Punjab State - General Knowledge (GK) | 12 Feb 2026
Punjab General Knowledge is a key area for aspirants preparing for state-level competitive examinations. This page offers a clear and exam focused overview of Punjab, covering its formation, geography, rivers, dams, history, demography, and cultural traditions. Structured for quick revision and factual clarity, the content is aligned with Punjab PCS and other state-level government exams, making it a reliable resource for effective preparation.
|
Formation |
1 November 1966 |
|
Capital |
Chandigarh (Union Territory; shared with Haryana) |
|
Population |
27,743,338 (≈ 2.77 crore) |
|
Area |
~50,362 sq. km |
|
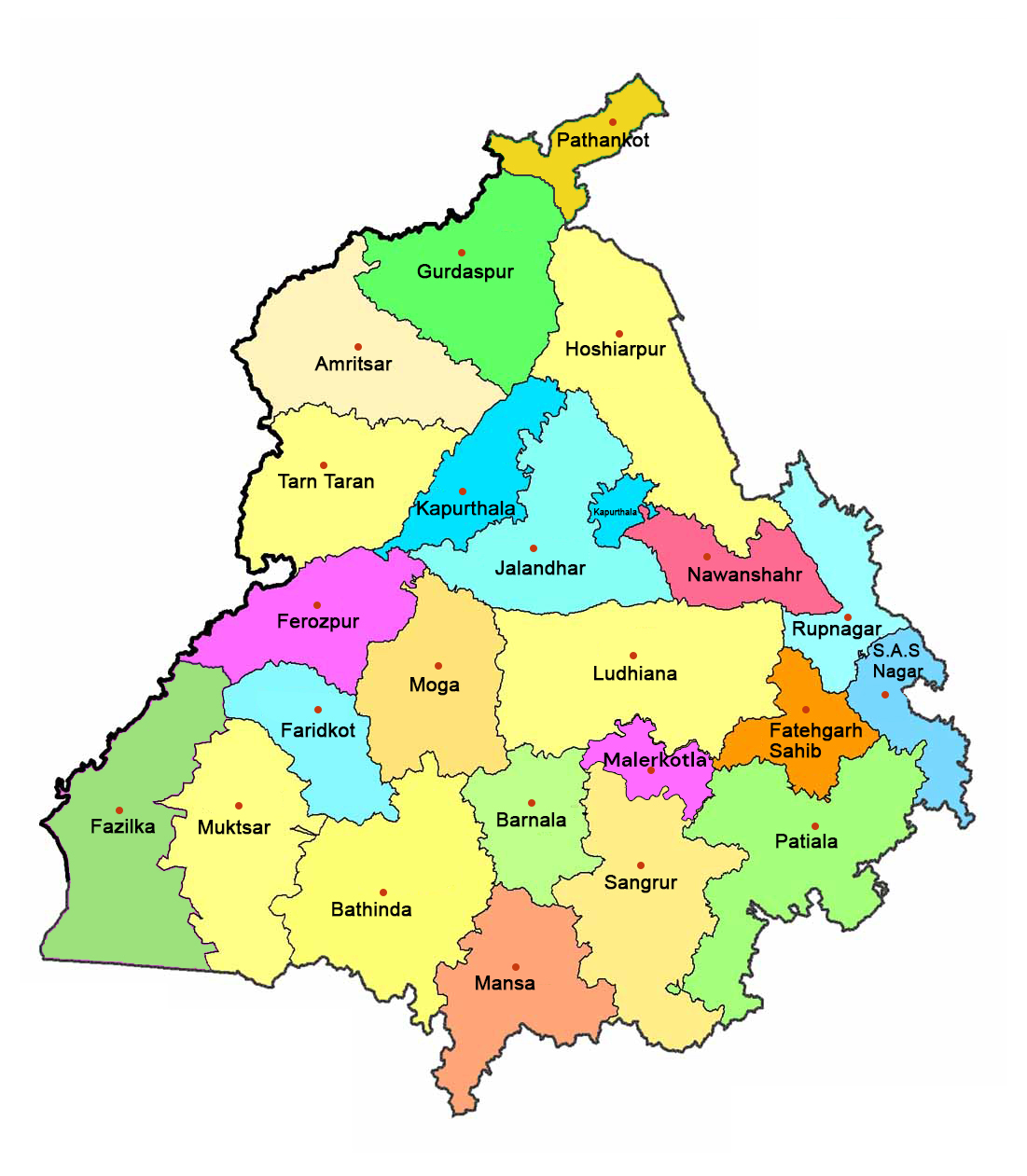
Total Districts |
23 (Malerkotla - 23rd District; formed in 2021) |
|
Latitudinal extent |
29°30′ N to 32°32′ N |
|
Longitudinal extent |
73°55′ E to 76°50′ E |
|
High Court |
Punjab & Haryana High Court (Chandigarh) |
|
Lok Sabha Seats |
13 |
|
Rajya Sabha Seats |
7 |
|
Vidhan Sabha Seats |
117 |
Punjab State: Symbols
Geography of Punjab
- Physiographic region: Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains
- Major rivers: Sutlej, Beas, Ravi (tributaries of Indus)
- Doabs:
- Bist Doab – Between Beas & Sutlej
- Bari Doab – Between Ravi & Beas
- Climate: Continental (hot summers, cold winters)
- Boundaries:
- International border: Pakistan (west)
- North: Jammu & Kashmir
- Northeast: Himachal Pradesh
- South/Southeast: Haryana
- Southwest: Rajasthan
- Wildlife sanctuaries:
- Harike Wetland
- Abohar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bir Moti Bagh Sanctuary
Major Rivers of Punjab and Their Origin
|
River |
Origin (Source) |
Remarks |
|
Sutlej |
Rakshastal Lake, near Mount Kailash (Tibet) |
Longest river flowing through Punjab |
|
Beas |
Beas Kund, near Rohtang Pass (Himachal Pradesh) |
Flows entirely in India |
|
Ravi |
Chamba district, Himachal Pradesh (near Rohtang range) |
Forms part of India–Pakistan river system |
|
Ghaggar (seasonal) |
Shivalik Hills, Himachal Pradesh |
Also known as Saraswati (ancient reference) |
Major Lakes / Wetlands of Punjab
|
Lake / Wetland |
Location (District) |
Type / Importance |
|
Harike Wetland (Harike Lake) |
Tarn Taran (near confluence of Beas & Sutlej) |
Largest wetland of Punjab; Ramsar Site |
|
Ropar Wetland (Rupnagar Lake) |
Rupnagar |
Ramsar Site; on Sutlej River |
|
Kanjli Wetland |
Kapurthala |
Ramsar Site; on Kali Bein rivulet |
|
Nangal Lake |
Nangal (Rupnagar) |
Man-made; linked to Bhakra-Nangal Project |
|
Ranjit Sagar Lake (Thein Dam) |
Pathankot |
Man-made; on Ravi River |
|
Mohali Wetland (Sukhna extension) |
SAS Nagar (Mohali) |
Seasonal wetland |
Major Dams in Punjab
|
Dam / Project |
River |
Location (District) |
Purpose / Importance |
|
Bhakra–Nangal Dam |
Sutlej |
Nangal (Rupnagar) |
Largest multipurpose project; irrigation, hydropower Bhakra–Nangal is one of the highest gravity dams in Asia. |
|
Ranjit Sagar Dam (Thein Dam) |
Ravi |
Pathankot |
Hydroelectric power & irrigation Ranjit Sagar Dam is the largest dam on Ravi River. |
|
Nangal Dam |
Sutlej |
Rupnagar |
Regulates water from Bhakra Dam |
|
Mukerian Hydel Project |
Beas |
Hoshiarpur |
Hydroelectric power |
|
Shahpur Kandi Dam |
Ravi |
Pathankot |
Irrigation & power; India–J&K project |
History of Punjab
- Indus Valley Civilization sites: Ropar (Rupnagar)
- Ancient period: The region was known as Sapta Sindhu (land of seven rivers) in Vedic literature.
- Medieval era: Punjab came under various rulers including the Mughals and later the Sikh Empire under Maharaja Ranjit Singh (1799).
- British period: Punjab was annexed by the British in 1849 after the Second Anglo-Sikh War.
- Partition of India (1947): Punjab was divided into West Punjab (Pakistan) and East Punjab (India).
- Post-Independence reorganization:
- Initially, East Punjab included present-day Punjab, Haryana, and Himachal regions.
- The Punjabi Suba Movement demanded a Punjabi-speaking state.
- Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966:
- Present-day Punjab was formed on 1 November 1966.
- Haryana was carved out as a separate state.
- Himachal Pradesh received its Punjabi-speaking hill areas.
- Chandigarh was made a Union Territory and joint capital of Punjab and Haryana.
Demography
- Total population (Census 2011): 27,743,338 (≈ 2.77 crore)
- Population rank among Indian states (2011): 16th
- Urban population: ~37%
- Rural population: ~63%
- Population density: 551 persons/sq. km
- Decadal growth rate (2001–2011): 13.9%
- Sex ratio: 895 females per 1000 males
- Literacy rate:
- Overall: 75.8%
- Male: ~80.4%
- Female: ~70.7%
- Largest populated district: Ludhiana
- Least populated district: Barnala
|
Folk Art, Culture, Paintings, Dances and Festivals of Punjab |
|
|
Dance Form |
Key Features |
|
Bhangra |
Energetic male dance; linked with Baisakhi harvest |
|
Giddha |
Female dance; expressive boliyan |
|
Jhumar |
Slow, graceful dance of western Punjab |
|
Sammi |
Traditional women’s dance from Sandal Bar region |
|
Kikli |
Playful girls’ dance |
|
Luddi |
Victory dance; celebrates bravery |
|
Malwai Giddha |
Male folk dance from Malwa region |
|
Folk Paintings & Art Forms |
|
|
Art / Painting |
Description |
|
Phulkari |
Traditional embroidery; floral motifs on dupattas & shawls |
|
Pidhni / Chowk-Poorna |
Floor and wall art made with rice paste |
|
Folk Theatre & Performative Arts |
|
|
Form |
Details |
|
Nautanki |
Traditional folk drama |
|
Saang / Swang |
Storytelling theatre |
|
Dhadi |
Ballads of Sikh warriors |
|
Folk Culture & Festivals |
|
|
Baisakhi |
Harvest festival & Sikh New Year |
|
Lohri |
Winter festival |
|
Hola Mohalla |
Martial traditions |
|
Gurpurab |
Sikh religious festivals |
A strong understanding of Punjab General Knowledge supports better performance in objective questions, descriptive exams, and interviews. This page covers frequently tested areas such as geography, history, culture, and administration. Regular revision and linking static facts with current affairs will improve retention. Use this resource as a quick reference to strengthen your Punjab GK preparation.
Start Preparing for Punjab PCS with Drishti IAS
Get comprehensive guidance and focused content tailored for the Punjab PCS
|
Related Resources |
|
|
PPSC Exam Syllabus |
|
|
PPSC Previous Year Papers |
|
|
PPSC Exam Pattern |
|
|
PPSC Exam Strategy |
|
|
Monthly CA Consolidations |
|