Ecuador & Peru | 23 Aug 2025
Indigenous communities in Ecuador and Peru opposed a new oil deal, citing risks of deforestation, river pollution, biodiversity loss, and ecological damage in the Amazon rainforests.
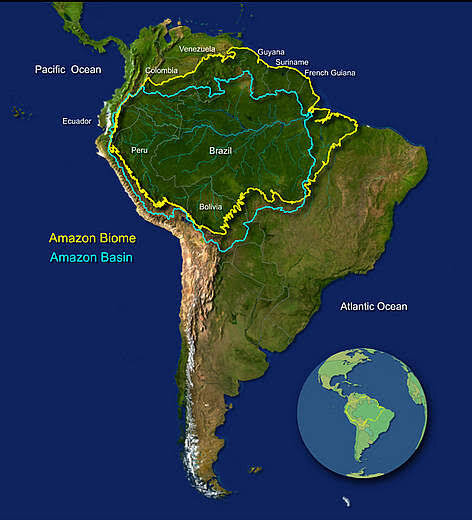
Amazon Rainforests
- About: The Amazon Rainforest is the largest tropical rainforest in the world, covering around 6.7 million sq km in the Amazon River basin of northern South America.
- About 60% of the rainforest is in Brazil, while the remaining area is shared among Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, Venezuela, and French Guiana, making it the largest drainage system globally.
- It is bounded by the Guiana Highlands (north), Andes Mountains (west), Brazilian Central Plateau (south), and the Atlantic Ocean (east).
- Ecological Significance: Covers over half of the world’s rainforest volume, crucial for biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and climate regulation.
- Though only 1% of Earth’s surface, it sustains around 10% of global wildlife, including habitats for river dolphins and over 70% of the world’s jaguars.
Ecuador
- Ecuador (with capital Quito) lies in western South America between Colombia and Peru. The Equator line passed through it.
- The Andes run through Ecuador, with Cotopaxi as the highest active volcano.
Peru
- Situated on the western coast of South America, Peru (capital- Lima) connects the Pacific Ocean, Andes Mountains and the Amazon Basin.
- It shares borders with Ecuador and Colombia (north), Brazil (east), and Bolivia and Chile (south).
- Key drainage includes the Amazon River and Lake Titicaca (world’s highest navigable lake, shared with Bolivia).
- About 60% of Peru is covered by the Amazon forest.
- Other features include Atacama Desert (southern Peru), Nazca Lines, and the Humboldt Current and El Niño.
| Read More: Galápagos Islands |