256 Criminals Killed in UP Encounters | 15 Oct 2025
Why in News?
Under the Mission Shakti 5.0 initiative, the Uttar Pradesh Police has intensified its crackdown on crime, neutralising or arresting several notorious criminals in multiple encounters over the past 20 days.
Key Points
- About: Mission Shakti 5.0 focuses on ensuring women’s safety, law and order, and strengthening public confidence in the police. It continues the government’s zero-tolerance policy towards crime and criminals.
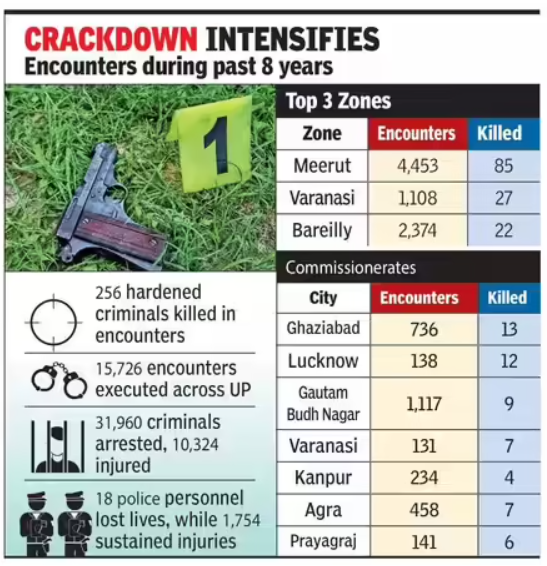
- Law and Order Record (2017–2025): Since 2017, UP Police have conducted 15,726 encounters, resulting in:
- 256 hardened criminals killed
- 31,960 arrested and 10,324 injured
- 18 police personnel martyred and 1,754 injured
- Zone-Wise Data:
- Meerut Zone: 4,453 encounters, 8,312 arrests, 85 killed, 3,131 injured (2 police martyred, 461 injured).
- Varanasi Zone: 1,108 encounters, 2,128 arrests, 27 killed, 688 injured.
- Agra Zone: 2,374 encounters, 5,631 arrests, 22 killed, 816 injured.
- Lucknow Zone: 846 encounters, 17 criminals killed.
- Prayagraj Zone: 572 encounters, 10 criminals killed.
- Additional Measures:
- Gangster Act, National Security Act (NSA), and property seizure laws invoked against organised crime syndicates.
- Continuous operations aim to dismantle criminal networks and block financial resources of mafias.
- The doctrine — “A criminal will either be in jail or out of the state” — guides the government’s approach.
- Impact:
- The sustained campaign has significantly reduced crime rates and enhanced the perception of safety in the state.
- It has restored public confidence in law enforcement and reinforced UP’s image as a safe and fear-free state.
Guidelines Related to Police Encounters in India
- Supreme Court Guidelines (2014): In People’s Union for Civil Liberties v. State of Maharashtra (2014), the Supreme Court issued detailed guidelines to ensure accountability and transparency in police encounters resulting in death.
- The Court made it mandatory to register a First Information Report (FIR) in all cases of encounter deaths and to conduct a magisterial inquiry, ensuring due legal process.
- The next of kin of the deceased must be involved during the inquiry process to maintain fairness and transparency.
- The investigation should be carried out by an independent agency, such as the Criminal Investigation Department (CID), to ensure impartiality and prevent conflict of interest.
- NHRC Guidelines (1997 & 2010):
- 1997: NHRC directed registration of encounter death cases, independent investigation by the State CID, and compensation to dependents if police are found guilty.
- 2010 (Amendment): Made it mandatory to report encounter deaths to the NHRC within 48 hours and to submit a detailed follow-up report within three months, including the post-mortem, inquest, and inquiry findings.