Dibru-Saikhowa National Park | 19 Aug 2025
Dibru-Saikhowa National Park (DSNP) in Assam is witnessing significant ecological changes due to native and invasive plant species.
Major Threats:
- Invasive Plants: Species like Chromolaena odorata, Ageratum conyzoides, Parthenium hysterophorus, and Mikania micrantha outcompete native flora, degrade grasslands, and threaten grassland-dependent fauna.
- Native Grassland Invaders: Bombax ceiba (Simalu) and Lagerstroemia speciosa (Ajar) alter natural vegetation, increasing shrubland and degraded forest cover.
- Flooding and Anthropogenic Pressures: Recurring Brahmaputra floods, forest villages, grazing, and resource extraction causing soil erosion, fragment habitats, and accelerating biodiversity loss.
- Land Use & Land Cover Changes (2000–2024): Conversion of Grasslands and semi-evergreen forests to shrubland and degraded forests reducing habitat for endemic and grassland-dependent species like Bengal florican, Hog deer, and Swamp grass babbler, and threatening endemic feral horses (around 200 individuals left).
Dibru-Saikhowa National Park (DSNP)
- Location: Located in Assam, is bounded by the Brahmaputra and Lohit Rivers(north) and Dibru River (south).
- Biosphere Reserve: In 1997, UNESCO designated the area as a Biosphere Reserve.
- Vegetation & Climate: Semi-evergreen, deciduous, littoral, swamp, and wet evergreen forests, including the largest Salix swamp forest in northeast India.
- It has a tropical monsoon climate with hot, wet summers and cool, dry winters.
- Flora & Fauna: Flora: Dillenia indica, Bischofia javanica, Bombax ceiba, Lagerstroemia parviflora.
- Fauna: tiger, elephant, leopard, jungle cat, bears, small Indian civet, squirrels, Gangetic dolphin, slow loris, Assamese macaque.
- It is an important Bird Area (IBA) with 382+ bird species, including greater and lesser adjutant storks, greater crested grebe.
Note:
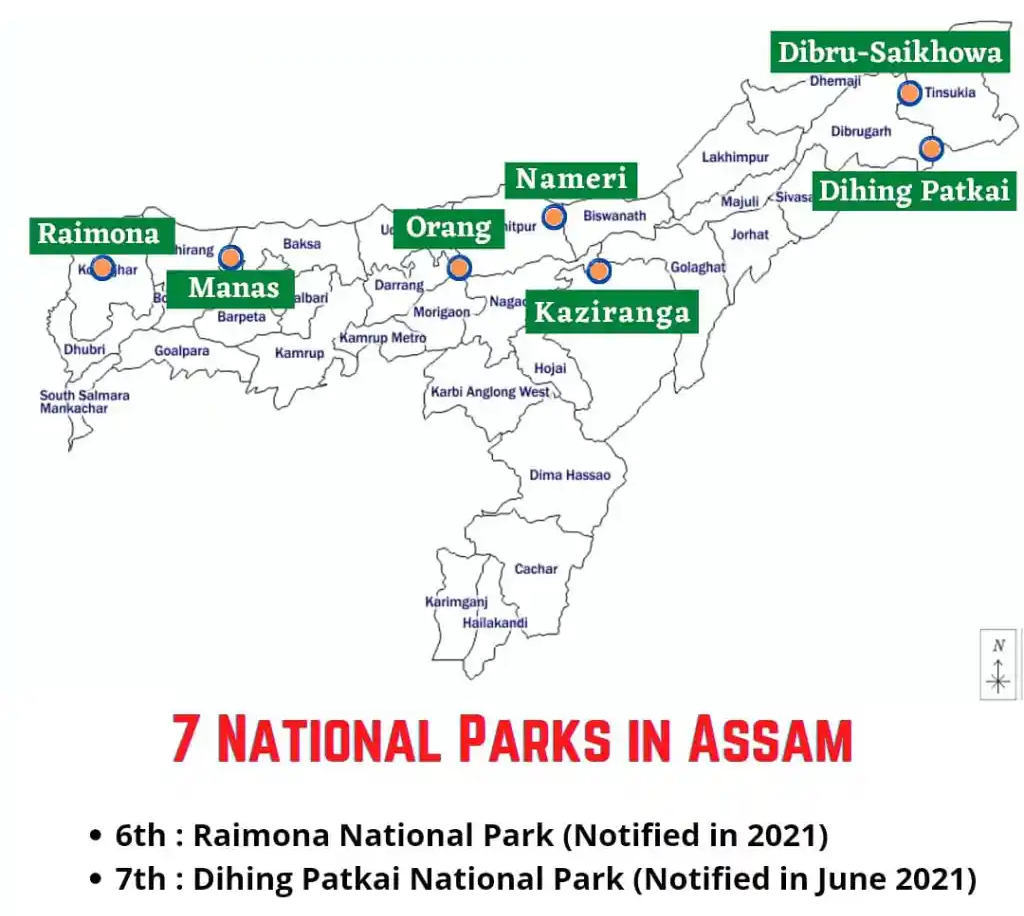
- Assam has 7 national parks:
| Read More:Concerns Over Drilling in Dibru-Saikhowa National Park |