Doctrine of Separation of Powers
For Prelims: Doctrine of Separation of Powers, Basic Structure of Constitution, Supreme Court, NJAC Act
For Mains: Doctrine of Separation of Power and issues, Basic Structure of Constitution
Why in News?
Recently, Vice-President of India has rekindled the debate over the doctrine of separation of powers by citing the Supreme Court's landmark 1973 Kesavananda Bharati case, which ruled that Parliament has the authority to amend the Constitution but not its basic structure.
What is the Doctrine of Separation of Powers?
- Separation of powers is the division of the legislative, executive, and judicial functions of government.
- Article 50 says that states shall take steps to separate the Judiciary from the Executive.
- The constitutional demarcation precludes the concentration of excessive power by any branch of the government.
- The Indian Constitution lays down the structure and defines and determines the role and functions of every organ of the State and establishes norms for their inter-relationships and checks and balances.
What are the Instruments of Checks & Balances?
- Legislature Control:
- On Judiciary: Impeachment and the removal of the judges. Power to amend laws declared ultra vires by the Court and revalidating it.
- On Executive: Through a no-confidence vote it can dissolve the Government. Power to assess works of the executive through the question hour and zero hour.
- Executive Control:
- On Judiciary: Making appointments to the office of Chief Justice and other judges.
- On Legislature: Powers under delegated legislation. Authority to make rules for regulating their respective procedure and conduct of business subject to the provisions of this Constitution.
- Judicial Control:
- On Executive: Judicial review i.e., the power to review executive action to determine if it violates the Constitution.
- On Legislature: Unamendability of the constitution under the basic structure doctrine pronounced by the Supreme Court in Kesavananda Bharati Case 1973.
What are the Issues with the Separation of Powers?
- Weakened Opposition in India: Democracy works on the principle of checks and balances. It is these checks and balances that prevent democracy from turning into majoritarianism.
- In a Parliamentary system, these checks and balances are provided by the opposition party.
- However, the majority of a single party in the Lok Sabha has diminished the role of an effective opposition in the Parliament.
- Judiciary Being Averse to Checks & Balances: The Supreme Court has held the 99th constitutional amendment, which provided for the establishment of the National Judicial Appointments Commission as ultra-vires.
- The NJAC could guarantee the independence of the system from inappropriate politicization, strengthen the quality of appointments, enhance the fairness of the selection process, promote diversity in the composition of the judiciary, and rebuild public confidence in the system.
- Judicial Activism: In many recent judgments, the SC has become hyper-activist in making judgements that are deemed as laws and rules. This transgresses the domain of legislature and executive.
- Executive Excesses: Executive in India is alleged of over-centralisation of power, weakening of public institutions and passing laws to strengthen law, order & security of the state but curbs freedom of expression as well.
What is the Basic Structure of the Constitution?
Way Forward
- The Constitution of India is an organic or living document and needs to be amended with the changing time and needs of the society.
- The framers of the Indian Constitution recognized that no generation possesses a monopoly on wisdom and cannot dictate what government should look like to future generations.
- However, such power of amendment must be used judiciously.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The Constitution of India defines its ‘basic structure’ in terms of federalism, secularism, fundamental rights and democracy.
- The Constitution of India provides for ‘judicial review’ to safeguard the citizens’ liberties and to preserve the ideals on which the Constitution is based.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Constitution of India does not define the basic structure, it is a judicial innovation.
- In Kesavananda Bharati vs State of Kerala case (1973), the Supreme Court ruled that the Parliament could amend any part of the Constitution so long as it did not alter or amend the basic structure or essential features of the Constitution.
- However, the court did not define the term ‘basic structure’, and only listed a few principles — federalism, secularism, democracy — as being its part.
- The ‘basic structure’ doctrine has since been interpreted to include the supremacy of the Constitution, the rule of law, Independence of the judiciary, doctrine of separation of powers, sovereign democratic republic, the parliamentary system of government, the principle of free and fair elections, welfare state, etc. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- There is no direct and express provision in the constitution empowering the courts to invalidate laws, but the constitution has imposed definite limitations upon each of the organs, the transgression of which would make the law void. The court is entrusted with the task of deciding whether any of the constitutional limitations has been transgressed or not. Hence, statement 2 is not correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Starting from inventing the ‘basic structure’ doctrine, the judiciary has played a highly proactive role in ensuring that India develops into a thriving democracy. In light of the statement, evaluate the role played by judicial activism in achieving the ideals of democracy. (2014)
Q2. Resorting to ordinances has always raised concern on violation of the spirit of separation of power doctrine. While noting the rationales justifying the power to promulgate ordinances, analyse whether the decision of the Supreme Court on the issue have further facilitated to resorting to this power. Should the power to promulgate the ordinances be repealed? (2015)
Q3. Do you think that Constitution of India does not accept principle of strict separation of powers rather it is based on the principle of ‘checks and balance’? Explain. (2019)
Q4. Judicial Legislation is antithetical to the doctrine of separation of powers as envisaged in the Indian Constitution. In this context justify the filing of large number of public interest petitions praying for issuing guidelines to executive authorities. (2020)
Supreme Court on Freedom of Speech of Ministers
For Prelims: Supreme Court, Fundamental Rights, Supreme Court on Freedom of Speech of Ministers
For Mains: Important Judgements, Freedom of Speech of Ministers
Why in News?
Recently, a Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court unanimously and rightly ruled out any additional curbs on free speech by ministers.
What is the Background?
- The case (Kaushal Kishor v the State of UP), relates to the Bulandshahar rape incident of 2016, in which the then Minister of the State termed the incident a ‘political conspiracy and nothing else’.
- A writ petition was filed by the survivors before the SC and the court raised an important question: “Can restrictions be imposed on a public functionary's freedom of speech and expression?”.
What is the Judgement of the Court?
- Majority Judgement:
- On Reasonable Restrictions:
- Like other citizens, ministers are guaranteed the right to freedom of expression under Article 19(1) (a), governed by the reasonable restrictions laid out in Article 19(2) — and those are enough.
- Because “The role of the court is to protect fundamental rights limited by lawful restrictions and not to protect restrictions and make the rights residual privileges.”
- On Collective Responsibility:
- The majority ruling also made a valid distinction on the government’s vicarious responsibility for ill-judged or hateful remarks made by its individual ministers.
- The flow of stream in collective responsibility is from the Council of Ministers to the individual ministers.
- The flow is not on the reverse, namely from the individual ministers to the Council of Ministers.
- It is not possible to extend the concept of collective responsibility to “any and every statement orally made by a Minister outside the House of the People/Legislative Assembly”.
- The majority ruling also made a valid distinction on the government’s vicarious responsibility for ill-judged or hateful remarks made by its individual ministers.
- Statement by an Individual Minister:
- The court also addressed the question of whether the statement of a minister, that is inconsistent with the fundamental rights of citizens, can result in a constitutional tort.
- A constitutional tort is a legal tool that provides for the state to be held vicariously accountable for the actions of its agents.
- A mere statement by a minister that goes against an individual’s fundamental rights may not be actionable, but becomes actionable if it results in actual harm or loss.
- The court also addressed the question of whether the statement of a minister, that is inconsistent with the fundamental rights of citizens, can result in a constitutional tort.
- On Reasonable Restrictions:
- Dissenting Judgement:
- Over a Hateful Public Discourse:
- The minority judgment expresses concern over a hateful public discourse - “hate speech, whatever its content, denies people dignity”.
- It speaks of the special duty of public functionaries and other persons of influence to be more responsible and restrained in their speech, to “understand and measure their words”.
- On Collective Responsibility:
- It is possible to attribute vicarious responsibility to the government if a minister’s view represents that of the government and is related to the affairs of the state.
- If such a statement is not consistent with the view of the Government, then it is attributable to the Minister personally.
- Statement by an Individual Minister:
- It holds the view that there should be a proper legal framework to define acts and omissions that amount to ‘constitutional tort’.
- Over a Hateful Public Discourse:
What is Article 19?
- Article 19 of the Constitution of India guarantees the right to freedom of speech and expression, and is typically invoked against the state.
- Article 19(1) in The Constitution Of India 1949, All citizens shall have the right
- (a) to freedom of speech and expression;
- (b) to assemble peaceably and without arms;
- (c) to form associations or unions;
- (d) to move freely throughout the territory of India;
- (e) to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India; and
- (f) omitted
- (g) to practise any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
- Article 19(2) in The Constitution of India 1949,
- Nothing in sub clause (a) of clause (1) shall affect the operation of any existing law, or prevent the State from making any law, in so far as such law imposes reasonable restrictions on the exercise of the right conferred by the said sub clause in the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality or in relation to contempt of court, defamation or incitement to an offence.
- Article 19(1) in The Constitution Of India 1949, All citizens shall have the right
Way Forward
- There are enough provisions in the statute book to deal with speech that promotes enmity and violence or results in cramping the freedoms of others.
- A lack of political will and a lack of political resolve by governments to act on hate speech, particularly when it involves one of their own, is the major problem, and there are no legal shortcuts to overcome it.
- A government can weaponize the same legal provisions that are designed to curb hate speech against citizens who disagree or dissent.
- The Parliamentary privileges are conferred on the members for the smooth functioning of the parliament. But these rights should always be in conformity with the fundamental rights because they are our representatives and work for our welfare.
- If the privileges are not in accordance with the fundamental rights, then the very essence of democracy for the protection of the rights of the citizen will be lost.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What do you understand by the concept of “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (2014)
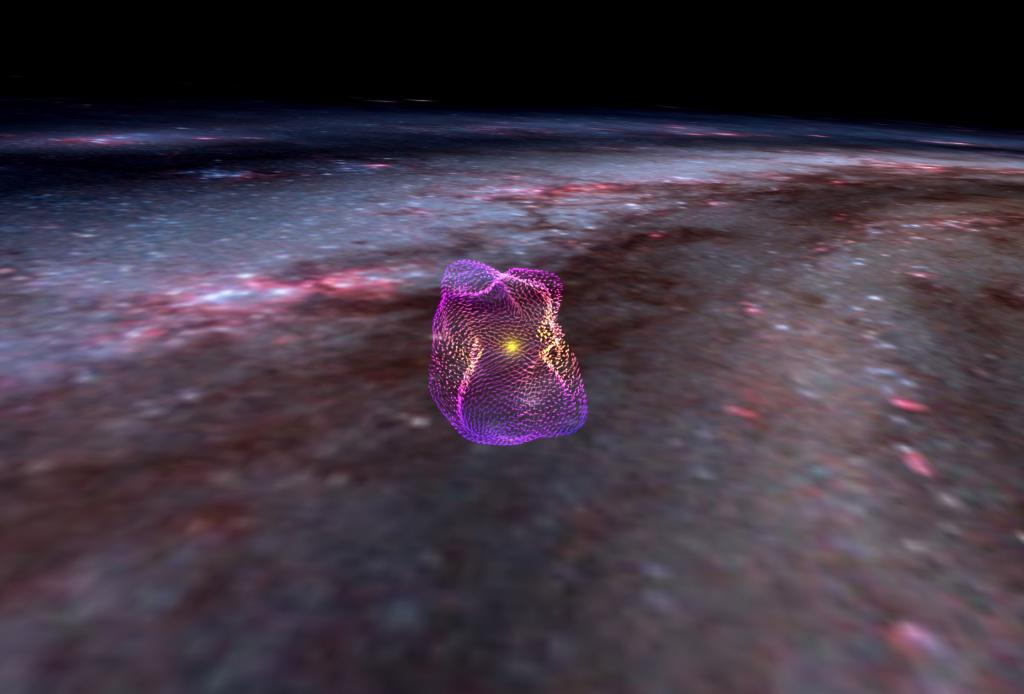
Local Bubbles
Why in News?
Recently, new research on a giant cosmic cavity that surrounds the solar system could reveal the universe’s secrets, including questions about the origins of stars.
- Researchers from the Center for Astrophysics (CfA) | Harvard & Smithsonian have generated a 3D magnetic map of the cavity called Local Bubble.
What are Local Bubbles?
- The Local Bubble is a 1,000-light-year-wide cavity or a superbubble. Other superbubbles also exist in the Milky Way.
- The Local Bubble is a large, low-density region in the interstellar medium (ISM) of our galaxy, the Milky Way.
- The interstellar medium is the material which fills the space between the stars.
- It's a cavity that is thought to have been created by a series of supernovae explosions that occurred about 30 to 50 million years ago.
What is a Supernova?
- A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion that occurs at the end of the life of a massive star.
- It is caused by the collapse of the core of the star, which can trigger a massive release of energy.
- Supernovae are also important for the enrichment of the interstellar medium with heavy elements and for the propagation of cosmic rays.
- There are two main types of supernovae:
- Type I:
- It is a supernova caused by the thermonuclear explosion of a white dwarf star that is part of a binary system.
- The white dwarf accretes material from its companion star, and when its mass exceeds a certain limit, it becomes unstable and detonates.
- Type II:
- It is caused by the gravitational collapse of the core of a massive star.
- When a star has exhausted the nuclear fuel in its core, its outer layers collapse inward, and the core becomes incredibly hot and dense.
- This causes a huge release of energy, which causes the star to explode.
- The explosion is so powerful that it can outshine an entire galaxy for a brief period of time, and the explosion debris can cause the formation of nebulae, dust and heavy elements.
- Type I:
How 3D Map of a Gigantic Cavity of Local Bubbles Observed?
- They used Gaia and Planck space based observatories launched by the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Gaia was used to identify the location and local concentration of cosmic dust.
- This helped them trace the boundaries of the Local Bubble.
- Planck provided information on the magnetic alignment of cosmic dust.
- This alignment can indicate the orientation of the magnetic field acting on the dust particles, allowing the researchers to generate a 3D magnetic field orientation on the surface of the Local Bubble.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
(a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
(b) ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
(c) Possibility of inter-galactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
(d) It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Ans: (b)
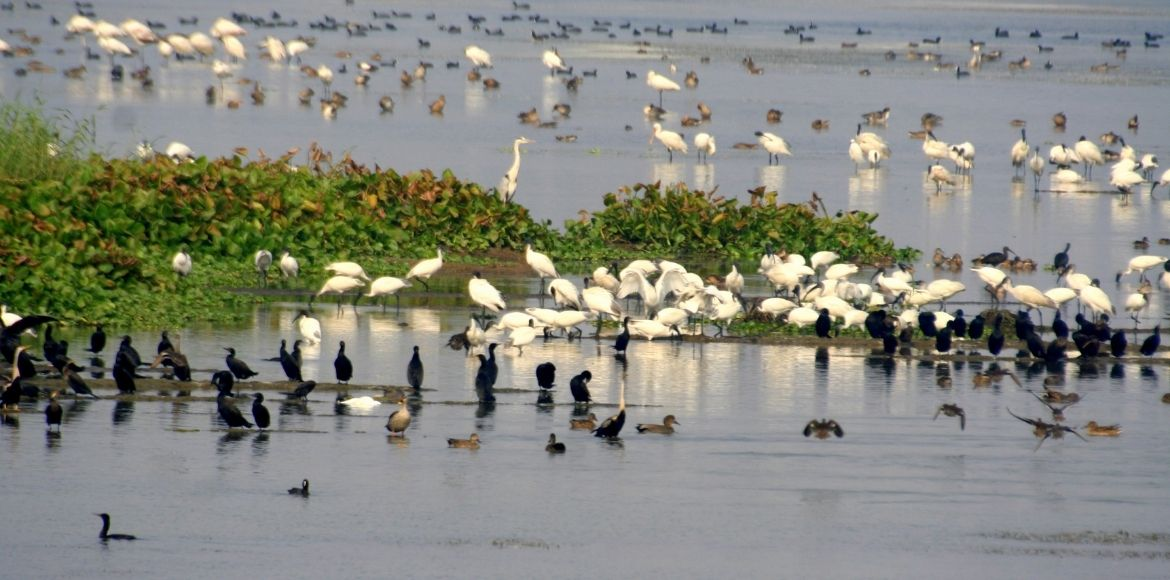
Asian Waterbird Census
Why in News?
A survey conducted as part of the Asian Waterbird Census (AWC) 2023 shows the populations of some migratory waterbirds, especially duck species visiting the Alappuzha region of Kerala, are falling.
What are the Highlights of the Survey?
- Major Missing Species:
- Duck species like Northern Shoveler, Common teal and Eurasian wigeon, sighted in the previous surveys, were totally missing this time around.
- Climate Change Impact:
- Climate change has affected the number of birds visiting the region. However, the precise impact of climate change on bird migration requires more detailed studies.
What is the Asian Waterbird Census?
- About:
- It is a citizen-science programme supporting conservation and management of wetlands and waterbirds worldwide.
- AWC is part of the global International Waterbird Census (IWC) coordinated by Wetlands International.
- AWC runs in parallel with other regional programmes of the IWC in Africa, Europe, West Asia, the Neotropics and the Caribbean.
- It is a citizen-science programme supporting conservation and management of wetlands and waterbirds worldwide.
- AWC in India:
- It was initiated in the Indian subcontinent in 1987 and since then has grown rapidly to cover major regions of Asia, from Afghanistan eastwards to Japan, Southeast Asia and Australasia.
- In India, AWC is jointly coordinated by the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and Wetlands International.
- Significance:
- It gives an idea of the birds at the wetland and the health of the wetland; the more the waterbirds, the more suitable the wetland is.
- It helps in better implementation of the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) and the Convention on Biological Diversity‘s (CBD).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to a conservation organization called ‘Wetlands International’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is an intergovernmental organization formed by the countries which are signatories to the Ramsar Convention.
- It works at the field level to develop and mobilize knowledge and use practical experience to advocate for better policies.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Soul of Steel Challenge
Why in News?
A ‘Soul of Steel’ challenge was launched in Uttarakhand on 14 January which aims to test one’s high-altitude endurance.
- The general area of the expedition would be the Nanda Devi National Park.
What is the Soul of Steel Challenge?
- The challenge is an initiative of CLAW Global and is being supported by the Indian Army.
- The idea behind Soul of Steel is pooling of skill sets and creating a challenge that will unlock the human ability to survive, stabilise and thrive in high altitude areas.
- It is based on the lines of the ‘Ironman triathlon’ long-distance triathlon challenge in Europe, which tests an individual’s grit and endurance.
- Apart from life skill training and youth development, the challenges would globally promote adventure tourism in Uttarakhand.
What is CLAW Global?
- CLAW (Conquer Land Air Water) Global, is a team of Special Forces veterans and people with disabilities from different nationalities, religion, abilities etc., to project the power of self-belief and collective effort to create a powerful perception of ability and freedom.
- It was set up in January 2019 by Major Vivek Jacob, a para special forces officer who retired after 14 years of service after a combat skydive injury.
- CLAW introduced ‘Operation Blue Freedom’ – a movement to express the powerful spirit and ability of people with disabilities.
Note
- Armed Forces Veterans Day is celebrated every year on January 14. On this day, in 1953, the First Indian Commander-in-Chief of the Indian Army, Field Marshal KM Cariappa formally retired from the Services.
- He led the Indian Forces to Victory in the 1947 war against Pakistan.
- The day was first observed in 2016.
First Aspirational District Deploying 5G Technology
Why in News?
Recently, Vidisha, an aspirational district of Madhya Pradesh became the first-ever district in India for on-ground deployment of innovative 5G use cases offered by startups.
What are the Highlights of the Initiative?
- It is a joint initiative by Vidisha District Administration and Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), Department of Telecommunications (DoT) under the guidance of Additional Secretary (Telecom) & Administrator Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF).
- The 5G will be deployed at community & district health centers, Model Schools, Agri & Dairy Farmers, and skill development centers for a period of 1 year and may be extended subsequently as per the need.
- These digital solutions will also be powered by BharatNet broadband to provide uninterrupted services to user communities of Vidisha.
What is the Aspirational District Programme?
- It was launched in 2018 which aims to transform districts that have shown relatively lesser progress in key social areas.
- Aspirational Districts are those districts in India, that are affected by poor socio-economic indicators.
- It covers 112 districts across the country.
- At the Government of India level, programme is anchored by NITI Aayog. In addition, individual Ministries have assumed responsibility to drive the progress of districts.
What is 5G Technology?
- 5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks.
- 5G works in 3 bands (Low, Mid and High frequency spectrum) - all of which have their own uses as well as limitations.
- It enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
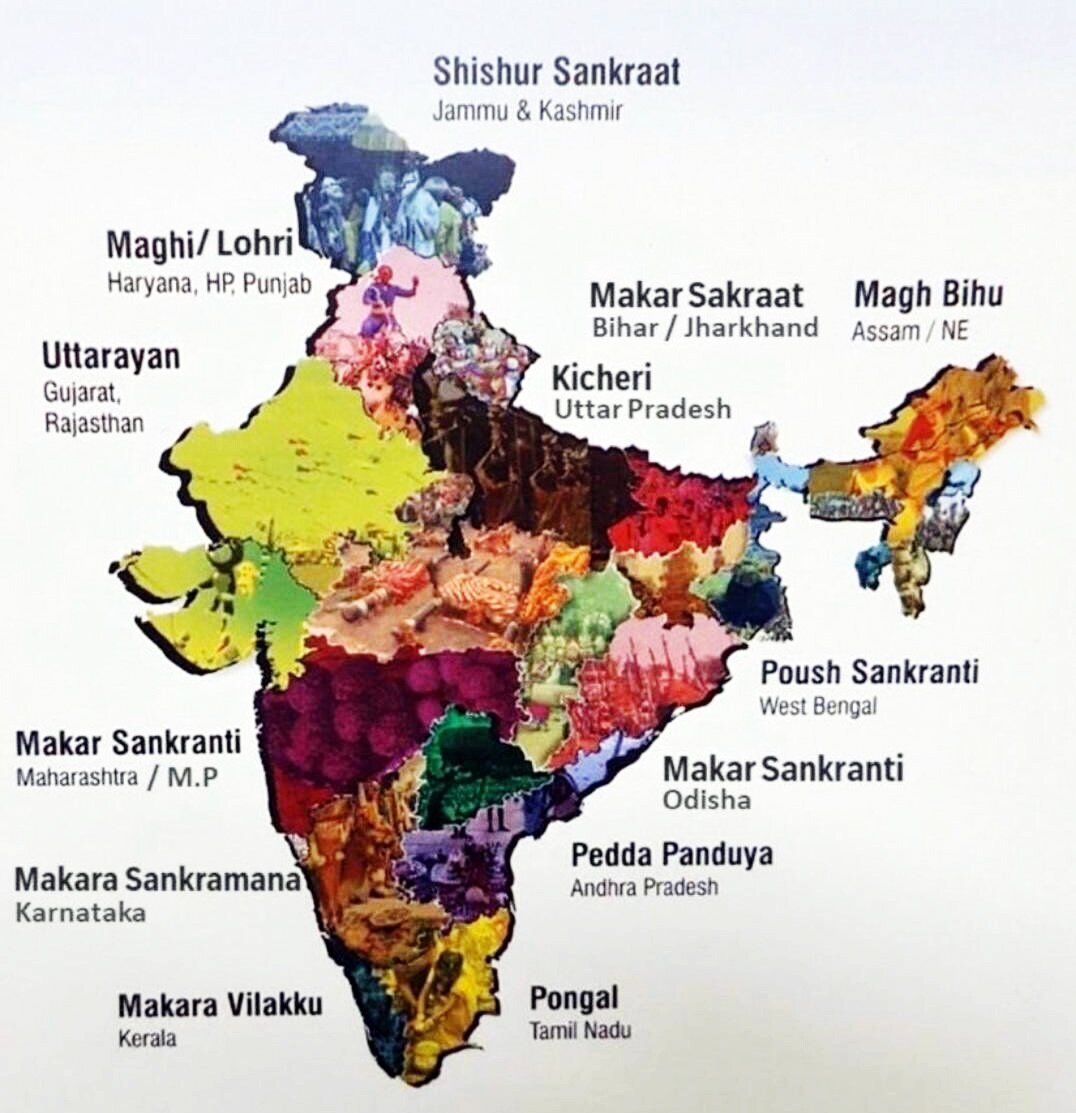
Makar Sankranti
Recently, the Prime Minister has greeted people across the nation on the occasion of harvest festivals Makar Sankranti, Bhogi, Lohri and Pongal. The festivals celebrate the hard work and enterprise of millions of farmers across the country.
Makar Sankranti denotes the entry of the sun into the zodiac sign of Makara (Capricorn) as it travels on its celestial path. The day marks the onset of summer and the six months auspicious period for Hindus known as Uttarayan – the northward movement of the sun.
The festivities associated with the day are known by different names in different parts of the country:
Read More: Harvest Festivals
India’s First Centre of Excellence in Online Gaming
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI, an autonomous society under MeitY) will facilitate in setting up India’s first Centre of Excellence in Online Gaming at Shillong by March 2023. This will help to catalyse startups and entrepreneurs from the entire North East Region to build the Next Generation Online Gaming Ecosystem.
The Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) will also set up a state-of-the-art facility under the National Institute of Electronics and IT (NIELIT) in Shillong to provide training on digital skills. The government will be re-launching Skill India through Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Viaks Yojana (PMKVY) 4.0, which will train around 50,000 youth in Meghalaya.
Read More: India’s Startup Ecosystem, North-East India
Constitution Literacy Campaign in Kerala
The first of its kind initiative in Kerala, a constitution literacy campaign jointly organised by the Kollam district panchayat, District Planning Committee, and the Kerala Institute of Local Administration (KILA). The aim is to declare Kollam as the first totally Constitution literate district.
As part of the campaign, the entire population of Kollam above the age of 10 will be briefed on the preamble of the Constitution and the historical background of the document, its basic principles, fundamental rights of citizens, and legal remedies.
Read More: Preamble, Indian Constitution
LHS 475 b
Recently, the James Webb Telescope confirmed the discovery of its first exoplanet, a planet that orbits another star.
The planet, formerly classified as LHS 475 b, the planet is almost exactly the same size as the Earth, 99% of Earth’s diameter. Researchers noted that the planet completes one orbit around its star in just two days. Although LHS 475 b is closer to its star than any planet in the solar system, its red dwarf star is less than half the temperature of the Sun, so the researchers are expecting that it still could have an atmosphere.
Red Dwarf Star: A small, low-mass, dim, and cool star. Many have big flares and mass ejections on their surfaces. The habitable zone of red dwarf stars is closer to the star than stars like our sun, making it easier to observe potentially habitable planets.
Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
Read More: Solar System, James Webb Telescope

.png)