Human Development Report 2021-22 | 09 Sep 2022
For Prelims: Human Development Report, Human Development Index(HDI), United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Gross national income (GNI), Sustainable Development Goals, Gender Inequality Index, Multidimensional Poverty Index.
For Mains: Human Development Report 2021-22.
Why in News?
According to the Human Development Report 2021-22, India’s rank on the Human Development Index (HDI) has slipped from 130 in 2020 to 132 in 2022, in line with a global fall in HDI scores in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
What is Human Development Report?
- About:
- Human Development Reports (HDRs) have been released since 1990 and have explored different themes through the human development approach.
- It's published by the Human Development Report Office for the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- Goal: The goal is to contribute toward the expansion of opportunities, choice and freedom.
- Theme: The theme for Human Development Report 2021-22 is Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives: Shaping our Future in a World in Transformation.
What is the Human Development Index?
- HDI is a composite index that measures average achievement in human development taking into account four indicators:
- Life expectancy at birth (Sustainable Development Goal 3),
- Expected years of schooling (Sustainable Development Goal 4.3),
- Mean years of schooling (Sustainable Development Goal 4.4),
- Gross national income (GNI) (Sustainable Development Goal 8.5).
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Human Development Index:
- Drop in Life Expectancy: A large contributor to the Human Development Index’s recent decline is a global drop in life expectancy, down from 72.8 years in 2019 to 71.4 years in 2021.
- The last two years have had a devastating impact on billions of people worldwide when crises like Covid-19 and the war in Ukraine hit back to back and interacted with sweeping social and economic shifts and dangerous planetary changes.
-
Top Performers:
-
European states were among the best overall performers, with as many as 8 in the top 10 of the list.
-
These are Switzerland (1, 0.962), Norway (2, 0.961), Iceland (3, 0.959), Denmark (6, 0.948), Sweden (7, 0.947), Ireland (8, 0.945), Germany (9, 0.942) and Netherlands (10, 0.941).
-
-
Asian Region:
-
At 73 and with an index value of 0.782, Sri Lanka emerged as the best performer in the Indian sub-continent. The island nation was followed by China (79 and 0.768), Bhutan (127 and 0.666), Bangladesh (129 and 0.661), India, Nepal (143 and 0.602) and Pakistan (161 and 0.544).
-
- Indian Perspective:
- Human Development Index: India’s HDI value stood at 0.633 in 2021, which was lower than the world average of 0.732. In 2020, too, India recorded a decline in its HDI value (0.642) in comparison to the pre-Covid level of 2019 (0.645).
- Life expectancy: In 2021, India’s life expectancy at birth was recorded at 67.2 years.
- Schooling: Expected years of schooling at 11.9 years, mean years of schooling at 6.7 years,
- Gross National Income: The gross national income per capita stood at USD 6,590.
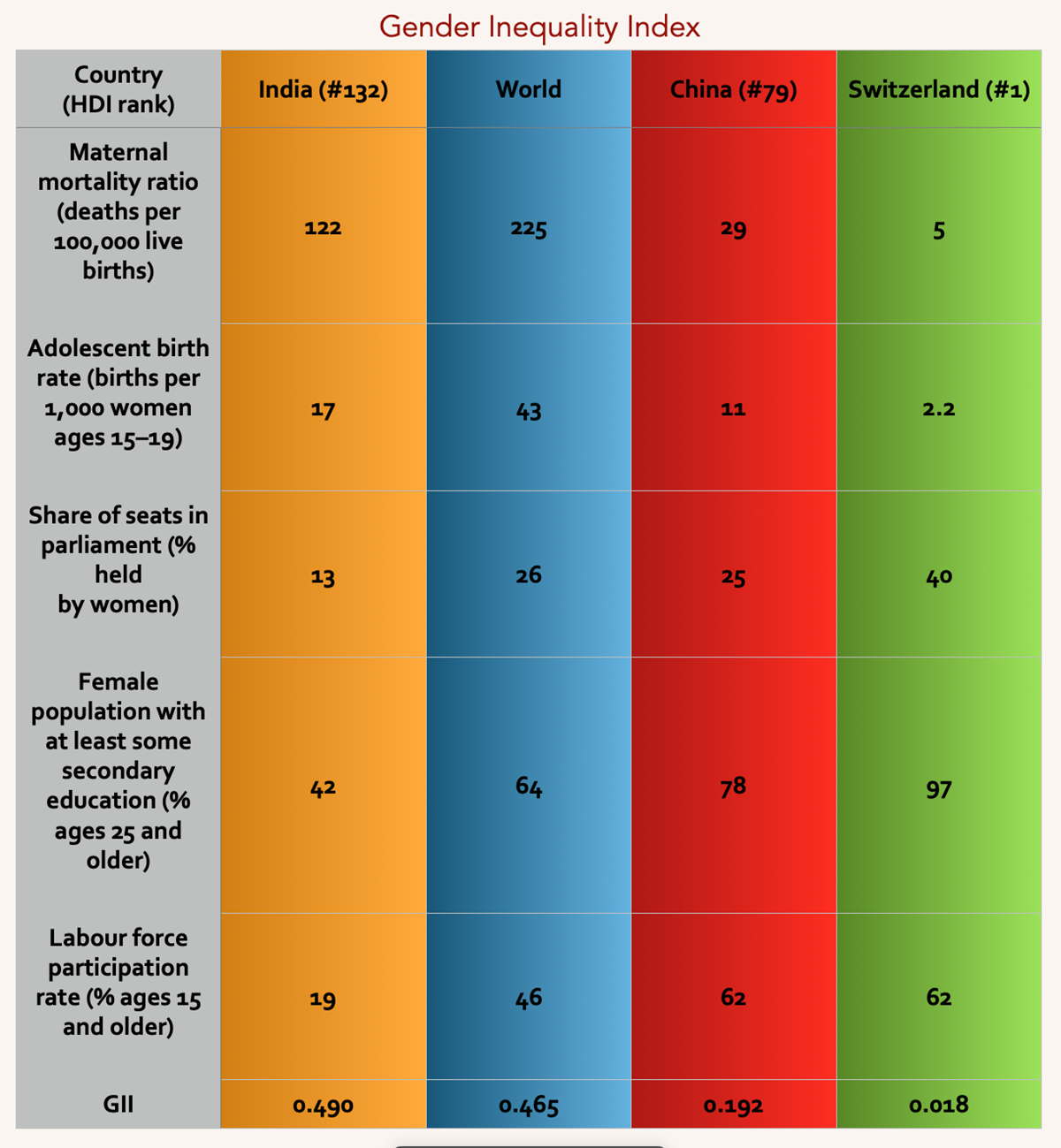
- Gender Inequality Index: India has been ranked 122 on the Gender Inequality Index.
- Drop in Life Expectancy: A large contributor to the Human Development Index’s recent decline is a global drop in life expectancy, down from 72.8 years in 2019 to 71.4 years in 2021.
-
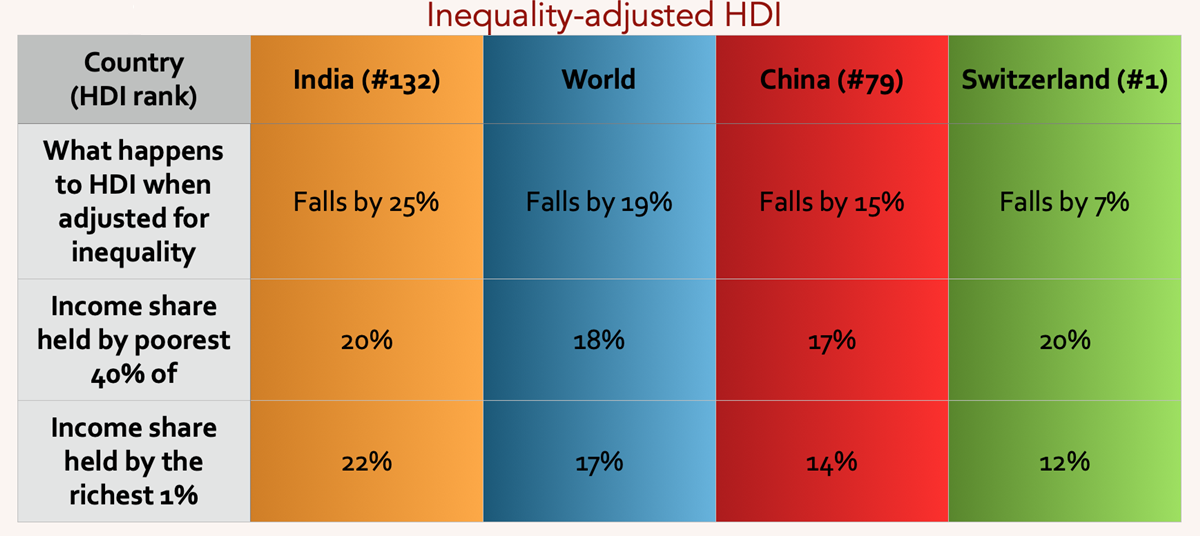
Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index:
-
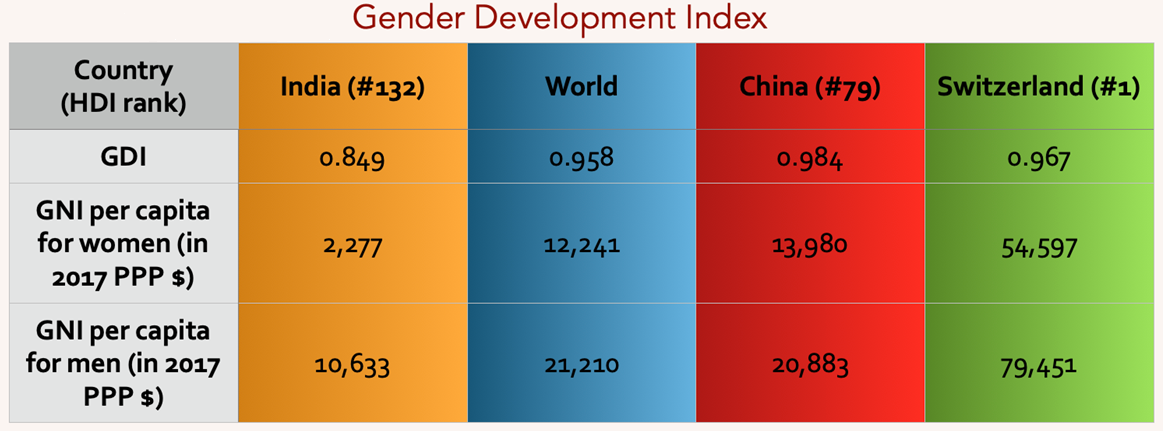
Gender Development Index:
- Gender Inequality Index:
-
GII presents a composite measure of gender inequality using three dimensions:
-
Reproductive health,
-
Empowerment and
-
The labour market.
-
-
In GII, India is at the 122nd rank.
-
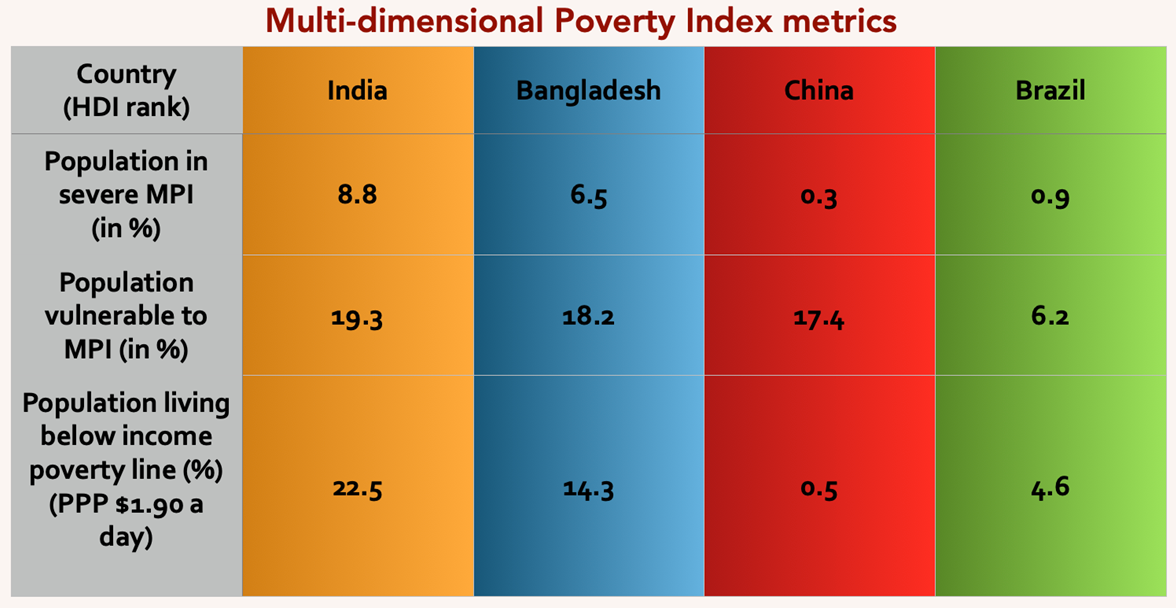
- Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI):
-
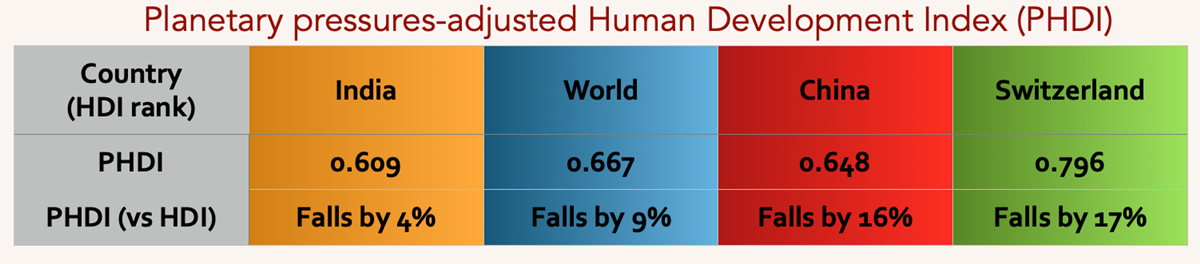
Planetary pressures-adjusted Human Development Index:
-
It adjusts the HDI for planetary pressures in the Anthropocene to reflect a concern for intergenerational inequality, similar to the Inequality-adjusted HDI adjustment — which is motivated by a concern for intragenerational inequality.
-
The PHDI value can be interpreted as the level of human development adjusted by carbon dioxide emissions per person (production-based) and material footprint per person to account for excessive human pressure on the planet.
-
- Other insights:
- Humans are not prepared for climate change: It stated that humans were unprepared for a world with climate crises like fires and storms and other planetary-level changes brought about due to the Anthropocene in recent years.
- Population Decline of Insects: Without an abundance of insect pollinators, humans face the mind-boggling challenge of growing food and other agricultural products at scale.
- As insects are important because of their diversity, ecological role and influence on agriculture, human health and natural resources.
- They create the biological foundation for all terrestrial ecosystems, further, they cycle nutrients, pollinate plants, disperse seeds, maintain soil structure and fertility, control populations of other organisms and provide a major food source for other taxa.
- Microplastic menace: Plastics are now everywhere, in country-sized garbage patches in the ocean, in protected forests and distant mountaintops and in people’s lungs and blood.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
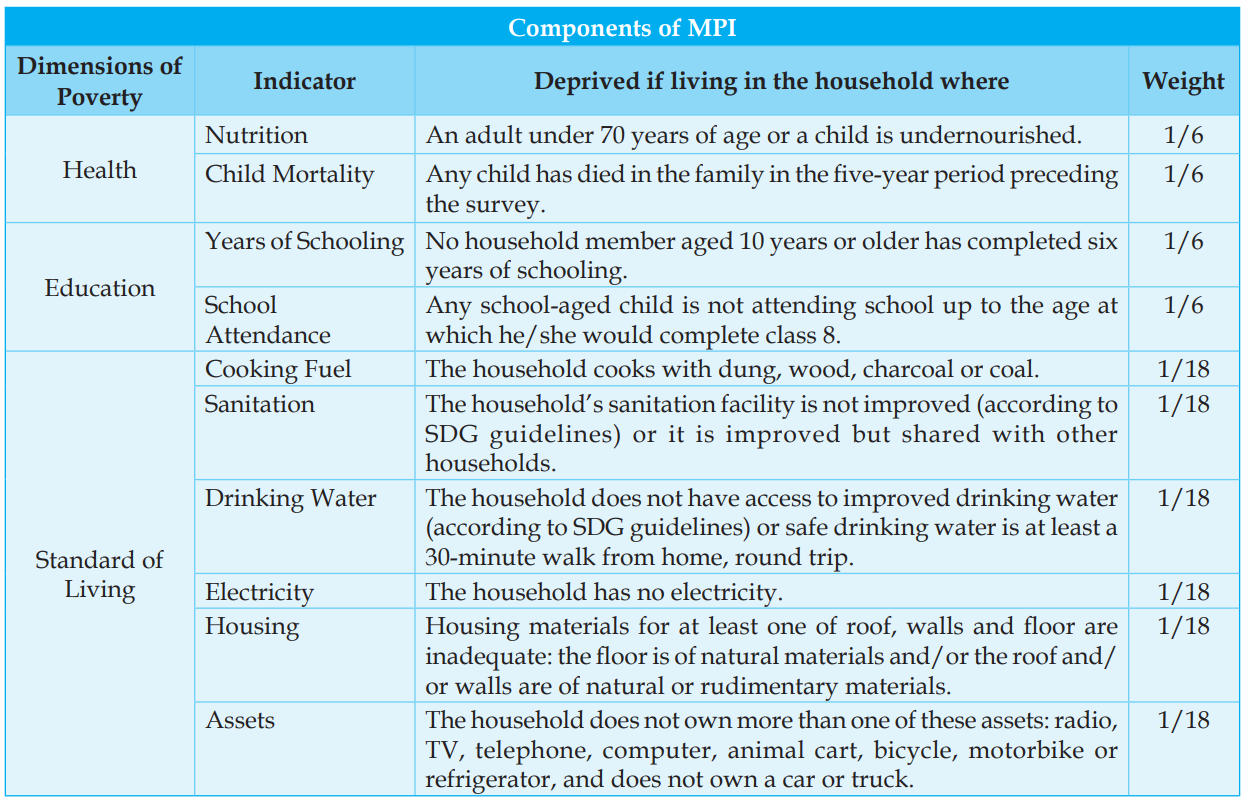
Q. The Multi-dimensional Poverty Index developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative with UNDP support covers which of the following? (2012)
- Deprivation of education, health, assets and services at household level
- Purchasing power parity at national level
- Extent of budget deficit and GDP growth rate at national level
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) reflects the deprivations that a poor person faces simultaneously with respect to education, health and living standards, as reflected in the following table. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Despite Consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (2016)