Donkey Route and Money Laundering | 11 Jul 2025
Why in News?
The Enforcement Directorate (ED) carried out searches at different locations across Punjab and Haryana in connection with the "donkey route" case involving illegal immigrants, under provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002.
Key Points
- The Donkey Route:
- The "Dunki" or "donkey" route has existed for decades, known for its perilous and illegal migration paths.
- It refers to the long-winding, often dangerous routes that people across the world take to reach the places they want to immigrate to. These journeys are undertaken due to a lack of requisite legal permits or financial resources.
- Rise in Indian Illegal Immigration to the US:
- According to Pew Research Center, the number of Indians illegally entering the US rose from 8,027 (in 2018–2019) to 7.25 lakh (in 2022–2023).
- India is the only country in the top five sources of immigration to the US outside Latin America.
- Since 2011, the undocumented Indian population in the US has grown by 70%.
- US Customs and Border Protection data shows the sharpest increase occurred between 2020 and 2023.
- According to Pew Research Center, the number of Indians illegally entering the US rose from 8,027 (in 2018–2019) to 7.25 lakh (in 2022–2023).
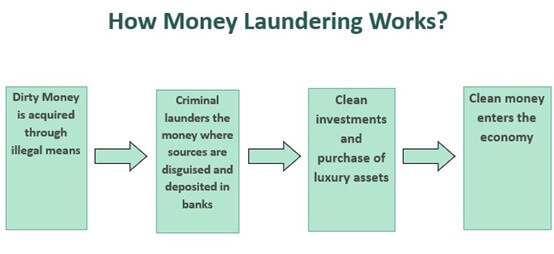
- Money Laundering:
- About:
- Money laundering is a complex process used by individuals and organisations to conceal the origins of illegally obtained money. It involves making illicit funds appear legitimate through a series of transactions.
- Methods of Money Laundering:
- Structuring (Smurfing): Breaking up large amounts of cash into smaller, less conspicuous amounts that are then deposited into bank accounts.
- Trade-Based Laundering: Using trade transactions to move value across borders and disguise the origins of illicit funds.
- Shell Companies: Creating companies with no legitimate business activity to funnel illicit funds through legitimate-looking transactions.
- Real Estate: Purchasing real estate with illicit funds and then selling it to convert the value into legitimate assets.
- About:
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002:
- Key Provisions:
- Defines money laundering as concealment, possession, acquisition, or use of proceeds from crime, projecting them as legitimate assets.
- Empowers the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to investigate offenses, conduct raids, and attach proceeds of crime.
- Mandates financial institutions to report suspicious transactions to the Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND) for scrutiny.
- Establishes Special Courts to expedite trials of money laundering cases, ensuring legal deterrence.
- Includes a wide range of predicate offenses under the Schedule of Offenses, covering economic offenses, corruption, drug trafficking, and terrorism.
- Effectiveness:
- Stronger deterrence: The PMLA deters financial crimes through strict investigation, prosecution, and asset confiscation in major fraud and economic offenses.
- Enhanced international cooperation: India collaborates with Interpol and the FATF (Financial Action Task Force) to track illicit funds.
- Better financial monitoring: Banks and financial institutions are obligated to implement Know Your Customer (KYC) norms, reducing money laundering risks.
- Key Provisions: