natural Sources:
- Volcanic eruptions release small amounts of mercury.
- Erosion of rocks and soil can release mercury into water bodies.
- Anthropogenic Sources:
- Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM): ASGM is a major source of mercury pollution, where mercury is used to extract gold from ore.
- Mercury is used to extract gold particles from ores, creating amalgams that are later heated to evaporate the mercury, leaving behind gold.
- Artisanal gold mining operations are responsible for 37% of global mercury pollution.
- Industrial Processes: Various industries, such as chlorine production, cement manufacturing, and waste incineration, emit mercury.
- The cement industry is responsible for around 11% of global anthropogenic mercury emissions.
- Waste Disposal: Improper disposal of e-waste products containing mercury, such as fluorescent bulbs and batteries, leads to mercury leaching into the environment.
- Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM): ASGM is a major source of mercury pollution, where mercury is used to extract gold from ore.
- Natural Sources:
- Associated Impact:
- Methylmercury accumulates in aquatic organisms like fish. People primarily come into contact with methylmercury through the consumption of fish and shellfish.
- This compound carries a higher risk of causing Minamata disease, a condition characterized by sensory impairment, tremors, and both auditory and visual deficits.
- This illness was initially observed in the residents of Minamata Bay, Japan, who consumed mercury-contaminated fish due to industrial waste pollution.
- Methylmercury accumulates in aquatic organisms like fish. People primarily come into contact with methylmercury through the consumption of fish and shellfish.
Note: Methylmercury and ethylmercury differ significantly. While methylmercury is linked to health issues, ethylmercury is utilized as a preservative in certain vaccines and is not associated with health concerns.
Way Forward
- Mercury-Removing Filters: Innovative mercury-removal filters for industrial emissions, wastewater treatment, and consumer products can be designed and deployed.
- These filters could selectively capture and adsorb mercury particles from air and water streams.
- Phytoremediation: Phytoremediation, allows plants to absorb and accumulate mercury from soil, water, or sediments. These plants can then be harvested and safely disposed of, effectively removing mercury from the environment.
- Implementing planetGOLD Program: There is a need for global implementation of the planetGOLD program, led by UNEP, which seeks to eliminate mercury from artisanal gold mining and create safer working conditions. It operates under the Minamata Convention on Mercury.
- Funded by the Global Environment Facility, the program provides financial and technical support to help miners transition away from mercury use.
- planetGOLD's mercury-free processing plant in Burkina Faso serves as a model for transitioning away from mercury.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Indiscriminate disposal of used fluorescent electric lamps causes mercury pollution in the environment. Why is mercury used in the manufacture of these lamps? (2010)
(a) A mercury coating on the inside of the lamp makes the light bright white
(b) When the lamp is switched on, the mercury in the lamp causes the emission of ultra-violet radiations
(c) When the lamp is switched on, it is the mercury which converts the ultra-violet energy into visible light
(d) None of the statement given above is correct about the use of mercury in the manufacture of fluorescent lamps
Ans: (b)
Nutrition's Role in Tuberculosis Prevention
For Prelims: Tuberculosis, ICMR, Nikshay Poshan Yojna
For Mains: Challenges to eliminating TB, India’s progress in eliminating TB
Why in News?
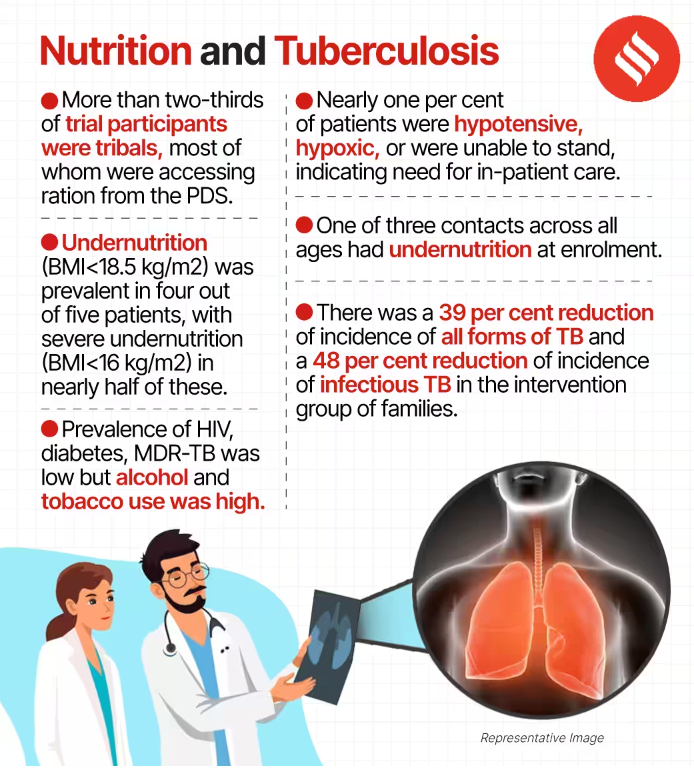
Recently, two studies conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and published in prestigious journals such as The Lancet and The Lancet Global Health, have unveiled a pivotal connection between nutrition and tuberculosis (TB) prevention.
- Reducing Activation of Tuberculosis by Improvement of Nutritional Status (RATIONS) trial shows correlation between nutritional support and the reduction of TB incidence.
- Weight gain's impact on TB mortality revealing how increased weight among malnourished TB patients correlates with reduced mortality rates.
Note:
- As per WHO, India accounts for 27% of the global TB incidence and 35% of total TB-related deaths.
- India is set to eliminate TB by 2025.
What are the Key Highlights of the Studies?
- A total of 5,621 people were given the nutrient-dense food for a year while 4,724 people received food parcels with no extra nutrition.
- At the end of the trial, there was a 39% reduction in TB incidence in the intervention group versus the control one.
- Weight gain decreased the risks of tuberculosis mortality in severely malnourished TB patients in Jharkhand.
- Instantaneous risk of death was reduced by 13% for a 1% weight gain and 61% for 5% weight gain.
- The study involved 2,800 severely malnourished TB patients in Jharkhand, with a prevalence of undernutrition in 4 out of 5 patients.
- Nutritional support was provided to individuals responding to TB drugs for six months, while the duration was 12 months for those with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
- An early weight gain in the first two months was associated with a 60% lower risk of TB mortality.
- Patients showed higher treatment success, better weight gain, and low rates of weight loss during follow-ups.
What is Tuberculosis?
- About:
- Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can practically affect any organ of the body. The most common ones are lungs, pleura (lining around the lungs), lymph nodes, intestines, spine, and brain.
- Transmission:
- It is an airborne infection that spreads through close contact with the infected, especially in densely populated spaces with poor ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Common symptoms of active lung TB are cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats.
- Treatment:
- TB is a treatable and curable disease.
- Anti-TB medicines have been used for decades and strains that are resistant to 1 or more of the medicines have been documented in every country surveyed.
- Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs.
- MDR-TB is treatable and curable by using second-line drugs such as Bedaquiline.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) is a more serious form of MDR-TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to the most effective second-line anti-TB drugs, often leaving patients without any further treatment options.
- Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs.
What are India's Initiatives to Combat TB?
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojna .
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.
- It was founded in 1911 with the name of Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA) and renamed as ICMR in 1949.
- It is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity
For Prelims: Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity, Digital Ecosystem, Know Your Customer, Point of Sale (POS), World Telecommunication Day.
For Mains: Reforms for Secure Digital Connectivity.
Why in News?
In order to promote Safe Telecom Utilisation, the government has introduced two reforms for mobile user protection to promote a cleaner and safer Digital Ecosystem.
- The two reforms, KYC (Know Your Customer) Reforms and Point of Sale (POS) registration Reform. These two reforms are in the direction of earlier reforms introduced with the launch of Sanchar Saathi, a citizen-centric portal that has empowered India's fight against the menace of cybercrimes and financial frauds.
What are the Reforms?
- KYC Reforms: KYC reforms play a pivotal role in safeguarding subscribers of telecom services from potential frauds and bolstering public confidence in the digital ecosystem.
- QR Code Scanning of Aadhaar: To prevent misuse of printed Aadhaar, demographic details are captured by scanning the QR code of printed Aadhaar during the KYC process.
- Mobile Number Disconnection: Disconnected mobile numbers will not be allocated to new customers for 90 days after disconnection, preventing immediate reuse.
- Complete KYC for SIM Replacement: Subscribers must complete KYC when replacing their SIM cards.
- Biometric Authentication: In addition to thumbprints and iris-based authentication, facial-based biometric authentication is permitted in Aadhaar E-KYC.
- Business Connections: Entities such as companies, organizations, trusts, and societies can obtain mobile connections after completing KYC for all end-users. Activation occurs only after successful KYC and physical verification of the entity's premises.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Registration Reforms: This reform aims to ensure the integrity of the distribution network by mandatorily registering Franchisees, Agents, and Distributors (PoS).
- The process involves robust verification and written agreements between PoS and Licensees. Any PoS engaged in illegal activities will be terminated and blacklisted for three years.
What is the Sanchar Saathi Portal?
- About:
- The Sanchar Saathi portal, developed by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) under the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), is revolutionizing the telecom sector in India.
- It was launched on World Telecommunication Day (17th May 2023).
- Objective:
- The primary objective of the Sanchar Saathi portal is to address various fraudulent activities prevalent in the telecom industry, such as identity theft, forged KYC, and banking fraud.
- By leveraging advanced technologies and frameworks, the portal aims to provide users with a secure and trustworthy telecommunication experience.
- The primary objective of the Sanchar Saathi portal is to address various fraudulent activities prevalent in the telecom industry, such as identity theft, forged KYC, and banking fraud.
- Reforms Introduced:
- CEIR (Central Equipment Identity Register):
- Implemented to block stolen or lost mobile phones.
- Users can submit IMEI numbers along with a copy of the police complaint to verify and block stolen devices.
- Integrated with Telecom Service Providers and Law Enforcement Agencies.
- Prevents stolen devices from being used in Indian networks and allows tracing by law enforcement when necessary.
- Know Your Mobile Connections:
- Allows users to check mobile connections registered in their name.
- Enables identification of unauthorized or fraudulent connections.
- Users can report fraudulent or unrequired connections, triggering re-verification and termination of reported connections.
- ASTR (Artificial Intelligence and Facial Recognition powered Solution for Telecom SIM Subscriber Verification):
- Developed to identify subscribers who obtain connections using fraudulent or forged documents.
- Utilizes facial recognition and data analytics techniques.
- Analyzes connections obtained through paper-based KYC documents.
- CEIR (Central Equipment Identity Register):
- Impact:
- Over 40 lakh fraudulent connections were identified and over 36 lakh were disconnected using the portal.
- Provides a secure and trustworthy telecommunication experience for users.
- Protects against identity theft, forged KYC, mobile device theft, and banking fraud.
Conclusion
- By introducing comprehensive reforms and harnessing technological tools like the 'Sanchar Saathi' portal and ASTR, the department has effectively identified and acted against fraudulent activities.
- This approach aligns with the government's mission to provide a secure and reliable communication environment for all citizens.
Agnibaan SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD)
Why in News?
Recently, AgniKul Cosmos, a space tech start-up based in Chennai, set to launch their groundbreaking Agnibaan SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator (SOrTeD), the world's first 3D-printed rocket into space.
- AgniKul Cosmos' journey is supported by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe).
What are the Key Highlights of AgniKul's SOrTeD?
- The Agnibaan SOrTeD is a customisable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages. It is powered by AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet, is a 3D-printed, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine that uses liquid oxygen and kerosene as propellants.
- Unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, Agnibaan SOrTeD will take off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory, executing precisely orchestrated maneuvers during its flight.
- It is capable of carrying payloads up to 100 kg to an altitude of 700 km in five different configurations.
- Agnibaan SOrTeD will be the first step towards launching the world’s first 3D-printed rocket into space.
What is 3D Printing?
- 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing which uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
- It is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which is cutting out/hollowing out a piece of metal or plastic with, for instance, a milling machine.
- 3D printing traditionally has been used for prototyping and has a lot of scope in making artificial limbs, stents, dental crowns, parts of automobiles and consumer goods, among others.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
For Prelims: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Neurodegenerative Disease, National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD), World Health Organization.
For Mains: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Challenges with it.
Why in News?
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a debilitating Neurodegenerative Disease, presents a range of challenges for both patients and caregivers in India.
- Despite its rare occurrence, ALS profoundly impacts the lives of those affected due to its progressive nature and lack of effective treatment.
What is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)?
- About:
- ALS is a rare and fatal type of motor neuron disease. It is characterized by progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain.
- It's often called Lou Gehrig's disease, after a famous baseball player who died from the disease.
- ALS is one of the most devastating of the disorders that affects the function of nerves and muscles.
- As motor neurons degenerate and die, they stop sending messages to the muscles, which causes the muscles to weaken, start to twitch (fasciculations), and waste away (atrophy).
- Eventually, the brain loses its ability to initiate and control Voluntary Movements.
- The movements that are under our control are called voluntary actions, such as walking, running, sitting etc.
- On the other hand, the movements that are not under our control are called involuntary movements.
- ALS is a rare and fatal type of motor neuron disease. It is characterized by progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain.
- Causes:
- Causes are not yet, in a few cases, genetics is involved.
- ALS research is looking into possible environmental causes of ALS.
- Symptoms:
- With ALS, there may be weakness in a limb that develops over a matter of days or, more commonly, a few weeks. Then, several weeks to months later, weakness develops in another limb. Sometimes the initial problem can be one of slurred speech or trouble swallowing.
- Treatment:
- There is no cure and proven treatment for ALS.
What are the Initiatives to Tackle ALS?
- The Government's National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD), 2021, introduced a significant provision offering financial aid of up to Rs. 50 lakh to patients afflicted by Rare Diseases and receiving treatment at designated Centers of Excellence.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) characterizes rare diseases as debilitating conditions with a prevalence of 1 or less per 1000 population.
- This policy initiative aims to support individuals, including those with conditions like ALS, by providing substantial financial assistance for their treatment.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India's Foreign Exchange Reserves
India's foreign exchange reserves have increased by USD 708 million to USD 602.16 billion for the week ended 11th August 2023, according to the latest data from the Reserve Bank of India.
- Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies, which can include bonds, treasury bills and other government securities.
- India’s Forex Reserve include:
- Foreign Currency Assets, Gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights, and Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- FCAs are assets that are valued based on a currency other than the country's own currency.
- Foreign Currency Assets, Gold reserves, Special Drawing Rights, and Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- The country's forex reserves reached an all-time high of USD 645 billion in October 2021.
Read more: Forex Reserves
Hurricane Hilary
- Hurricane Hilary is a major Category 4 hurricane that formed in the eastern Pacific Ocean on 16th August 2023.
- Hurricanes are categorized on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, which rates them on a scale of 1 to 5 based on wind speed.
- Hurricanes that reach category three or higher are classified as major hurricanes.
- It is the first tropical storm to hit Southern California since 1939.
- Hurricane Hilary is heading towards California because of a combination of factors, such as a high-pressure system over the western U.S., a low-pressure system over the eastern Pacific, and an El Niño event that warms the ocean water near the equator.
- These factors create a favorable environment for tropical cyclones to form and move northward along the coast of Mexico and Central America.
- However, most of these storms weaken or turn westward before reaching California, because of the cold water, cold currents, and unfavorable winds along the U.S. West Coast.
- Hilary is an exception because it has maintained its strength and followed a more northerly track than usual.
Spain Clinches Women FIFA World Cup 2023
The Women FIFA World Cup 2023 jointly hosted by Australia and New Zealand, featuring 32 teams concluded recently.
- The final match was held on 20 August 2023 where Spain defeated England 1-0 to lift their first-ever World Cup trophy. With this win, Spain also became only the second nation to clinch both the men’s and the women’s World Cups after Germany.
- The competition has seen four past champions: USA, Germany, Japan and Norway.
Read more: FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022
Onam
The exciting and colorful Onam festival has started in Kerala, bringing happiness, unity, and a lot of cultural beauty. The festival spans 10 days, commencing on Atham (the first day of Onam) and culminating on Thiruvonam (the final day).
- It is a major harvest festival in Kerala and is celebrated to honour the home-coming of Asura king Mahabali who brought about peace and prosperity in Kerala.
- It is also one of the three major festivals of Kerala, celebrated during the month of Chingam, the first month in the Malayalam calendar, Kollavarsham.
- The other two major festivals of the state are Vishu and Thiruvathira.
- A central aspect of Onam involves crafting Pookkalam, intricate flower rangolis. Alongside, a variety of rituals enrich the festivities, including Vallam Kali (boat races), Pulikali (tiger dances), Kummattikali (mask dances), and Onathallu (martial arts), among other captivating traditions.
Read more: Onam