Assam General Knowledge (GK) for APSC & State Exams | 18 Feb 2026
Assam GK is an important part of preparation for APSC, Assam Police, and other state-level exams. This page provides key facts about Assam’s geography, history, rivers, national parks, state symbols, demography, tribes, and culture in a concise, exam-focused format. It serves as a quick revision guide for static state knowledge.
|
Formation |
26 January 1950 (as a state after India became a Republic) |
|
Capital |
Dispur (suburb of Guwahati) |
|
Population |
31,205,576 (≈ 3.12 crore, Census 2011) |
|
Area |
~78,438 sq. km |
|
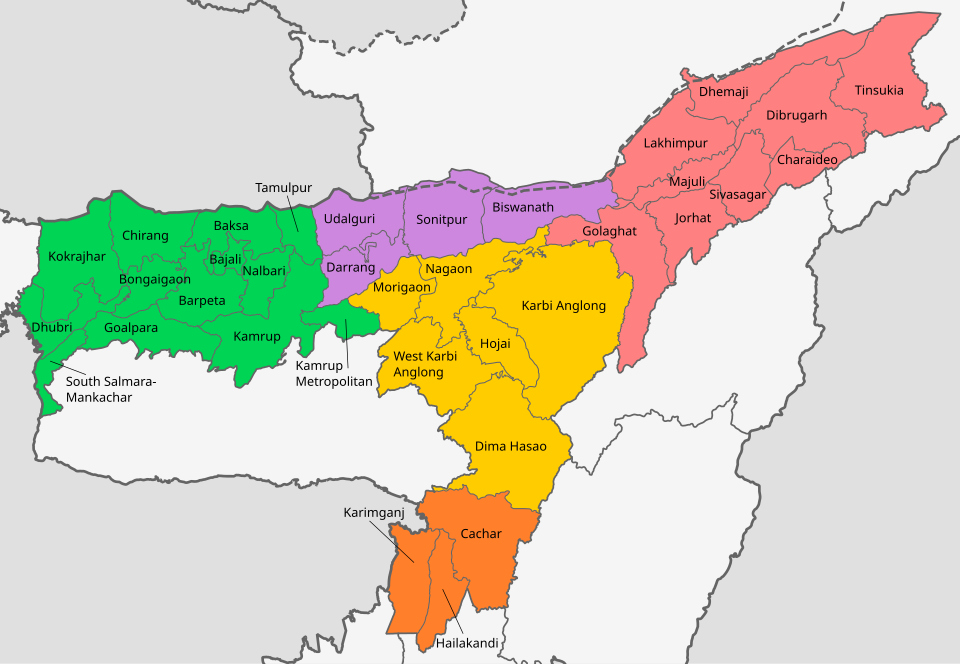
Total Districts |
35 |
|
Latitudinal extent |
24°8′ N to 28°2′ N |
|
Longitudinal extent |
89°41′ E to 96°0′ E |
|
High Court |
Gauhati High Court (Guwahati) |
|
Lok Sabha Seats |
14 |
|
Rajya Sabha Seats |
7 |
|
Vidhan Sabha Seats |
126 |
Assam State Symbols
Geography of Assam
- Physiographic region: Brahmaputra and Barak river plains, hills in Karbi Anglong & North Cachar
- Major rivers: Brahmaputra, Barak, Subansiri, Manas, Dhansiri, Kopili
- Doabs / Valleys: Brahmaputra Valley, Barak Valley
- Climate: Subtropical monsoon (high rainfall, hot summers, mild winters)
- Boundaries:
- North: Arunachal Pradesh, Bhutan
- East: Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram
- South: Meghalaya, Bangladesh
- West: West Bengal, Bhutan
- National Parks & Wildlife Sanctuaries:
- Wildlife sanctuaries:
- Garampani Wildlife Sanctuary
- Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bornadi Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chakrasila Wildlife Sanctuary
- Burachapori Wildlife Sanctuary
- Panidehing Wildlife Sanctuary
- Hollongapar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Pabitora Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sonai Rupai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bherjan - Borajan - Padumoni Wildlife Sanctuary
- East K. Anglong Wildlife Sanctuary
- Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary
- Marat Longri Wildlife Sanctuary
- Nambor - Doigrung Wildlife Sanctuary
- Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Borail Wildlife Sanctuary
- Deepar Beel Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bordoibam Bilmukh Bird Wildlife Sanctuary
- North K. Anglong Wildlife Sanctuary (Proposed)
Major Rivers of Assam and Their Origin
|
River |
Origin (Source) |
Remarks |
|
Brahmaputra |
Angsi Glacier, Tibet (as Yarlung Tsangpo) |
Flows west to east through Assam; major flood river |
|
Barak |
Manipur hills |
Divides into Surma & Kushiyara in Bangladesh |
|
Subansiri |
Tibet |
Major tributary of Brahmaputra |
|
Manas |
Bhutan |
Tiger reserve area, enters Assam in northern valley |
|
Dhansiri |
Nagaland |
Tributary of Brahmaputra |
|
Kopili |
Meghalaya |
Hydropower projects; tributary of Brahmaputra |
Major Lakes / Wetlands of Assam
|
Lake / Wetland |
Location |
Type / Importance |
|
Deepor Beel |
Guwahati |
Ramsar Site; freshwater lake & bird habitat |
|
Maguri Beel |
Tinsukia |
Important wetland for migratory birds |
|
Urpad Beel |
Goalpara |
Freshwater lake, local fishing |
|
Gaurisagar Lake |
Sivasagar |
Historical tank built by Ahom kings |
|
Son Beel |
Karimganj |
Largest wetland in Barak Valley |
Major Dams / Hydroelectric Projects in Assam
|
Dam / Project |
River |
Location |
Purpose / Importance |
|
Khandong Dam |
Umrong |
Jaintia Hills (Meghalaya) |
Hydroelectric power |
|
Kopili Dam |
Kopili |
Nagaon / Karbi Anglong |
Hydropower, irrigation |
|
Ranganadi Dam |
Ranganadi |
Arunachal Pradesh (affects Assam) |
Hydropower; part of Brahmaputra basin projects |
History of Assam
- Ancient period:
- Early settlers: Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burman tribes
- Known in Puranic texts as Pragjyotisha
- Medieval era:
- Ahom dynasty (1228–1826) ruled for 600+ years
- Resistance against Mughals (Battle of Saraighat, 1671)
- British period:
- Came under British control after Treaty of Yandabo (1826)
- Assam formed as separate province in 1874
- Post-independence:
- Initially included modern Assam, Meghalaya, Nagaland & Mizoram
- Nagaland became state in 1963
- Meghalaya in 1972
- Mizoram in 1987 (statehood)
Demography
- Total population (2011): 31,205,576 (≈ 3.12 crore)
- Population rank (2011): 15th
- Urban population: ~14%
- Rural population: ~86%
- Population density: 398 persons/sq. km
- Decadal growth rate (2001–2011): 17.07%
- Sex ratio: 958 females per 1000 males
- Literacy rate:
- Overall: 72.2%
- Male: 77.85%
- Female: 66.27%
- Largest populated district: Nagaon
- Least populated district: Dima Hasao
Folk Dance
|
Dance Form |
Key Features |
|
Bihu Dance |
Energetic, performed during Rongali Bihu; both male & female participation |
|
Sattriya |
Classical dance from Vaishnavite monasteries (Satras) |
|
Bagurumba |
Bodo folk dance; graceful & rhythmic movements |
|
Jhumur |
Performed by tea tribe communities |
|
Bhaona |
Devotional dance-theatre by Assamese Vaishnavism |
Major Tribes of Assam
|
Tribe |
Main Area / Districts |
|
Bodo |
Kokrajhar, Chirang, Baksa, Udalguri |
|
Mishing (Miri) |
Majuli, Dhemaji, Lakhimpur |
|
Karbi |
Karbi Anglong |
|
Dimasa (Kachari) |
Dima Hasao, Cachar |
|
Rabha |
Goalpara, Kamrup |
|
Tiwa (Lalung) |
Morigaon, Nagaon |
|
Deori |
Lakhimpur, Sonitpur |
|
Sonowal Kachari |
Dibrugarh, Lakhimpur |
|
Mech |
Western Assam |
|
Hajong |
Goalpara, Dhemaji |
|
Zeme |
Dima Hasao |
|
Kuki |
Dima Hasao |
|
Hmar |
Cachar, Dima Hasao |
Static GK is the backbone of state-level exams, and staying current is key. Use this Assam GK page for regular revision of important facts and figures relevant to competitive exams. Combine it with current affairs and previous year questions to strengthen your preparation and improve accuracy in state-related sections.
We hope this concise guide helps you streamline your revision. Bookmark this page for quick access before your exam, and share it with fellow aspirants to help them succeed too.
|
Related Resources |
|
|
APSC CCE Exam Pattern |
|
|
APSC CCE Previous Year Papers |
|
|
APSC CCE Exam Syllabus |
|
|
APSC Exam Strategy |
|
|
Monthly CA Consolidations |
|