Bihar's First Nuclear Power Plant | 26 Jun 2025
Why in News?
Bihar will be among the first six states in India to receive its first atomic power plant under the country's new Nuclear Energy Mission.
Key Points
About First Nuclear Power Plant
- Announcement and Approval: During the 5th Eastern Region Power Ministers' meeting in Patna, the Union Power Minister announced the Centre's approval for Bihar to set up a nuclear power plant based on Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology.
- The meeting, attended by representatives from Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, marked a key step towards advancing nuclear energy in the eastern region.
- Significance for Bihar: The project is expected to ensure a stable electricity supply, attract industrial investment, generate employment, and drive technological advancement in the state.
- Given Bihar’s historical challenges with power deficits and limited infrastructure, the initiative marks a transformative shift in its energy landscape.
Nuclear Energy Mission
- Ambitious Capacity Expansion: It aims to increase India’s nuclear power capacity from the current 8,180 MW (as of January 30, 2025) to 100 GW by 2047, positioning nuclear energy as a major pillar in India’s energy mix and supporting long-term energy security and sustainability.
- Focus on Indigenous Technology: The mission prioritizes the research and development of indigenous technologies, especially Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), with an allocation of ₹20,000 crore.
- The goal is to develop and operationalize at least five indigenously designed SMRs by 2033, leveraging India’s expertise in Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs).
- It also seeks to set up one nuclear power plant in each state to enhance India's energy security.
- Private Sector Participation: Legislative changes are planned to amend the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010, to encourage private sector investment and collaboration.
- This will facilitate faster deployment of nuclear projects, innovation, and economic growth, with private entities contributing land, capital, and funding, while NPCIL manages reactor operations.
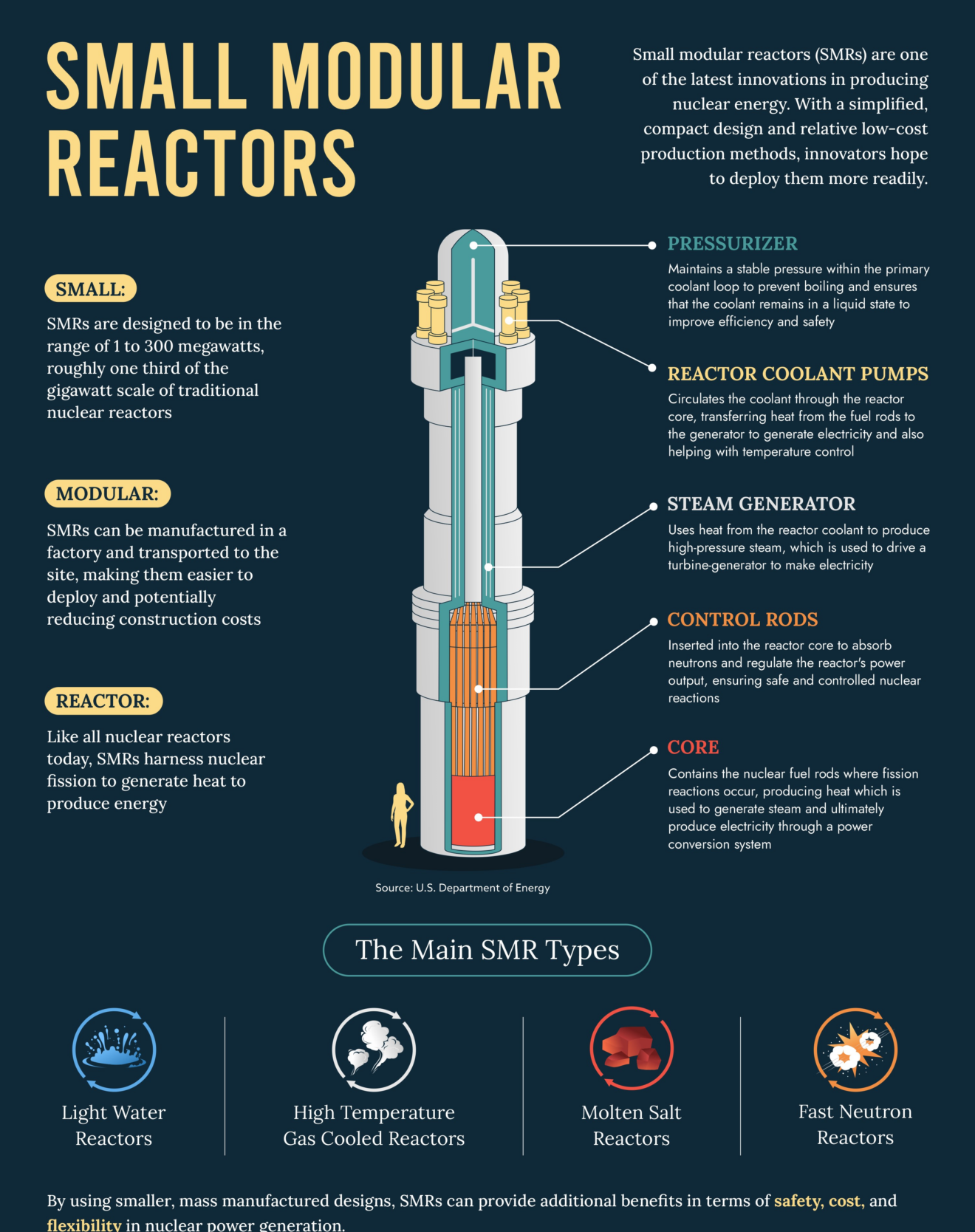
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a capacity of up to 300 MW(e), about one-third of traditional reactors.
- SMRs represent an advanced, cost-effective, and safer nuclear technology suitable for regions with moderate power demands, especially where large-scale plants are not feasible.
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is working on SMRs for repurposing retiring coal-based power plants and meeting the energy needs of remote areas.
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) is also focusing on developing reactors such as high-temperature gas-cooled reactors for hydrogen generation and molten salt reactors to utilize India’s vast thorium resources.
Other Recent Developments in Power Sector
- Battery Energy Storage Projects: In addition to the nuclear plant, the Central Government has approved a 1,000 MW battery storage capacity project in Bihar.
- This project will support renewable energy integration and enhance grid stability, with viability gap funding of ₹18 lakh per megawatt.
- The Prime Minister had also laid the foundation stone for a 500 MWh Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) project in Siwan on 20th June 2025.
- Additional Support to Bihar: To support peak summer demand, the Centre has also agreed to supply an additional 500 MW of electricity to Bihar for the next three to six months.
- The state was also commended for installing eight million smart meters and achieving a substantial reduction in technical and commercial losses, indicating significant progress in the power sector.