2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium | 28 Oct 2025
For Prelims: India Mobile Congress, Bharat 6G Alliance, Telecom Technology Development Fund, International Telecommunication Union
For Mains: Bharat 6G Vision and its alignment with Digital India and Viksit Bharat 2047, Challenges in India’s 6G deployment and the roadmap for readiness
Why in News?
At the India Mobile Congress(IMC) 2025, India highlighted its growing leadership in next-generation telecom through the 2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium, marking a key step towards building a self-reliant, innovative, and globally connected 6G ecosystem for Viksit Bharat 2047.
- The IMC is Asia's most prominent technology expos, jointly organized by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) and the Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI).
What are the Key Outcomes of 2nd International Bharat 6G Symposium at IMC 2025?
- New Delhi Declaration on 6G: At the Symposium, global research alliances including Bharat 6G, 6G-IA (European organization), ATIS’ Next G Alliance (North American organization), and others issued a Joint Declaration to shape 6G as a global public good.
- The declaration outlines five core principles for 6G networks that are trusted and secure, resilient and reliable, open and interoperable, inclusive and affordable, and sustainable and globally connected.
- The declaration also calls for skills development and global collaboration to build a future-ready, inclusive 6G ecosystem aligned with India’s 6G Vision 2030.
- Economic Vision: The symposium highlighted India’s 6G roadmap aiming for USD 1.2 trillion GDP impact by 2035 and 10% of global 6G patents, along with a threefold growth in satellite communications by 2033.
- The Symposium showcased India’s indigenous 4G stack as a milestone toward technological self-reliance and export readiness.
- Focus on Collaboration and Inclusivity: The symposium urged stronger global collaboration, indigenous R&D, and industry- academia synergy to build an inclusive 6G framework.
- It highlighted India’s shift from a technology consumer to a co-creator and global leader, backed by milestones like the rollout of one lakh indigenous 4G towers.
What is Bharat 6G Vision?
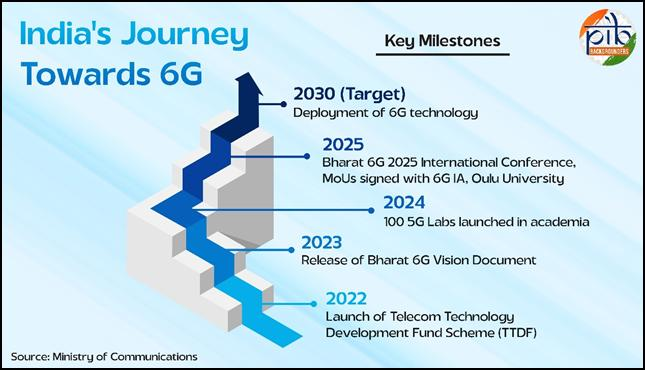
- Bharat 6G Vision: Launched in 2023, Bharat 6G Vision aims to position India as a global leader and co-creator in next-generation wireless communication.
- It aligns with the Viksit Bharat 2047 goals, focusing on affordability, sustainability, and universal access by 2030.
- Features of the Vision:
- Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA): An industry-led, government-facilitated body uniting telecom operators, academia, startups, and R&D institutions.
- It focuses on domains like spectrum, technology, sustainability, applications, and use cases.
- Bharat 6G Alliance signed a Memorandum of Understanding with global alliances including Next G Alliance (USA), 6G-IA (Europe), 6G Forum (South Korea), 6G Flagship (Finland), 6G Brazil, and others to collaborate on research and global standards.
- As of July 2025, the alliance comprises over 80 member organizations.
- It is also working with Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI) and National Association of Software and Services Companies(NASSCOM) to leverage national expertise and ensure resilient, trusted supply chains.
- Bharat 6G Mission:Aims to make India a global co-creator and leader in 6G technologies by 2030.
- Focuses on indigenous innovation, capacity building, and skills development.
- Emphasizes sustainability, security, and inclusivity in telecom development.
- Seeks to ensure that 6G innovation originates in India and benefits both national and global communities.
- Infrastructure: The government funded two advanced testbeds, the 6G THz Testbed and the Advanced Optical Communication Testbed to promote research and innovation in next-generation telecom technologies.
- It also sanctioned 100 5G labs across academic institutions in FY 2023–24 to build a 6G-ready academic and startup ecosystem, and approved 104 research proposals on 6G network systems.
- India’s Initiatives for 6G Ecosystem:
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF): Launched in 2022 to fund R&D in 5G and 6G technologies.
- TTDF supports domestic companies, startups, and academic institutions developing telecom products for affordable rural connectivity.
- As of September 2025, 115 projects worth Rs 310.6 crore have been approved, with durations of 1–5 years.
- Technology Innovation Hub (TIH) at IIIT Bangalor: Set up under National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS), to pioneer Advanced Communication Systems for 5G+ and 6G.
- Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF): Launched in 2022 to fund R&D in 5G and 6G technologies.
6G (Sixth-Generation)
- It is the successor to 5G cellular technology. 6G will use higher radio frequencies to deliver data with near-zero delay, enabling speeds up to 1,000 times faster than 5G.
- The 6G Technology has been named ‘International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT) 2030’ by International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the specialised agency for Information and Communication Technologies of the United Nations.
- 6G will power real-time applications like remote surgery, smart robotics, and immersive virtual experiences, while AI integration will make networks smarter, faster, and more efficient.
What are the Challenges Related to 6G Implementation in India?
- Infrastructure Readiness: India’s current 5G rollout is still expanding, and the shift to 6G will demand dense fiber networks, advanced semiconductors, and indigenous hardware, areas where domestic capability is still limited.
- Limited R&D Ecosystem: Despite initiatives like the Bharat 6G Mission, India’s research output, patents, and private investment in frontier telecom technologies remain modest compared to global leaders like China and US.
- Spectrum and Standards Gap: The allocation and regulation of terahertz (THz) bands for 6G are still evolving globally, leaving India with uncertainty in planning its 6G roadmap.
- Talent and Skill Shortage: There’s a shortage of trained professionals in AI, photonics, and network engineering needed for indigenous 6G innovation.
- Affordability and Digital Divide: High deployment costs could widen the gap between urban and rural connectivity if not supported by inclusive policies.
- Security and Privacy Risks: With ultra-fast data transfer and massive device connectivity, ensuring cybersecurity and data protection becomes more complex.
What Steps are Needed to Ensure Successful Implementation of India’s 6G Vision?
- Promote Indigenous Manufacturing: Integrate 6G components under Production Linked Initiative (PLI) Schemes for telecom, semiconductors, and electronics to reduce import dependency and enhance domestic production.
- Skill Development and Human Capital: Expand 5G Labs in academic institutions to create a 6G-ready talent pool and promote interdisciplinary courses in AI, IoT, photonics, and network engineering.
- Spectrum Policy and Regulation: Formulate a forward-looking National Spectrum Strategy for THz frequencies and encourage global harmonization through participation in ITU and global standard-setting bodies.
- Inclusive Access and Affordability: Align 6G rollout with Digital India and BharatNet to ensure equitable access in rural and remote regions, avoiding a new digital divide.
Conclusion
India’s 6G journey reflects its shift from a technology adopter to a global innovator. With initiatives like the Bharat 6G Alliance, and strong global partnerships, the country is building a secure, inclusive, and future-ready telecom ecosystem paving the way for a self-reliant and digitally empowered Viksit Bharat by 2047.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. India’s 6G Vision aims to position the country as a global co-creator in next-generation telecom. Discuss. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Bharat 6G Vision 2030?
Launched in 2023, it aims to make India a global leader and co-creator in 6G, focusing on affordability, sustainability, and universal access by 2030.
2. What is the Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF)?
Launched in 2022, TTDF funds R&D and indigenous innovation in 5G and 6G technologies to boost rural connectivity and domestic manufacturing.
3. What is the Bharat 6G Alliance?
An industry-led and government-facilitated body uniting telecom operators, academia, startups, and R&D institutions to drive indigenous innovation and develop global 6G standards.
4. What is IMT-2030?
It is the official name for 6G technology designated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the UN agency for ICT standards.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)