SPUN Atlas Highlights Gaps in Mycorrhizal Fungi Conservation | 30 Jul 2025
The Society for the Protection of Underground Networks (SPUN) has launched the Underground Atlas, which shows that over 90% of mycorrhizal fungi hotspots lie outside protected areas, despite their key role in nutrient cycling and carbon sequestration.
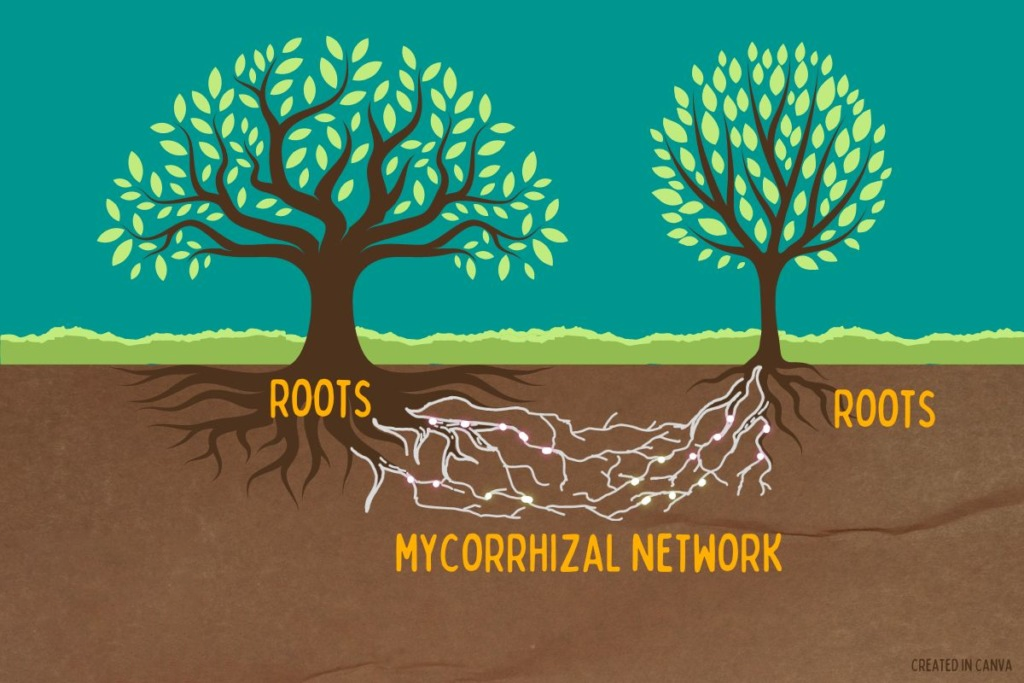
- Role in Ecosystem: Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with over 80% of plants, aiding nutrient absorption like phosphorus and playing a key role in carbon sequestration by utilizing CO2 from plant roots.
- They store around 13 billion tonnes of CO2 annually, or one-third of global fossil fuel emissions.
- Types of Mycorrhizal fungi:
- AM (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal) fungi: They penetrate root cells, common in crops and grasses.
- Hotspots: Brazilian Cerrado, Southeast Asia, West Africa
- EcM (Ectomycorrhizal) fungi: They wrap around roots, common in forest trees like oak and pine.
- Hotspots: Canada, Siberia, Central Europe, Western US.
- AM (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal) fungi: They penetrate root cells, common in crops and grasses.
- Recognising the ecological significance of fungi and other soil organisms, the FAO launched the Global Soil Biodiversity Observatory (GLOBSOB) at COP15 of the Convention on Biological Diversity in Canada, a global effort to monitor, protect, and integrate soil life into environmental policy.
| Read More: Flora Fauna and 'Funga' |